Takes a series of features that match the input specification and performs snapping on the features that lie within the specified tolerance from other features that match the input specification. You can use this transformer to perform cleaning operations on data during a translation.
The difference between the AnchoredSnapper and the Snapper is that anchor features are considered to be accurate and consequently do not move.
Input Ports
Features that may have Candidate features snapped to them. Arcs are snapped as linear features, and ellipses are snapped as polygonal features.
Features that may be snapped to Anchor features. Arcs are snapped as linear features, and ellipses are snapped as polygonal features.
Output Ports
Candidates whose geometry is changed by the transformer.
Candidates that leave the transformer without being changed.
The anchors that were used during snapping. If a candidate was snapped to a point along the segment of an anchor, a new node is inserted into the anchor’s geometry.
Parameters
Transformer
If you select Group By attributes, only those features with the same Group By attribute values will be snapped together.
Note: How parallel processing works with FME: see About Parallel Processing for detailed information.
This parameter determines whether or not the transformer should perform the work across parallel processes. If it is enabled, a process will be launched for each group specified by the Group By parameter.
Parallel Processing Levels
For example, on a quad-core machine, minimal parallelism will result in two simultaneous FME processes. Extreme parallelism on an 8-core machine would result in 16 simultaneous processes.
You can experiment with this feature and view the information in the Windows Task Manager and the Workbench Log window.
No: This is the default behavior. Processing will only occur in this transformer once all input is present.
By Group: This transformer will process input groups in order. Changes on the value of the Group By parameter on the input stream will trigger batch processing on the currently accumulating group. This will improve overall speed if groups are large/complex, but could cause undesired behavior if input groups are not truly ordered.
Parameters
When Snapping Type is End Point Snapping:
- The transformer snaps endpoints of features that enter via the Candidate port to endpoints of features that enter via the Anchor port. Anchor features are not output.
- Point features can be used as Anchor or Candidate features, and Candidate points will be snapped together (or to a linear base feature) as well.
- The transformer will not alter area features.
When Snapping Type is Vertex Snapping:
- The transformer snaps vertices of features that enter via the Candidate port to vertices of features that enter via the Anchor port. Anchor features are not output.
- Point features can be used as Anchor or Candidate features, and Candidate points will be snapped together (or to a linear Anchor feature) as well.
- The transformer will alter area features.
When this parameter is set to Segment Snapping:
- The transformer snaps vertices of curves or points that enter via the Candidate port to lines of features that enter via the Anchor port, if their distances are within the specified tolerance. Anchor features are not output.
- The transformer snaps vertices of Candidate segments to Anchor segments if their distances are within the specified tolerance at any point along the segment.
- Candidate segments which cross Anchor segments will have new vertices introduced at the point of intersection, but the Candidate segments will not be split.
- Segment snapping may cause duplicate points, where segments have degenerated to a point.
- Area features are altered by this operation as its vertices and segments are snapped.
- If a segment and a point are both within tolerance, the transformer will snap to a vertex in preference to a segment, even when the segment is closer.
Snapping Tolerance specifies the distance, in ground units, that the snapping occurs between features.
This parameter applies only when the end point of a feature is being snapped.
- NEVER: the endpoint of a line is moved when it is snapped and no additional vertex is added.
- ALWAYS: the original end point (start point) of the line becomes the second from the end (start) and a new vertex is added to complete the snap.
- FORWARD_ONLY: a new vertex is added only when doing so creates an angle greater than 90 degrees with the original line segment. In this case, if adding the vertex would cause a less than 90-degree angle, the old end point is still moved.
Advanced Cleaning Parameters
When Snapping Type is Segment Snapping, this transformer performs data cleaning that is meant to improve the robustness of the results when they are used in other algorithms by ensuring that no two vertices in the snapped output are within cleaning tolerance of each other.
If Cleaning Tolerance Mode is set to Auto, a cleaning tolerance will automatically be calculated for the cleaning operation, based on the size of the inputs. If set to Custom, the user may specify a Cleaning Tolerance.
If Cleaning Tolerance Mode is Custom, the Cleaning Tolerance specifies the distance, in ground units, that cleaning occurs between features.
Usage Notes
- Any feature that undergoes dimensional collapse as a result of being snapped will be logged as "degenerate" and dropped. "Dimensional collapse" refers to a line or area that becomes a point, or an area that becomes a line.
- A short cleanup step is performed after snapping. This step will remove duplicate points, and may create aggregates to preserve overlapping, directed segments.
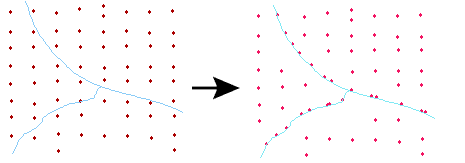
Example
FME Licensing Level
FME Professional Edition and above
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Transformer Categories
Search FME Knowledge Center
Search for samples and information about this transformer on the FME Knowledge Center.
Tags Keywords: FixedSnapper BaseSnapper