Reprojects feature coordinates from one coordinate system to another using the Gtrans reprojection engine from the National Land Survey of Sweden (Lantmäteriet).
Typical Uses
- Reprojecting features when explicitly using the Gtrans engine is desired
- Reprojecting features in select local coordinate systems not supported elsewhere
How does it work?
The GtransReprojector receives raster, vector, or point cloud features and reprojects their coordinates from one coordinate system to another, using the Gtrans engine and translation files.
Gtrans is widely used for coordinate transformation within Sweden as it is officially recommended, translates between numerous local coordinate systems, and supports rubbersheeting transformations.
The transformation is configured by selecting a Gtrans Translation File appropriate for the Source and Destination Coordinate System. For raster features, the Reverse Translation File must be identified as well.
Output features’ coordinate system will show as Unknown, as these features no longer have an FME coordinate system tag. If the output coordinate system is known to have an exact match in FME’s coordinate system library, it can be tagged manually with a CoordinateSystemSetter.
Translation Files
A selection of Gtrans Translation Files are provided with FME.
Only reprojections defined here or with a user-provided Gtrans Translation File (see below) may be performed with this transformer.
|
File Type |
Description |
Location |
|---|---|---|
|
*.tf, *.tfi |
Translation File - a text file containing parameters defining a reprojection from one coordinate system to another.
|
[FME Install Directory]\Reproject\Gtrans\Sys |
|
*.tr1, *.tr2 |
Triangulation File - a binary file used for the interpolation of residuals.
|
[FME Install Directory]\Reproject\Gtrans\Sys |
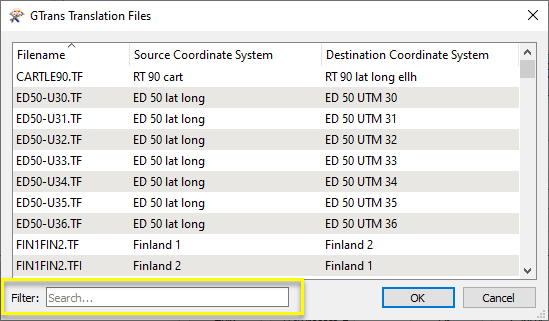
Each *.tf/*.tfi file corresponds to a line item in the Gtrans Translation Files library accessed in the parameters dialog.
Note that when using the Filter option, FME searches the file names of the *.tf/*.tfi files - not the Source and Destination Coordinate Systems.
Geoid Files
When reprojecting between geoids, this transformer needs additional resource files.
|
File |
Description |
Location |
|---|---|---|
|
geoid.def |
Geoid Definition File - a text file containing parameters describing geoids. A default version is provided with FME. User-provided geoids may also be used - see below. |
[FME Install Directory]\Reproject\Gtrans\Sys |
|
*.grd |
Binary Grid files for specific geoids. |
[FME Install Directory]\Reproject\Gtrans\Sys |
Gtrans User Data
Users may provide their own transformations and definitions by placing the appropriate files as directed:
|
File(s) |
Description |
Location |
|---|---|---|
|
*.tf, *.tfi |
Translation File - a text file containing parameters defining a reprojection from one coordinate system to another.
The Translation File should reference the correct geoid.def and any required *.bin files. User-defined translations are placed in the same location as the provided Translation Files. |
[FME Install Directory]\Reproject\Gtrans\Arkiv |
|
geoid.def |
Geoid Definition File - a text file containing parameters describing geoids. A default version is provided with FME. The user version of this file is placed in a different location than the default geoid.def provided with FME. |
[FME Install Directory]\Reproject\Gtrans\Arkiv |
|
*.bin |
Binary Grid files for specific geoids. |
[FME Install Directory]\Reproject\Gtrans\Arkiv |
Rasters
Additional parameters are available for raster features, specifying how the reprojected cells are to be interpolated. Both the forward and Reverse Translation Files for the reprojection must be provided.
This transformer is not affected by raster band and palette selection.
