Takes a set of topologically connected linework and creates topologically correct polygon features where the linework forms closed shapes.
Input Ports
The input lines must be topologically correct and must neither self-intersect nor intersect each other. They must close at their endpoints. If these conditions are met, any area features implied by the input lines are created. (You can use the Snapper, Intersector, and MRF2DCleaner to clean data that does not meet these conditions before it enters this transformer.) This transformer can also create polygons and donuts (holes/islands). Any lines that cannot be formed into polygons are joined together to create maximum length linestrings.
Output Ports
Contains the output polygons.
Contains any lines that did not close. If Create Donuts is checked, it also contains degenerate polygons.
Contains any geometries that were rejected.
Parameters
Transformer
The default behavior is to use the entire set of input features as the group. This option allows you to select attributes that define which groups to form – each set of features that have the same value for all of these attributes will be processed as an independent group.
No attributes other than the Group By ones will be carried across from the Input features to the output features.
Note: How parallel processing works with FME: see About Parallel Processing for detailed information.
This parameter determines whether or not the transformer should perform the work across parallel processes. If it is enabled, a process will be launched for each group specified by the Group By parameter.
Parallel Processing Levels
For example, on a quad-core machine, minimal parallelism will result in two simultaneous FME processes. Extreme parallelism on an 8-core machine would result in 16 simultaneous processes.
You can experiment with this feature and view the information in the Windows Task Manager and the Workbench Log window.
Yes: This transformer will process input groups in order. Changes on the value of the Group By parameter on the input stream will trigger batch processing on the currently accumulating group. This will improve overall speed if groups are large/complex, but could cause undesired behavior if input groups are not truly ordered.
No: This is the default behavior. Processing will only occur in this transformer once all input is present.
Polygon Parameters
Specifies whether curve endpoints must be connected in X,Y, and Z before being joined together (as opposed to just X, and Y). Note that if this is set to No, then the Connect in Z Mode parameter will specify how the Z values of segments that are not connected in 3D should be treated.
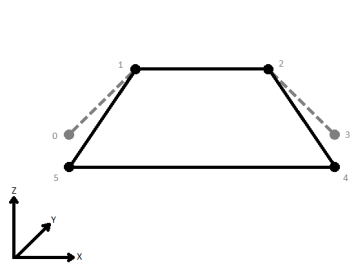
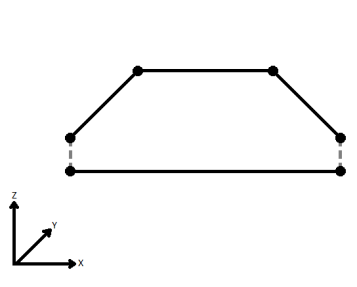
When viewed in 2D (ignoring Z), a path (which may define the border of a polygon) may appear to be closed as shown in the left figure below. This same path, when viewed in 3D, may appear to be open as shown in the right figure below.
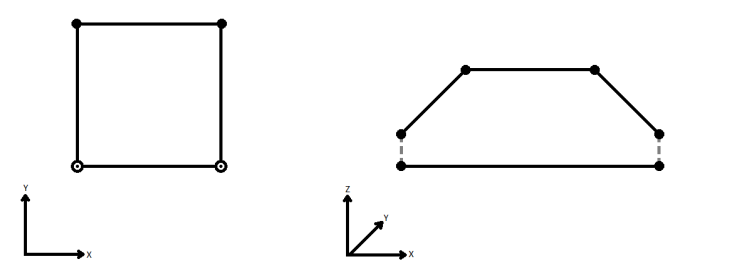
To specify how (and if) paths should be closed in 3D, select one of the listed modes.
| Mode | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
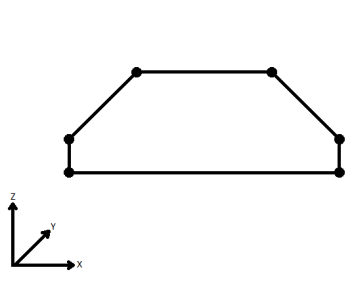
| Extend | The Curve is extended so that all vertices are left at their original location. |
|
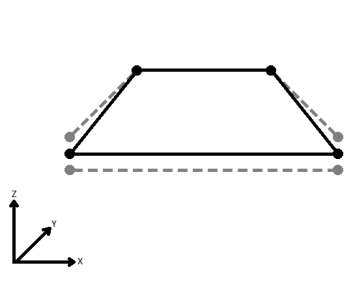
| Average | Subsequent vertices that are not connected, but share an x and a y value are combined into one vertex, whose Z value is the average of the original two. |
|
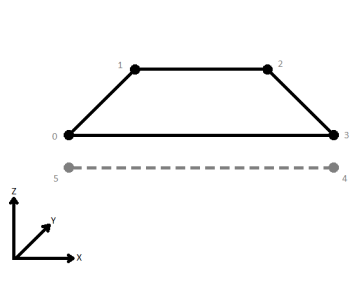
| First Wins | Subsequent vertices that are not connected, but share an x and a y value are combined into one vertex, whose Z value is taken from the first encountered vertex. |
|
| Last Wins | Subsequent vertices that are not connected, but share an x and a y value are combined into one vertex, whose Z value is taken from the last encountered vertex. |
|
| Ignore | Z values are ignored. No change is made to the way the nodes are connected. |
|
If set to Yes, then when lines originating from different input curves are concatenated into a longer curve in the output, they will be left as separate segments in a path. The default is No, which means that such lines will be joined into longer lines in the output unless they have different properties (e.g. traits, measures, geometry name).
