Adds a number of attributes to the feature, supplying them with constants, attribute values, and expressions. Any feature that enters the transformer emerges with a new set of attributes as defined in the transformer’s parameters dialog.
Input Ports
This transformer accepts any feature.
Output Ports
Features with the created attributes.
Parameters
Enabling this setting allows the user to set an attribute value based on the attributes of features prior or subsequent to the current feature. Attributes of prior features are referenced as feature[-1].AttrName, feature[-2].AttrName, etc. Attributes of subsequent features are referenced as feature[+1].AttrName, feature[+2].AttrName, etc. The attributes of the currently processed feature are accessed directly without a prefix, such as AttrName.
When retrieving the value of a prior feature, any changes made by the AttributeCreator to that feature will take effect.
This parameter specifies the maximum number of prior features that can be referenced by the AttributeCreator. If Multiple Feature Attribute Support is enabled, this must be a value from 0 to 100.
This parameter specifies the maximum number of subsequent features that can be referenced by the AttributeCreator. If Multiple Feature Attribute Support is enabled, this must be a value from 0 to 100.
This parameter specifies the desired behavior when the specified attribute does not exist, has a null value, or has an empty string value. Such attributes can be thought of as unresolved attributes. For example, since there are no features prior to the first input feature, the AttributeCreator will fail to resolve the value of feature[-1].AttrName for the first input feature. If this parameter is set to Use Empty String, the AttributeCreator will resolve all unresolved attributes with an empty string. As another example, if the value of feature[2].AttrName is the empty string and Use Other Value is specified, then the empty string will be treated as an unresolved attribute, and will be resolved as the value specified under Attribute Replacement Value.
If this parameter is set to Use Attribute Value of Closest Feature, then the unresolved attributes will be resolved as the corresponding attribute of the closest feature, if such a feature exists. When looking for closest features, features with unresolved attributes are skipped. For example, if the value of feature[-2].AttrName is unresolved, then to resolve the value of feature[-2].AttrName the AttributeCreator will look at the closest features to feature[-2], alternating between features prior to and subsequent to feature[-2]. It will first look at feature[-3].AttrName, followed by feature[-1].AttrName if needed, and then feature[-4].AttrName if needed, until all prior and subsequent features specified have been exhausted. If the attribute remains unresolved within the specified prior and subsequent features, then it will be resolved as the value specified in the Attribute Replacement Value parameter.
This parameter specifies the value used to resolve unresolved attributes when the If Attribute Value is Missing, Null, or Empty parameter is set to Use Attribute Value of Closest Feature (but there is no closest value found) or Use Other Value.
- Attribute Name: Enter a new attribute name in each Attribute Name field. The name entered can be an existing attribute, a constant, a user parameter or an expression. If a user parameter or expression is used, then the attribute name will be the value as computed at runtime.
- Value: Enter values associated with attribute names.
Example
Features with the created attributes.
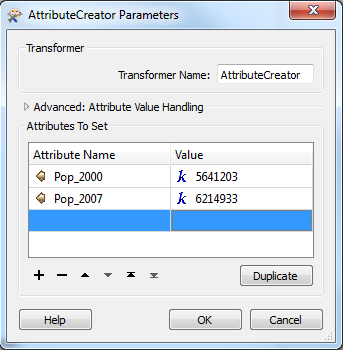
In Workbench, the new attributes are added to the transformer:
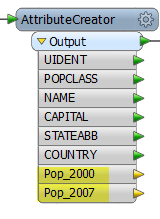
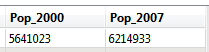
And if you output to an Inspector, the attributes and values appear in the Table View:
Suppose we are given the dataset below:
| ID | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|
|
0 |
49.1640 |
-123.061 |
|
1 |
49.1643 |
-123.063 |
|
2 |
49.1642 |
-123.062 |
|
3 |
49.1642 |
-123.064 |
If the Number of Prior Features and Number of Subsequent Featuresparameters are both set to 2, then when the first feature is read, the AttributeCreator has access to the following features:
| Feature Reference | ID | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|
|
feature[-2] |
<missing> |
<missing> |
<missing> |
|
feature[-1] |
<missing> |
<missing> |
<missing> |
|
current feature |
0 |
49.1640 |
-123.061 |
|
feature[+1] |
1 |
49.1643 |
-123.063 |
|
feature[+2] |
2 |
49.1642 |
-123.062 |
Note that some attributes are missing because no features exist prior to the first feature.
