Replaces the geometry of the feature with either its two-dimensional bounding box, its two-dimensional minimum oriented bounding box, or its three-dimensional bounding cube.
If a feature’s bounding box has zero area, it will become a line or a point.
Parameters
Choose 2D Bounding Box (which means the axis-aligned or rectilinear bounding box), 2D Oriented Bounding Box, or 3D Bounding Cube.
If a 3D Bounding Cube is chosen but the original geometry is 2D, a 2D Bounding Box will be created instead.
Optionally, you can calculate the lengths of the shortest and longest sides of the chosen bounding box or cube. They will appear as attributes in the Box output port.
Example
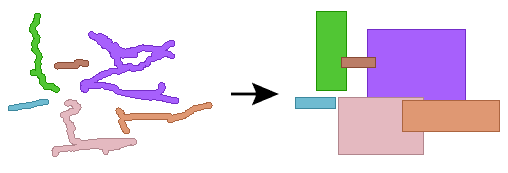
- To accumulate the bounding box of a number of features, use the BoundingBoxAccumulator.
- To retrieve the bounds of a feature into attributes, use the BoundsExtractor.
- To replace the geometry of a feature with a box whose values come from attributes, use the 2DBoxReplacer.
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Transformer Categories
Search FME Knowledge Center
Search for samples and information about this transformer on the FME Knowledge Center.
Tags Keywords: MBR "minimum bounding rectangle" neatline "envelope oriented" "bounding box"