Examples
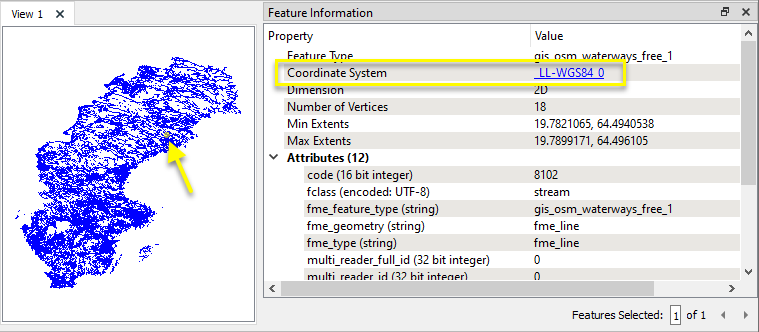
In this example, we have a shapefile of waterways in Sweden, extracted from OpenStreetMap. We want to reproject the features to an appropriate national coordinate system using the Gtrans engine.
Note that the source data is tagged as lat/long geographic coordinates, WGS84.
The features are routed into a GtransReprojector.
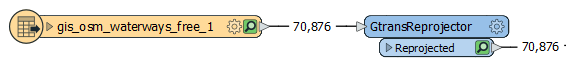
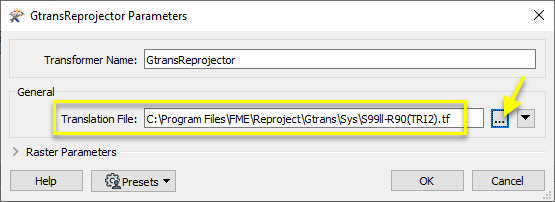
In the parameters dialog, a Translation File is selected.
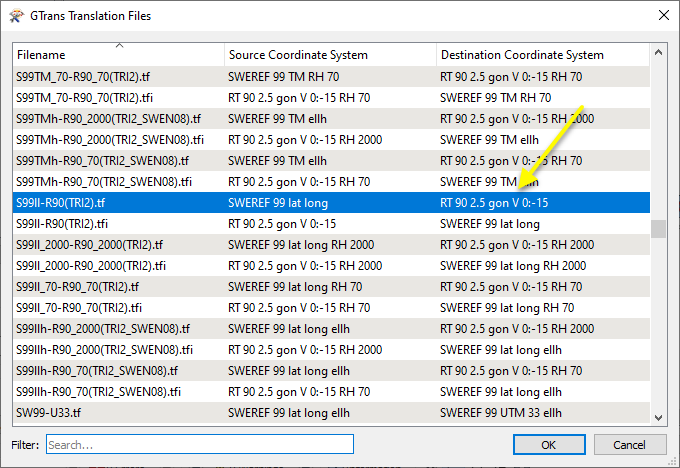
The Translation File was selected from the Gtrans Translation Files gallery, via the ellipsis button. Note that the chosen Source Coordinate System is SWEREF 99 lat long, an equivalent to LL-WGS84.
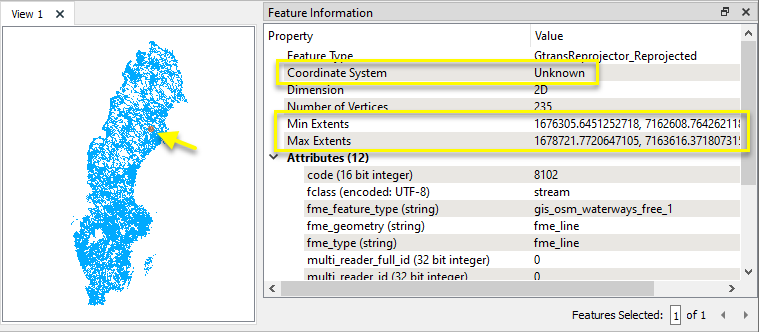
The output features have been reprojected. Note that FME no longer knows what the Coordinate System is - if the Destination Coordinate System has a known FME equivalent, it could be tagged using a CoordinateSystemSetter.
