Computes relative position of Candidate input features relative to Base input features.
The geometry of a Candidate feature is restricted to point and area, while Base features can only be lines.
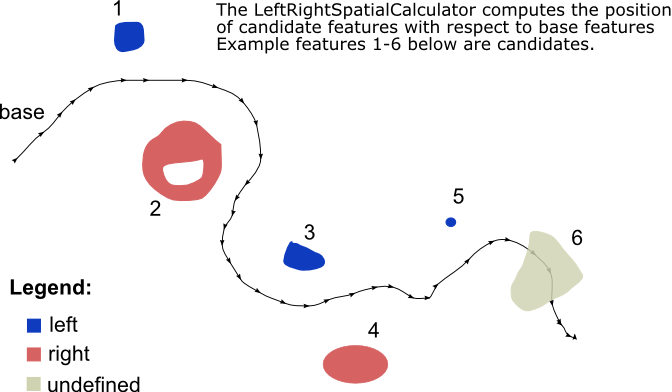
See the example below. The Base lines are considered to be oriented from the start point to the end point (digitization sense). A Candidate feature is:
- located to the LEFT of a Base feature if looking down the Base line in the direction of the orientation (from start to finish);
- located to the RIGHT if the Candidate is on the right of a Base feature;
- UNDEFINED if the Base and Candidate features intersect, or if the Base feature has a single point.
Output Port
Before being sent out through the Output port, each Candidate feature will have a list of its relative positions to each of the Base features attached to it. Each element of the list has two pieces of information:
- a "base_id" which identifies the base
- the computed relative "position"
Base features are dropped after being used.
Parameters
Transformer
If you choose Group By attributes, Candidates are only compared against Basesthat have the same values in these attributes.
Note: How parallel processing works with FME: see About Parallel Processing for detailed information.
This parameter determines whether or not the transformer should perform the work across parallel processes. If it is enabled, a process will be launched for each group specified by the Group By parameter.
Parallel Processing Levels
For example, on a quad-core machine, minimal parallelism will result in two simultaneous FME processes. Extreme parallelism on an 8-core machine would result in 16 simultaneous processes.
You can experiment with this feature and view the information in the Windows Task Manager and the Workbench Log window.
Yes: This transformer will process input groups in order. Changes on the value of the Group By parameter on the input stream will trigger batch processing on the currently accumulating group. This will improve overall speed if groups are large/complex, but could cause undesired behavior if input groups are not truly ordered.
No: This is the default behavior. Processing will only occur in this transformer once all input is present.
Parameters
If you choose Yes (default), the algorithm will use only the center of mass of passed in Candidates instead of the whole geometry.
If you choose Yes, the algorithm will compute only at the point on the Base line that is closest to the first or "center of mass" point.
Define whether only a Single Base will be supplied, or whether Multiple Bases will be supplied. If you choose Bases First, all Base features will enter the transformer first, before any Candidate features.
Choose the Base attribute whose value will be used to identify it in the list of relative positions attached to each output Candidate.
Specify the name of the list attribute that will be added onto all output Candidate features, and that will contain the relative positions.
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Transformer Categories
Search FME Knowledge Center
Search for samples and information about this transformer on the FME Knowledge Center.
Tags Keywords: relative position