Connects input linear (arcs and lines) features in the order they enter, forming path features.
Note: For some datasets, it may be necessary to use a Sorter to order the data correctly before it enters this transformer.
If the end point of one input segment does not match the following segment's start point, geometry will be added to connect them in the following way. If the first segment is a line, then a point will be appended to it to extend it to the following segment's start point. If the first segment is an arc and the following segment is a line, then a point will be added to the beginning of the line to extend it to the first segment's end point. Otherwise, if both segments are arcs, then a two-point line will be inserted between these segments in the resulting path.
The feature being created is output whenever a Connection Break Attribute value changes. When this happens, the feature with the differing attribute is not added to the current output feature; instead, it begins the next feature to be output.
If consecutive input segments are lines, they will not be combined into a single line in the output path; they will remain as separate segments. Also, if only one segment is input for a set of Connection Break Attribute values, the output will still be a path (containing that single segment).
If supplied, a list is made of all the attributes of each feature that was connected when creating the output path.
Note: List attributes are not accessible from the output schema in Workbench unless they are first processed using a transformer that operates on them, such as ListExploder or ListConcatenator. All list attribute transformers are displayed in the Contents pane of the Transformer Help under Lists. Alternatively, AttributeExposer can be used.
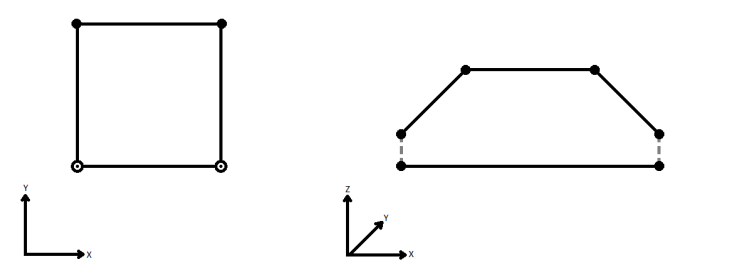
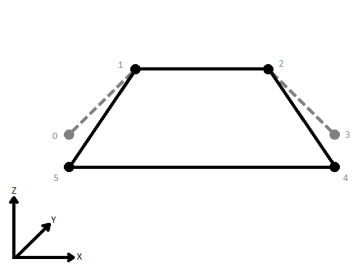
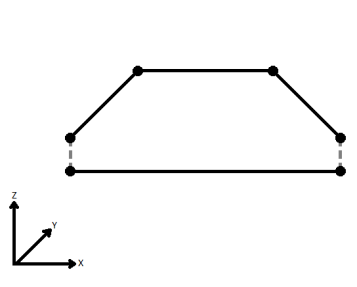
When viewed in 2D (ignoring Z), a path (which may define the border of a polygon) may appear to be closed as shown in the left figure below. This same path, when viewed in 3D, may appear to be open as shown in the right figure below.
To specify how (and if) paths should be closed in 3D, select one of the listed modes.
| Mode | Description | Example |
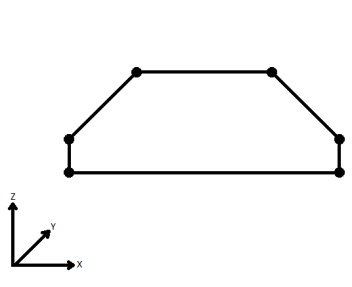
|---|---|---|
| Extend | The Curve is extended so that all vertices are left at their original location. |
|
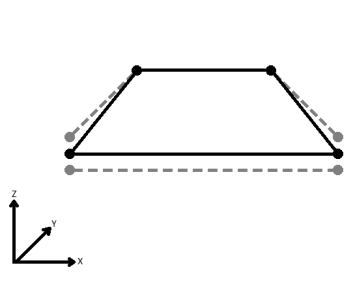
| Average | Subsequent vertices that are not connected, but share an x and a y value are combined into one vertex, whose Z value is the average of the original two. |
|
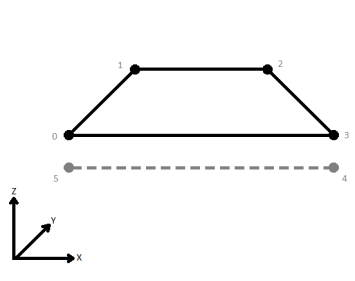
| First Wins | Subsequent vertices that are not connected, but share an x and a y value are combined into one vertex, whose Z value is taken from the first encountered vertex. |
|
| Last Wins | Subsequent vertices that are not connected, but share an x and a y value are combined into one vertex, whose Z value is taken from the last encountered vertex. |
|
| Ignore | Z values are ignored. No change is made to the way the nodes are connected. |
|
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Transformer Categories
Search FME Knowledge Center
Search for samples and information about this transformer on the FME Knowledge Center.