Accesses the Dropbox file storage service to upload, download, or delete files and folders or list the contents of a folder from a Dropbox account.
Typical Uses
- Manage datasets on Dropbox by uploading, downloading, and deleting files and folders
- Transfer a file's contents (such as XML or raster) into or out of an attribute in FME
- Read downloaded Dropbox data using the FeatureReader, or upload data written by the FeatureWriter to Dropbox
- Retrieve file and folder names, paths, links and other information from Dropbox to use elsewhere in a workspace.
How does it work?
Depending on your choice of actions, it will upload or download files, folders, and attributes; list information from the service; or delete items from the service. On uploads, link attributes are added to the output features. On List actions, file/folder information is added as attributes.
In this example, the DropboxConnector is used to download an Autodesk AutoCAD DWG file from Dropbox. After creating a valid web connection to a Dropbox account (which can be done right in the Dropbox Account parameter), the path and filename to download both from and to are entered.
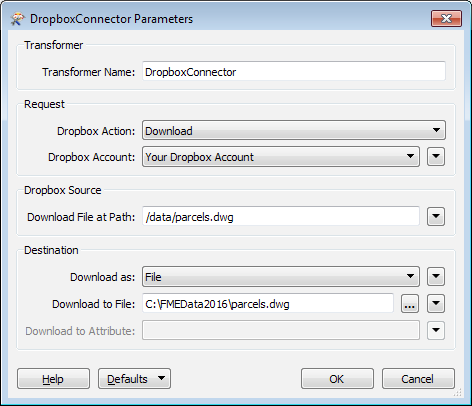 s
s
A FeatureReader is added to read the newly downloaded dataset. Here, the ParcelLines feature type will be further processed elsewhere in the workspace.
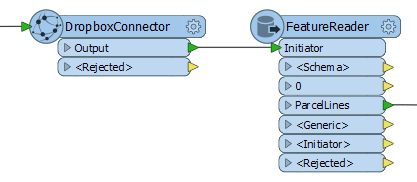
By executing the download here in the workspace, the source dataset will be refreshed every time the workspace is run.
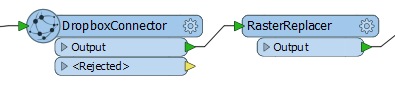
In this example portion of a workspace, the DropboxConnector is used to download a raster orthoimage from Dropbox into an attribute.
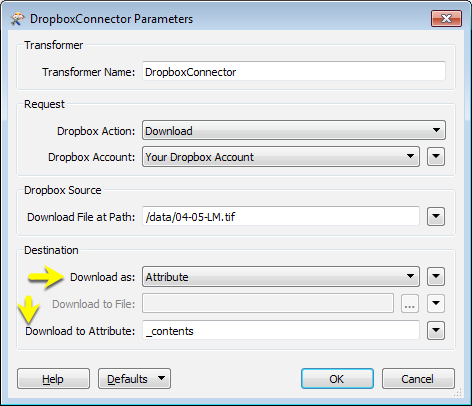
The file is read from Dropbox, and the contents stored as a blob attribute. Then a RasterReplacer is used to interpret the blob into a usable raster format.
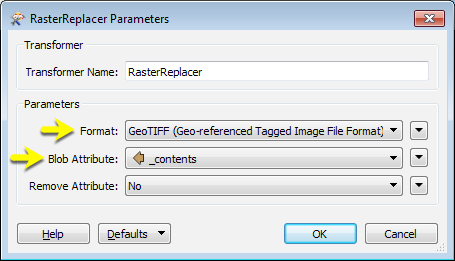
The combination of these two transformers avoids having to download the image to local storage and re-read it. A similar technique can be used for point cloud files, using the PointCloudReplacer transformer.
Usage Notes
This transformer cannot be used to directly move or copy files between different Dropbox locations. However, multiple DropboxConnectors can be used to accomplish these tasks.
The performance of this transformer is dependent on the amount of memory allocated to the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). The following environment variables allow you to specify memory available to Java Plugins:
- FME_JVM_MIN_HEAP_SIZE: Initial heap size for initializing the JVM. Default value is 1024K.
- FME_JVM_MAX_HEAP_SIZE: Maximum heap size for initializing JVM. Default value is 16384K.
If unset, the JVM applies the default values. If set, the values must be multiples of 1024K (for example, 4M and 64M, or 4096K and 32768K).
Note: To pass additional parameters used by FME to the Java Virtual Machine, use the JAVA_TOOL_OPTIONS environment variable.
