StringReplacer
Parameters
This parameter specifies which attributes will have substrings replaced.
This parameter specifies the substring that will be replaced. (Also see the Replacement Text and Set Attribute Value To parameters.)
The Replacement Text parameter specifies the substring that will replace instances of the replacement substring.
If the replacement text contains & or \0, then it is replaced in the substitution with the portion of string that matched the regular expression.
If replacement text contains \#, where # is a digit between 1 and 9, then it is replaced in the substitution with the portion of string that matched the n-th parenthesized subexpression of the regular expression.
Special character sequences can be used in both the Text to Match and Replacement Text parameters.
Characters can be expressed as regular characters but they can also include any number of control characters.
Special character sequences (Advanced Editor only) are interpreted as shown below:
| Sequence | Description |
|---|---|
|
Ctrl+Shift+h (^H) |
Backspace (0x08) |
|
Ctrl+Shift+l (^L) |
Form feed (0x0c) |
|
Ctrl+Shift+j (^J) |
Newline (0x0a) |
|
Ctrl+Shift+r (^M) |
Carriage return (0x0d) |
|
Ctrl+Shift+i (^I) |
Tab (0x09) |
|
Ctrl+Shift+k (^K) |
Vertical tab (0x0b) |
Defining Special Characters
You can define special characters through the Basic or Advanced Editors. Click Open Editor from the parameter menu:
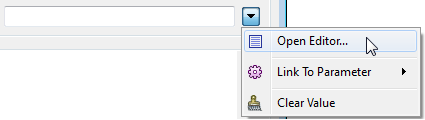
Basic Text Editor
Select Constant from the String Type column (or, in some transformers, the Value column) and click on the empty field in the column:
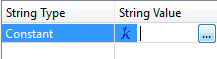
Click the browse button to the right of the column to open an Edit Value dialog. In this editor, enter characters using the shortcut keys from the table above.
Advanced Text Editor
Enter characters using the shortcuts from the table above.
Note: To see tab characters, click the Options menu on the bottom left and select Show Spaces/Tabs.
This parameter specifies whether the Text to Match parameter is a plain string or a regular expression.
If the parameter is set to Yes, Advanced Regular Expressions (AREs) are supported. An ARE is one or more branches, separated by "|", matching anything that matches any of the branches.
If the parameter is set to Yes, the Regex Editor will be available in the parameter menu.
This table lists the special characters:
| Special Character | Description |
|---|---|
| | | separates "branches" (or choices) |
| * | a sequence of 0 or more matches of what precedes it |
| + | a sequence of 1 or more matches of what precedes it |
| ? | a sequence of 0 or 1 matches of what precedes it |
| . | matches any single character |
| ^ | matches the start of the value |
| $ | matches the end of the value |
| [ ] | enclose a set of character choices |
| ( ) | enclose a "subexpression" -- whatever matches each subexpression is placed into the _matched_parts{} list attribute |
| a | any character can be listed to be matched |
- Yes: The transformer will perform case-sensitive substring matching.
- No: The transformer will perform case-insensitive substring matching.
If the Text To Match parameter is not found, the attribute value will be set to the value specified by this parameter. For more information about options for setting this parameter, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Examples
In this example, a pure substitution of text is made without any use of regular expression functionality. This is the simplest kind of substring replacement.
Source String: Bobby
Text to Find: obb
Replacement Text: ill
Use Regular Expression: no
Case Sensitive: yes
Result: Billy
In this example, a pattern matching zero or more ’b’ characters is replaced with nothing.
Source String: Bobby
Text to Find: b*
Replacement Text:
Use Regular Expression: yes
Case Sensitive: yes
Result: Boy
In this example, a pattern matching zero or more ’b’ characters followed by a y is duplicated in the result (prepended by hyphens)
Source String: Bobby
Text to Find: b*y
Replacement Text: --\\0-\\0
Use Regular Expression: yes
Case Sensitive: yes
Result: Bo--bby-bby
See the StringSearcher transformer help for additional regular expression examples.
To replace pairs of substrings, use the StringPairReplacer transformer.
To search for regular expression matches in a string without doing any replacement, use the StringSearcher transformer.
Additional Resources
Test regular expressions with the Regex Editor in the parameter menu.
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Transformer Categories
Search FME Knowledge Center
Search for samples and information about this transformer on the FME Knowledge Center.