TFFIL Lantmäteriet 2006-08-24
Överräkning mellan SYSTEM:
SWEREF 99 13 30 Ellh-> SWEREF 99 lat long ellh
/
FSYSTEM SWEREF 99 13 30 Ellh/
HTYP ELLIPSOID METER/
TSYSTEM SWEREF 99 lat long ellh/
LATLONG DEG/
HTYP ELLIPSOID METER/
ELLIPSOID GRS 80/
PROJ GAUSS
G 13 30 0 DEG
0
150000
1
/
STOP /GEOID SWEN08_RH2000 grid
Geoidhöjdsmodell för SWEREF 99,
bilinjär interpolation i grid SWEN08_RH2000.grd, geografiska lat long
Gridstorlek: 801x376
lat-min: 54° long-min: 10°
lat-max: 70° long-max: 25°
dlat: 0°.02 dlong: 0°.04
/
ELLIPSOID GRS 1980
/
GRIDSYSTEM SWEREF 99 lat long
/
HSYSTEM RH 2000
/
GRIDFIL SWEN08_RH2000.grd
/
GEOID SWEN08_RH70 grid
Geoidhöjdsmodell för SWEREF 99,
bilinjär interpolation i grid SWEN08_RH70.grd, geografiska lat long
Gridstorlek: 801x376
lat-min: 54° long-min: 10°
lat-max: 70° long-max: 25°
dlat: 0°.02 dlong: 0°.04
/
ELLIPSOID GRS 1980
/
GRIDSYSTEM SWEREF 99 lat long
/
HSYSTEM RH 70
/
GRIDFIL SWEN08_RH70.GRD
/Usage Notes
- FME has a Workspace Parameter, Reprojection Engine, that may be set to either FME (CS-Map) or Esri. This transformer will override this parameter setting.
- The Reprojector provides similar functionality, and will use the default library (CS-Map or Esri) set in FME. It supports some Swedish coordinate systems, but will not use the Gtrans definitions or reprojection engine.
- To reproject coordinates stored as attribute values, consider using the GtransAttributeReprojector.
Working With Coordinate System Transformers
FME inherently supports coordinate system transformations and reprojections.
Coordinate systems generally have a name and a definition, and the syntax of that definition can vary greatly between both spatial data formats and other coordinate system libraries. Custom and local coordinate systems can also be defined in FME, further complicating matters. For in-depth information, see the Working With Coordinate Systems documentation.
Reprojections are generally done with the FME Reprojection Engine, which is based on the CS-Map coordinate system library. This default can be overridden on a per-workspace basis, using the Workspace Parameters > Translation > Reprojection Engine parameter, and set to Esri. Where appropriate, FME will use the Esri Reprojection Engine if it is selected there, with or without an Esri product being installed.
Coordinate System Support
These transformers perform various coordinate system-related tasks, but do not reproject the data.
|
Looks up coordinate system names and definitions between FME’s internal format and common third-party and open source representations, storing the results as an attribute. |
|
|
Retrieves the name of the feature's assigned FME coordinate system into an attribute. |
|
|
Removes the coordinate system from features, without modifying geometry or coordinates. |
|
|
Assigns a specified coordinate system to features, without modifying geometry or coordinates. |
|
|
Assigns a specified local coordinate system to features, without modifying geometry or coordinates. |
Coordinate System Reprojection
Different coordinate system libraries (engines) not only contain coordinate system definitions, they also have unique reprojection algorithms. FME’s generic reprojection transformers, in the first table below, default to using the FME (CS-Map) library.
A selection of other libraries is also available, some of which are specific to certain areas of the world or software platforms.
Inherent reprojections, as in a workspace with different input and output coordinate systems selected, default to using the FME (CS-Map) library.
If you are reprojecting explicitly with a transformer in the workspace, using library-specific transformers is recommended. In the case of CsmapReprojector versus the Reprojector (with default engine), the library may be identical, but the CSMapReprojector handles vertical coordinate calculations whereas the Reprojector does not.