Configuration
Input Ports
This transformer accepts any feature.
Output Ports
The output of this transformer will vary depending on the Dropbox Action performed.
- After an Upload action, URLs to the file may be saved to the Sharable Link and Direct Download Link attributes.
- A Download action can save to either a file or attribute.
- A Delete action will save the number of files/folders deleted to the Deleted File Count attribute.
- Finally, a List action will output a new feature for each file/folder found in the path specified. Each of these new features will have attributes listing various pieces of information about the object.
Features that cause the operation to fail are output through this port. An fme_rejection_code attribute, having the value ERROR_DURING_PROCESSING, will be added, along with a more descriptive fme_rejection_message attribute which contains more specific details as to the reason for the failure.
Rejected Feature Handling: can be set to either terminate the translation or continue running when it encounters a rejected feature. This setting is available both as a default FME option and as a workspace parameter.
Parameters
| Dropbox Action |
The type of operation to perform. Choices include:
|
| Dropbox Account |
Performing operations against a Dropbox account requires the use of OAuth2 authentication using a Web Connection. To create a Dropbox connection, click the 'Dropbox Account' drop-down box and select 'Add Web Connection...'. The connection can then be managed via Tools -> FME Options... -> Web Connections. |
The remaining parameters available depend on the value of the Request > Dropbox Action parameter. Parameters for each Dropbox Action are detailed below.
Dropbox Path
|
Delete File at Path |
Path to a file/folder on Dropbox to delete. |
Output Attributes
|
Deleted File Count |
Specify the attribute that will store a count of the number of files/folders that were deleted. |
Dropbox Source
|
Download File at Path |
The Dropbox path to the file to download. |
Destination
| Download as |
Select whether to store the downloaded data in a File or Attribute.
|
| Download to File | Specify the path to the file that will store the downloaded file. |
| Download to Attribute | Specify the attribute that will store the contents of the downloaded file. Valid for Download as Attribute only. |
Dropbox Path
|
List Contents at Path |
The path on Dropbox to list the contents of. |
Output Attributes
Default attribute names are provided, and may be overwritten.
|
File or Folder Name |
Specify the attribute to hold the name of an object on Dropbox. |
|
Full Path |
Specify the attribute to hold the full path of an object on Dropbox. |
|
File Size |
Specify the attribute to hold the size of a file object on Dropbox. |
| Revision | Specify the attribute to hold the revision string of an object on Dropbox. |
|
Last Modified |
Specify the attribute to hold the last modified date of an object on Dropbox. |
|
File or Folder Flag |
Specify the attribute to hold the type (file or folder) of an object on Dropbox. |
Source
|
Upload from |
The type of data to be uploaded.
When working with large objects, File is a better choice than Attribute Content as the data will be streamed directly from disk and not require that the object be stored entirely in memory on a feature. |
|
File to Upload |
The file to be uploaded to Dropbox if Upload from is set to File. |
|
Source Folder |
The folder to be uploaded to Dropbox if Upload from is set to Folder. |
|
Include Subfolders |
Choose whether to upload subfolders of the Source Folder or not. |
|
Attribute to Upload as File |
The data to be uploaded, supplied from an attribute if Upload from is set to Attribute Content. |
| Data Encoding | The encoding type of Attribute to Upload as File. |
Dropbox Destination
| Upload to Path | The path on Dropbox to upload the source file to. To upload to the root directory, enter “/”. |
| Upload with File Name | The name of the file created from the data supplied in Attribute to Upload as File. The name must include a filename extension (for example, .txt, .jpg, .doc). |
Output Attributes
| Shared Link |
Specify the output attribute that will store a temporary publicly accessible URL that links to the file on Dropbox. |
| Direct Download Link |
Specify the output attribute that will store a URL that links to the file on Dropbox. The URL can only be used by authenticated users. |
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters. There are a number of tools and shortcuts that can assist in constructing values, generally available from the drop-down context menu adjacent to the value field.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
| A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. | |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Working with User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
No |
| Dependencies | Dropbox account |
| FME Licensing Level | FME Professional Edition and above |
| Aliases | DropboxCaller |
| History | |
| Categories |
FME Knowledge Center
The FME Knowledge Center is the place for demos, how-tos, articles, FAQs, and more. Get answers to your questions, learn from other users, and suggest, vote, and comment on new features.
Search for all results about the DropboxConnector on the FME Knowledge Center.