Specifies that coordinate "cycles" within a polygon are allowable and will be constructed; such polygons might be considered invalid by other parts of FME or by output formats. A "cycle" is a line segment that occurs twice in the same polygon's boundary (once in each direction).
Specifies if the direction of the input curves needs to be considered while building polygons. If set to Yes, only curves that are tip-to-tail will result in polygons, all others will be output through the “Incomplete” port.
Attribute Accumulation
If Drop Incoming Attributes is chosen, the output feature will not preserve any input attributes. If Merge Incoming Attributes is chosen, the output feature will merge all input attributes. If Get Attributes from One Representative Feature is chosen, the output feature will get attributes from only one input feature.
Generate List
If you enter a List Name, a list will be created on each output feature, containing an element for each input feature which contributed to that geometry, in order of appearance.
This parameter can also be used to preserve attributes from input features.
Note: List attributes are not accessible from the output schema in Workbench unless they are first processed using a transformer that operates on them, such as ListExploder or ListConcatenator. All list attribute transformers are displayed in the Contents pane of the Transformer Help under Lists. Alternatively, AttributeExposer can be used.
Snapping Pre-Processing Parameters
When this parameter is set to None, no snapping takes place.
When this parameter is set to End Point Snapping, the transformer:
- Snaps end points of lines together if their distances are within the specified tolerance.
When this parameter is set to Vertex Snapping, the transformer does the following:
- Snaps vertices of lines together if their distances are within the specified tolerance.
When two features are snapped together, the feature that entered the factory most recently is the one that is modified.
Snapping Tolerance specifies the distance, in ground units, that the snapping occurs between features.
Create Donuts
If checked, the resulting polygons will contain holes created by any other resulting polygons they completely contained. Following this, any holes that share a common edge will be dissolved together to make a larger hole.
If unchecked, the resulting polygons are output via the Area port. Note that if you want to create donut polygons, you will need to use the DonutBuilder.
Yes: Polygons that are holes of another polygon will not be output.
No: Polygons that are holes of another polygon will be output.
Attribute Accumulation
Merge Attributes
If Merge Hole is chosen, attributes from all features will be merged, and in case of conflicts, the value of Conflict Resolution will be used. If Prefix Hole is chosen, then all incoming attributes will be presented with a prefix set in Prefix parameter. If Only Use Hole is chosen, only attributes from holes will be used.
This parameter is enabled when Accumulation Mode is set to Merge Hole. Use Outer Shell and Use Hole will give priority to outer shells and holes respectively in case of attribute conflicts.
The value is used as a prefix for holes when Accumulation Mode is Prefix Hole.
Generate List
If you enter a list name in this field, then a list will be created on each output donut feature, containing an element for each input feature that became a hole on that geometry, in order of appearance.
Note: List attributes are not accessible from the output schema in Workbench unless they are first processed using a transformer that operates on them, such as ListExploder or ListConcatenator. All list attribute transformers are displayed in the Contents pane of the Transformer Help under Lists. Alternatively, AttributeExposer can be used.
Example
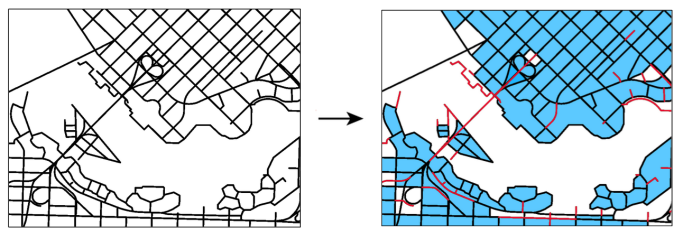
The example below illustrates a set of topologically connected linework on the left and the output of the AreaBuilder transformer on the right. In the output, the topologically correct polygons are highlighted in blue where the linework formed closed shapes, while the lines that did not close are shown in red.
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Transformer Categories
Search FME Knowledge Center
Search for samples and information about this transformer on the FME Knowledge Center.
Tags Keywords: CAD fenceline island ring PolygonBuilder Polygonizer