Converts a given angle from one coordinate system to another.
Typical Uses
- Determining angles for text and symbol rotation
- Reprojecting angles stored as attribute values
How does it work?
The ReprojectAngleCalculator receives features with geometry and reprojects a given angle from one coordinate system to another.
The transformer starts with two points. One is the first coordinate of the input feature’s geometry, and the second is calculated from that point using the Original Line Angle and Original Line Length. Both of these points are reprojected from the Source Coordinate System to the Destination Coordinate System. A new angle is calculated from the reprojected points and added to the output feature as an attribute value.
The Original Line Angle may be provided as an attribute value, constant value, expression, user parameter, or conditional value.
Original Line Length is also required to perform the calculation, in the Source Coordinate System’s ground units. The length may be provided as an attribute, expression, constant, parameter, or conditional value. A length of one (1) is often appropriate for calculating rotation around a point, such as text and symbol rotation angles.
Both the Source and Destination Coordinate Systems must be specified explicitly.
Reprojections are generally performed using the FME (CS-Map) library, however, this transformer will honor the Workspace Parameter Reprojection Engine, and will use the Esri Reprojection Engine if it is selected there, with or without an Esri product being installed.
Z values are not supported.
This transformer assumes all coordinate systems are Cartesian.
Examples
In this example, we have a CAD file containing traffic signal locations and labels. The original file is projected as UTM83-10, but we want to know what will happen to the label rotation if we reproject to BCPOLY-83.
Note that the label's autocad_rotation value is zero (0).
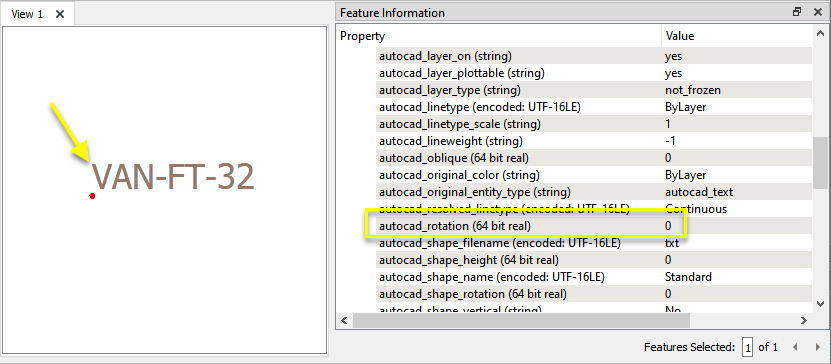
The features are routed into a ReprojectAngleCalculator.
Note that three format-specific attributes have been exposed - autocad_text_size, autocad_text_string, and autocad_rotation. This was done in the Autodesk AutoCAD DWG/DXF Reader parameters, Format Attributes, so that we can access their values.
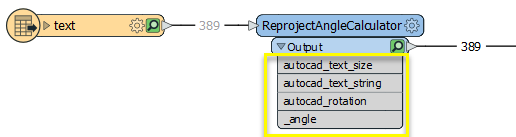
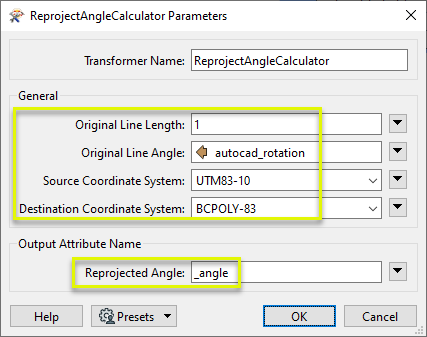
In the parameters dialog, we set Original Line Angle to the exposed autocad_rotation attribute, and the Original Line Length to 1 (meter, in ground units).
Both the Source and Destination Coordinate Systems are specified explicitly.
The Reprojected Angle attribute is named _angle (the default name).
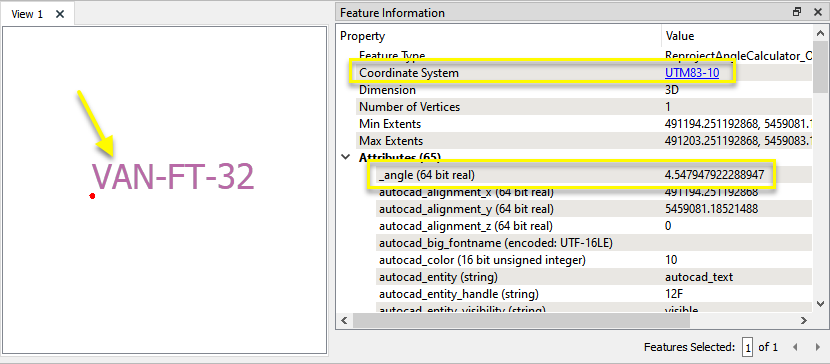
The output feature has a new attribute - _angle - with the value of the reprojected angle.
Note that the Coordinate System has not changed and is still UTM83-10. The feature itself has not been reprojected, its geometry not altered. The reprojection to BCPOLY-83 has only been used to calculate the _angle value.
Usage Notes
- This transformer requires that features have geometry to provide an initial coordinate. Non-spatial features will not produce valid output. To create geometry for non-spatial data with coordinates as attributes, consider using a VertexCreator.
Working With Coordinate System Transformers
FME inherently supports coordinate system transformations and reprojections.
Coordinate systems generally have a name and a definition, and the syntax of that definition can vary greatly between both spatial data formats and other coordinate system libraries. Custom and local coordinate systems can also be defined in FME, further complicating matters. For in-depth information, see the Working With Coordinate Systems documentation.