Generic Reprojection Transformers
|
|
|
Library |
|---|---|---|
|
Reprojects x and y coordinates stored as attributes from one coordinate system to another. |
FME (default) or Esri |
|
|
Reprojects one or more features to a local coordinate system centered on the bounding box containing all features. |
FME (default) or Esri |
|
|
Converts a given angle from one coordinate system to another. |
FME (default) or Esri |
|
|
Converts a given length from one coordinate system to another. |
FME (default) or Esri |
|
|
Reprojects feature x and y coordinates from one coordinate system to another. |
FME (default) or Esri |
Library-Specific Reprojection Transformers (Recommended)
|
|
|
Library (External Links) |
|---|---|---|
|
Reprojects x, y, and optionally z coordinates stored as attributes from one coordinate system to another using the CS-MAP library. |
||
|
Reprojects feature x, y, and optionally z coordinates from one coordinate system to another using the CS-Map library. |
||
|
Reprojects feature coordinates from one coordinate system to another using the Esri reprojection library. |
||
|
Great Britain Northern Ireland Republic of Ireland |
Reprojects feature coordinates from one coordinate system to another using the Grid InQuestII engine from Ordnance Survey, for use in Great Britain, Ireland, and Northern Ireland. |
|
|
Sweden |
Reprojects coordinates stored as attributes from one coordinate system to another using the Gtrans reprojection engine from the National Land Survey of Sweden (Lantmäteriet). |
|
|
Sweden |
Reprojects feature coordinates from one coordinate system to another using the Gtrans reprojection engine from the National Land Survey of Sweden (Lantmäteriet). |
|
|
Reprojects coordinates stored as attributes from one coordinate system to another using the PROJ library. |
||
|
Reprojects feature coordinates from one coordinate system to another using the PROJ library. |
||
|
Switzerland |
Reprojects feature coordinates from one coordinate system to another in Switzerland, using the Reframe library from the Federal Office of Topography (swisstopo). |
Configuration
Input Ports
Features with geometry to be reprojected.
Output Ports
Features reprojected as specified in parameters.
Parameters
|
Translation File |
Enter the path and filename of the desired Translation File. Files may be selected from the Gtrans Translation File gallery via the ellipsis button. |
|
Reverse Translation File |
If reprojecting rasters, the inverse Translation File must also be provided. Enter the path and filename. Files may be selected from the Gtrans Translation File gallery via the ellipsis button. |
|
Interpolation Type |
Select a method for interpolating reprojected cell values:
|
||||||||||
|
Cell Size |
Select a method for resizing cells:
|
||||||||||
|
Tolerance (cells) |
Sets the tolerance, in cells, for approximating reprojected cell locations. Using the default value of 0.0, every cell will be reprojected. If a value greater than 0.0 is specified, some cell locations will be approximated. The difference between an approximated cell location and the true cell location should be at most the tolerance value. For example, if a value of 0.5 is specified, each approximated cell location should be maximum one-half of a pixel away from its true location. Increasing the Tolerance value may improve performance. |
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters. There are a number of tools and shortcuts that can assist in constructing values, generally available from the drop-down context menu adjacent to the value field.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more.
When setting values - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors - strings and expressions containing String, Math, Date/Time or FME Feature Functions will have those functions evaluated. Therefore, the names of these functions (in the form @<function_name>) should not be used as literal string values.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
|
Special Characters |
A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| Date/Time Functions | Date and time functions are available in the Text Editor. |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Creating and Modifying User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Dialog Options - Tables
Transformers with table-style parameters have additional tools for populating and manipulating values.
|
Row Reordering
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
|
|
Cut, Copy, and Paste
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
Cut, copy, and paste may be used within a transformer, or between transformers. |
|
Filter
|
Start typing a string, and the matrix will only display rows matching those characters. Searches all columns. This only affects the display of attributes within the transformer - it does not alter which attributes are output. |
|
Import
|
Import populates the table with a set of new attributes read from a dataset. Specific application varies between transformers. |
|
Reset/Refresh
|
Generally resets the table to its initial state, and may provide additional options to remove invalid entries. Behavior varies between transformers. |
Note: Not all tools are available in all transformers.
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
No |
| Dependencies | Gtrans software and Translation Files, included with FME. |
|
Operating System Restrictions |
Windows only. |
| Aliases | |
| History |
FME Community
The FME Community is the place for demos, how-tos, articles, FAQs, and more. Get answers to your questions, learn from other users, and suggest, vote, and comment on new features.
Search for all results about the GtransReprojector on the FME Community.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver and/or the Open Government Licence – Canada.
Example contains data © OpenStreetMap contributors.
Keywords: SWEREF99 "National Land Survey of Sweden" Sweden