The first selected band of raster A is combined with the first selected band of raster B, the second selected band of raster A is combined with the second selected band of raster B, and so on.
Input Ports
Input features have the following restrictions:
- All input features must have raster geometry.
- Paired rasters must have the same number of rows and columns.
- Paired rasters must have the same number of selected bands.
- Paired bands must both have the same nodata value, or they both must have no nodata value.
- Bands may not contain a palette.
Output Ports
Unselected bands are appended to the output raster, unchanged. The unselected bands of raster A are appended first, followed by the unselected bands of raster B.
Parameters
Transformer
To perform a calculation on more than one pair of rasters, a set of Group By attributes must be specified. Each group must contain one A raster and one B raster.
Group By attributes are always added to the output feature.
Note: How parallel processing works with FME: see About Parallel Processing for detailed information.
This parameter determines whether or not the transformer should perform the work across parallel processes. If it is enabled, a process will be launched for each group specified by the Group By parameter.
Parallel Processing Levels
For example, on a quad-core machine, minimal parallelism will result in two simultaneous FME processes. Extreme parallelism on an 8-core machine would result in 16 simultaneous processes.
You can experiment with this feature and view the information in the Windows Task Manager and the Workbench Log window.
No: This is the default behavior. Processing will only occur in this transformer once all input is present.
By Group: This transformer will process input groups in order. Changes of the value of the Group By parameter on the input stream will trigger batch processing on the currently accumulating group. This will improve overall speed if groups are large/complex, but could cause undesired behavior if input groups are not truly ordered.
Using Ordered input can provide performance gains in some scenarios, however, it is not always preferable, or even possible. Consider the following when using it, with both one- and two-input transformers.
Single Datasets/Feature Types: Are generally the optimal candidates for Ordered processing. If you know that the dataset is correctly ordered by the Group By attribute, using Input is Ordered By can improve performance, depending on the size and complexity of the data.
If the input is coming from a database, using ORDER BY in a SQL statement to have the database pre-order the data can be an extremely effective way to improve performance. Consider using a Database Readers with a SQL statement, or the SQLCreator transformer.
Multiple Datasets/Feature Types: Since all features matching a Group By value need to arrive before any features (of any feature type or dataset) belonging to the next group, using Ordering with multiple feature types is more complicated than processing a single feature type.
Multiple feature types and features from multiple datasets will not generally naturally occur in the correct order.
One approach is to send all features through a Sorter, sorting on the expected Group By attribute. The Sorter is a feature-holding transformer, collecting all input features, performing the sort, and then releasing them all. They can then be sent through an appropriate filter (TestFilter, AttributeFilter, GeometryFilter, or others), which are not feature-holding, and will release the features one at a time to the transformer using Input is Ordered By, now in the expected order.
The processing overhead of sorting and filtering may negate the performance gains you will get from using Input is Ordered By. In this case, using Group By without using Input is Ordered By may be the equivalent and simpler approach.
In all cases when using Input is Ordered By, if you are not sure that the incoming features are properly ordered, they should be sorted (if a single feature type), or sorted and then filtered (for more than one feature or geometry type).
As with many scenarios, testing different approaches in your workspace with your data is the only definitive way to identify performance gains.
Parameters
This parameter sets the operation that will be performed:
| + | add |
| - | subtract |
| * | multiply |
| / | divide |
|
Minimum Maximum Average |
takes the minimum, maximum or average of A and B |
For example, if you select the plus sign (+), the two input rasters A and B will be added together (and therefore, the output raster will be A+B).
If Preserve Interpretation is set to Yes, each output band will have the same interpretation as its input bands when the input bands share the same interpretation. If the input bands have different interpretations, or Preserve Interpretation is set to No, the interpretation of each output band will be automatically determined.
Note that when converting between different data types, a Bounded Cast is used. As a result, when a calculated value does not fit in the destination interpretation, the corresponding destination value will either be set to the minimum or maximum value possible in the destination data type.
If Accumulate Attributes is set to Yes, then the attributes from the original features will be merged onto the output feature. Group By attributes are always added to the output feature.
Example
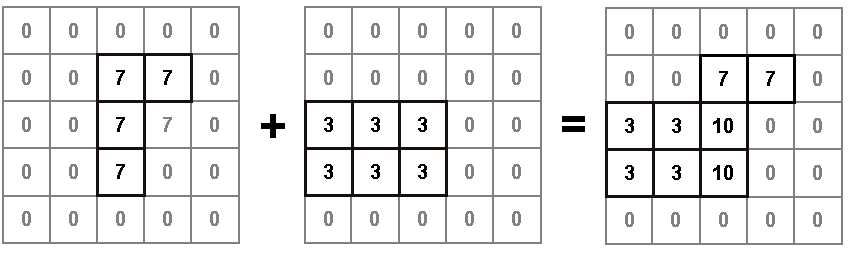
Related Transformers
- You can modify band selection with the RasterSelector.
- Nodata values can be set with the RasterBandNodataSetter or removed with the RasterBandNodataRemover.
- Palettes may be resolved using the RasterPaletteResolver or removed using the RasterPaletteRemover.
- You can use the RasterSingularCellValueCalculator to operate on a raster and a scalar.
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Transformer Categories
FME Licensing Level
FME Professional edition and above
Search FME Knowledge Center
Search for samples and information about this transformer on the FME Knowledge Center.
Tags Keywords: raster "bounded cast" palette band