Reprojections are generally done with the FME Reprojection Engine, which is based on the CS-Map coordinate system library. This default can be overridden on a per-workspace basis, using the Workspace Parameters > Translation > Reprojection Engine parameter, and set to Esri. Where appropriate, FME will use the Esri Reprojection Engine if it is selected there, with or without an Esri product being installed.
Coordinate System Support
These transformers perform various coordinate system-related tasks, but do not reproject the data.
|
Looks up coordinate system names and definitions between FME’s internal format and common third-party and open source representations, storing the results as an attribute. |
|
|
Retrieves the name of the feature's assigned FME coordinate system into an attribute. |
|
|
Removes the coordinate system from features, without modifying geometry or coordinates. |
|
|
Assigns a specified coordinate system to features, without modifying geometry or coordinates. |
|
|
Assigns a specified local coordinate system to features, without modifying geometry or coordinates. |
Coordinate System Reprojection
Different coordinate system libraries (engines) not only contain coordinate system definitions, they also have unique reprojection algorithms. FME’s generic reprojection transformers, in the first table below, default to using the FME (CS-Map) library.
A selection of other libraries is also available, some of which are specific to certain areas of the world or software platforms.
Inherent reprojections, as in a workspace with different input and output coordinate systems selected, default to using the FME (CS-Map) library.
If you are reprojecting explicitly with a transformer in the workspace, using library-specific transformers is recommended. In the case of CsmapReprojector versus the Reprojector (with default engine), the library may be identical, but the CSMapReprojector handles vertical coordinate calculations whereas the Reprojector does not.
Generic Reprojection Transformers
|
|
|
Library |
|---|---|---|
|
Reprojects x and y coordinates stored as attributes from one coordinate system to another. |
FME (default) or Esri |
|
|
Reprojects one or more features to a local coordinate system centered on the bounding box containing all features. |
FME (default) or Esri |
|
|
Converts a given angle from one coordinate system to another. |
FME (default) or Esri |
|
|
Converts a given length from one coordinate system to another. |
FME (default) or Esri |
|
|
Reprojects feature x and y coordinates from one coordinate system to another. |
FME (default) or Esri |
Library-Specific Reprojection Transformers (Recommended)
|
|
|
Library (External Links) |
|---|---|---|
|
Reprojects x, y, and optionally z coordinates stored as attributes from one coordinate system to another using the CS-MAP library. |
||
|
Reprojects feature x, y, and optionally z coordinates from one coordinate system to another using the CS-Map library. |
||
|
Reprojects feature coordinates from one coordinate system to another using the Esri reprojection library. |
||
|
Great Britain Northern Ireland Republic of Ireland |
Reprojects feature coordinates from one coordinate system to another using the Grid InQuestII engine from Ordnance Survey, for use in Great Britain, Ireland, and Northern Ireland. |
|
|
Sweden |
Reprojects coordinates stored as attributes from one coordinate system to another using the Gtrans reprojection engine from the National Land Survey of Sweden (Lantmäteriet). |
|
|
Sweden |
Reprojects feature coordinates from one coordinate system to another using the Gtrans reprojection engine from the National Land Survey of Sweden (Lantmäteriet). |
|
|
Reprojects coordinates stored as attributes from one coordinate system to another using the PROJ library. |
||
|
Reprojects feature coordinates from one coordinate system to another using the PROJ library. |
||
|
Switzerland |
Reprojects feature coordinates from one coordinate system to another in Switzerland, using the Reframe library from the Federal Office of Topography (swisstopo). |
Configuration
Input Ports
Features with geometry.
Output Ports
Features with a reprojected angle value added to an attribute.
Parameters
|
Original Line Length |
Specify a distance, in the Source Coordinate System’s ground units. |
|
Original Line Angle |
Specify an angle, in the Source Coordinate System. Angle is measured counterclockwise from horizontal in degrees. |
|
Source Coordinate System |
Specify the coordinate system of the input features. |
|
Destination Coordinate System |
Specify the coordinate system the Original Line Angle is to be reprojected to. Note that the feature itself will not be reprojected, and this parameter is only used for calculation of the Reprojected Angle Attribute. |
|
Reprojected Angle |
Name the attribute to contain the reprojected angle value. |
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters. There are a number of tools and shortcuts that can assist in constructing values, generally available from the drop-down context menu adjacent to the value field.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more.
When setting values - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors - strings and expressions containing String, Math, Date/Time or FME Feature Functions will have those functions evaluated. Therefore, the names of these functions (in the form @<function_name>) should not be used as literal string values.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
|
Special Characters |
A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| Date/Time Functions | Date and time functions are available in the Text Editor. |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Creating and Modifying User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Dialog Options - Tables
Transformers with table-style parameters have additional tools for populating and manipulating values.
|
Row Reordering
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
|
|
Cut, Copy, and Paste
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
Cut, copy, and paste may be used within a transformer, or between transformers. |
|
Filter
|
Start typing a string, and the matrix will only display rows matching those characters. Searches all columns. This only affects the display of attributes within the transformer - it does not alter which attributes are output. |
|
Import
|
Import populates the table with a set of new attributes read from a dataset. Specific application varies between transformers. |
|
Reset/Refresh
|
Generally resets the table to its initial state, and may provide additional options to remove invalid entries. Behavior varies between transformers. |
Note: Not all tools are available in all transformers.
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
No |
| Dependencies | None |
| Aliases | |
| History |
FME Community
The FME Community is the place for demos, how-tos, articles, FAQs, and more. Get answers to your questions, learn from other users, and suggest, vote, and comment on new features.
Search for all results about the ReprojectAngleCalculator on the FME Community.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver and/or the Open Government Licence – Canada.