FME Transformers: 2024.1
Calculates the planar or sloped area of polygon geometries and adds the results as attributes.
Typical Uses
-
Retrieving area values as attributes
How does it work?
The AreaCalculator receives features with any type of geometry, and calculates areas as follows:
-
Area polygons (2D) - plane area
-
Area polygons with z values - plane or sloped area
-
Raster - plane area of raster extents
-
3D object - cumulative area of all surfaces
-
Other geometries (including point clouds) - receive an area of zero (0)
Area values are stored in a specified attribute.
Units are square ground units according to the feature's coordinate system. A multiplier may be applied to scale the values and convert to different units of measure.
Aggregates are supported.
Examples
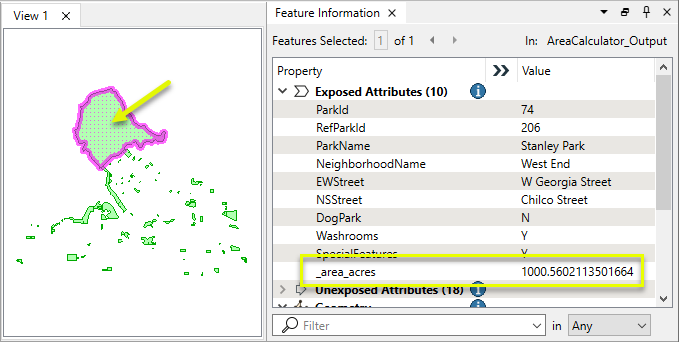
In this example, we have a set of park polygons and want to extract the area of each feature in acres. Note that the coordinate system is UTM-83, with ground units in meters.
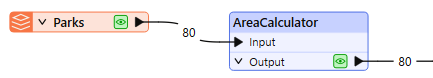
The features are routed into an AreaCalculator.
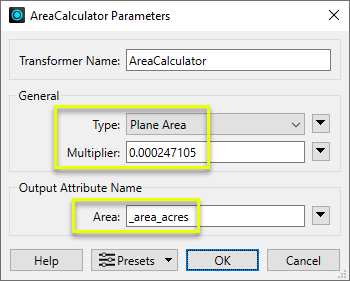
In the parameters dialog, Multiplier is set to the square meters to acres conversion factor, and the new attribute name _area is modified to _area_acres to remind us of the unit conversion.
The output features have a new _area_acres attribute, containing the area values.
Usage Notes
-
Alternatively, the @Area() function can be used in expressions to calculate area values.
-
In general, features in a geographic projection (lat/long) should be reprojected to an appropriate coordinate system before calculating areas. The Reprojector or CommonLocalReprojector may be useful.
Creating and Modifying Area Features
These transformers work with polygons in a variety of ways.
|
|
Function |
Transformer Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Creating areas from topologically connected lines where they form closed shapes. |
Creates polygons from topologically correct linear features. |
|
|
Creating areas from individual linear features. |
Converts a linear feature to an area by connecting the end point to the start point. |
|
|
Combining touching or overlapping areas to create larger areas. |
Combines overlapping and/or adjacent areas into larger contiguous areas by removing shared and interior edges. |
|
|
Calculating areas. |
Calculates the planar or sloped area of polygon geometries and adds the results as attributes. |
|
|
Cleaning up overlaps and gaps to create contiguous coverage. |
Repairs area topologies by resolving gaps and overlaps between adjacent areas. |
|
|
Generalizing areas. |
Generalizes area geometry by connecting and combining neighboring features and/or filling in holes and details. |
|
|
Converting donut areas to non-donut areas by connecting holes to the perimeter. |
Builds connections between donut holes with the outer boundary of a donut, resulting in a polygon-equivalent representation of the input donut. |
|
|
Converting areas within areas to donut holes. |
Cuts holes in area features where they fully enclose another area, creating donut polygons. |
|
|
Separating donut areas into their parts. |
Separates donut polygons into outer shell and hole polygons. |
|
|
Counting the number of holes in a donut area. |
Adds a new attribute whose value is the number of holes in the feature. If the feature is not a polygonal feature, 0 will be returned. |
|
|
Finding polygon overlaps and extracting them into new geometry. |
Performs an area-on-area overlay (intersection of polygons) so that all input areas are intersected against each other and resultant area features are created and output. The resultant areas can accumulate attribute from any overlapping polygons. |
|
|
Finding intersections between lines and polygons, splitting either where they intersect. |
Performs a line-on-area overlay, either splitting lines where they intersect area boundaries or subdividing areas where split by lines. Attributes may be shared between related lines and areas (spatial join). |
|
|
Identifying points that fall within polygons, and sharing attributes between them. |
Performs a point-in-polygon overlay. Points may receive containing area attributes, and areas may receive contained point attributes (spatial join). |
Configuration
Input Ports
This transformer accepts any feature.
Output Ports
Features with area values as specified in parameters.
The dynamic <Rejected> port appears when a parameter is set to a non-literal value that might make processing impossible.
For example, if a numeric parameter such as Line Width, Count Start, or Decimal Places is set to an expression, attribute value, or user parameter, it is possible to pass in a non-numeric value that cannot be used. Decimal Places = Cat cannot be processed, so the feature will be output via this port.
Rejected features will have an fme_rejection_code attribute explaining the reason for rejection.
Rejected Feature Handling: can be set to either terminate the translation or continue running when it encounters a rejected feature. This setting is available both as a default FME option and as a workspace parameter.
Parameters
|
Type |
Select the type of area calculation to perform:
Raster and full 3D geometry (solid and mesh) area calculations are not affected by this choice. Raster area is the raster extents (plane area) and 3D area is the cumulative area of all 3D surfaces. |
|
Multiplier |
Specify a value to optionally scale the area values. Default is 1. |
|
Area |
Name the attribute to contain the area of the feature. |
Editing Transformer Parameters
Transformer parameters can be set by directly entering values, using expressions, or referencing other elements in the workspace such as attribute values or user parameters. Various editors and context menus are available to assist. To see what is available, click  beside the applicable parameter.
beside the applicable parameter.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more.
When setting values - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors - strings and expressions containing String, Math, Date/Time or FME Feature Functions will have those functions evaluated. Therefore, the names of these functions (in the form @<function_name>) should not be used as literal string values.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
|
Special Characters |
A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| Date/Time Functions | Date and time functions are available in the Text Editor. |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Creating and Modifying User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Table Tools
Transformers with table-style parameters have additional tools for populating and manipulating values.
|
Row Reordering
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
|
|
Cut, Copy, and Paste
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
Cut, copy, and paste may be used within a transformer, or between transformers. |
|
Filter
|
Start typing a string, and the matrix will only display rows matching those characters. Searches all columns. This only affects the display of attributes within the transformer - it does not alter which attributes are output. |
|
Import
|
Import populates the table with a set of new attributes read from a dataset. Specific application varies between transformers. |
|
Reset/Refresh
|
Generally resets the table to its initial state, and may provide additional options to remove invalid entries. Behavior varies between transformers. |
Note: Not all tools are available in all transformers.
For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
No |
| Dependencies | None |
| Aliases | |
| History |
FME Community
The FME Community is the place for demos, how-tos, articles, FAQs, and more. Get answers to your questions, learn from other users, and suggest, vote, and comment on new features.
Search for all results about the AreaCalculator on the FME Community.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver, Open Government Licence - British Columbia, and/or Open Government Licence – Canada.