After the second feature is read, the window of prior and subsequent features available to AttributeCreator shifts to produce the following:
| Feature Reference | ID | Latitude | Longitude |
|---|---|---|---|
|
feature[-2] |
<missing> |
<missing> |
<missing> |
|
feature[-1] |
0 |
49.1640 |
-123.061 |
|
current feature |
1 |
49.1643 |
-123.063 |
|
feature[+1] |
2 |
49.1642 |
-123.062 |
|
feature[+2] |
3 |
49.1642 |
-123.064 |
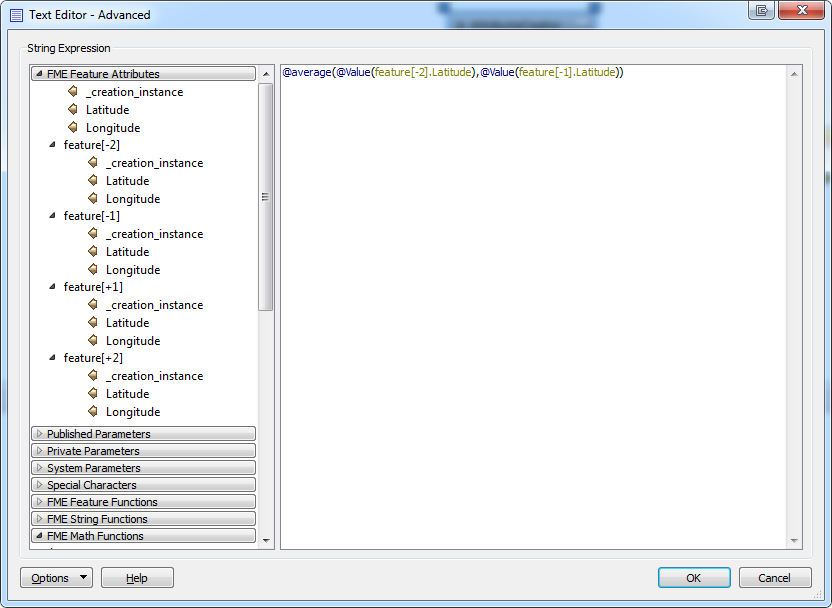
The following settings can be used to compute the average latitude and longitude of the two features prior to the currently processed feature:
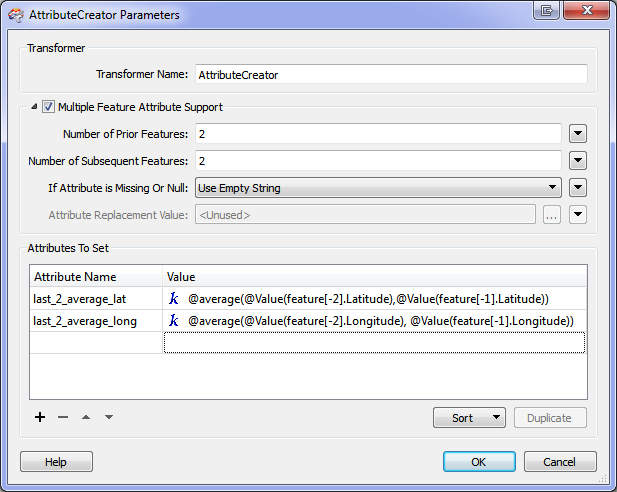
When using multi feature mode, the Advanced Editor sorts the attributes for the current feature above the attributes of prior and subsequent features.
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Transformer Categories
Search FME Knowledge Center
Search for samples and information about this transformer on the FME Knowledge Center.
Tags Keywords: AttributeSetter NullAttributeCreator