Creates a buffer zone of specified size around or inside input geometry. Works similarly to the Bufferer, but is designed for use with features in Geographic coordinates. Reprojects input features into the Dynamic Equal Distance projection, buffers them, then reprojects back into the original Geographic coordinates.
Typical Uses
- Creating fixed size zones around features, such as rights-of-way or setbacks
- Determining spatial relationships based on proximity
- Creating variable size zones around features to represent attribute values
- Creating a buffer in different units than the input data
How does it work?
The GeographicBufferer accepts 2D point, curve (line), and area geometries. It reprojects the input features, including those with geographic (lat/long) coordinates, to Dynamic Equal Distance projection, and then creates buffers according to the parameter settings for units, size, and style.
The buffers are then reprojected to match the original coordinate system of the input features, and are output.
Point and lines may be expanded, creating surrounding polygons with points offset by the specified Buffer Amount in ground units. Areas may be expanded or shrunk, using positive or negative Buffer Amounts.
The attributes of the original features are retained, and the buffer is output, discarding the original geometry.
A selection of end cap and corner styles is available.
In this example, we create buffer zones around rapid transit lines. The source data is KML, in a geographic lat/long projection.
As the ground units are in degrees, the data must be reprojected before making calculations in units like meters or feet. The GeographicBufferer will take care of that.
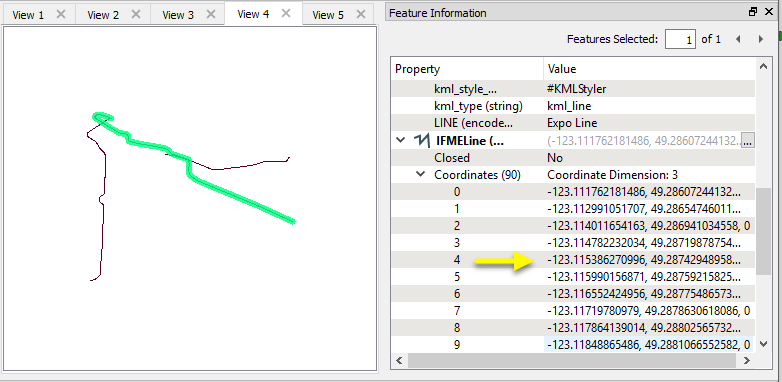
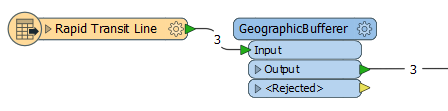
The lines are routed into the Input port.
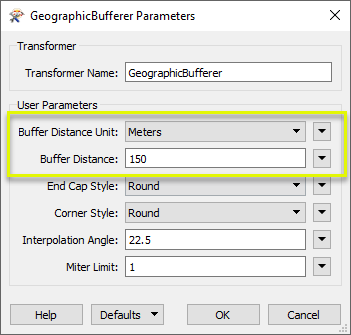
In the parameters dialog, we select Meters as our ground unit of choice, and set a Buffer Distance of 150.
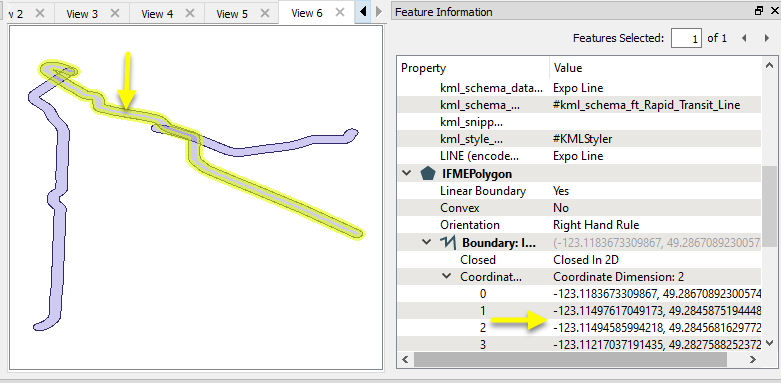
The resulting Output buffer polygons retain the attributes of the original features, and are projected in the original lat/long coordinate system.
For more examples of using buffering, see Bufferer.
Usage Notes
- This transformer creates buffers that are of equal width on either side of a linear input feature. To create offsets to either the left or right-hand side of a feature, use the OffsetCurveGenerator along with a Reprojector.
- To buffer features not in Geographic (lat/long) coordinates, consider the Bufferer.
- Areas will be buffered on one side only - externally for a positive Buffer Amount, and internally for a negative Buffer Amount.
- Features must have a coordinate system defined, or they will be output via the Rejected port. The CoordinateSystemSetter may be of use to specify coordinate system if it is missing.
- The GeographicBufferer will buffer features in any valid coordinate system (geographic or other), and so may be used to create flexible workspaces that can buffer regardless of input coordinate systems and units.
Configuration
Input Ports
Points, curves (lines), or areas. Only 2D geometries are accepted as input, and they must have a valid coordinate system defined.
Output Ports
Each point in the output curve will be the specified amount, measured in ground units, away from the input geometry. If the specified buffer amount is too small, a feature with a null geometry is output.
The original geometry is not output.
Features without a coordinate system defined, or without valid point, curve, or area geometries are output through this port along with an additional attribute, fme_rejection_code, to indicate the reason for rejection.
Rejected Feature Handling: can be set to either terminate the translation or continue running when it encounters a rejected feature. This setting is available both as a default FME option and as a workspace parameter.
Parameters
| Buffer Distance Unit |
This parameter specifies the measurement units used by the Buffer Distance parameter. Choices include:
|
| Buffer Distance | If a positive (negative) buffer amount is specified, the input feature is expanded (shrunk). A buffer amount of 0 will leave the input geometry unmodified. |
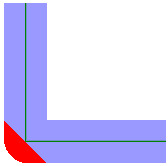
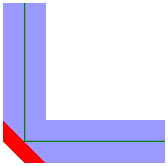
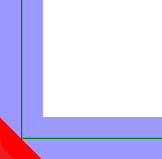
| End Cap Style |
When buffering a line, you can specify the end-cap style. As these diagrams illustrate, these caps can be Round (default) or Square, but you can also set this parameter to None. Round
Square
None
|
| Corner Style |
When buffering a line or area, you can specify the corner style. As the diagrams below illustrate, the corner styles can be Round (default), Bevel (chopped), or Miter (pointed). If Miter is used, a limit must be specified using the Miter Limit parameter. If a corner is too pointed for the miter limit, the corner will instead be bevelled. Round
Bevel
Miter
|
| Interpolation Angle |
This parameter controls the smoothness of the stroked arcs in the output buffer boundaries. It specifies what angles should be used to construct a circular arc. As this parameter decreases in value, the smoothness of the arc connectors increases. This parameter is used for the Round End Cap Style and the Round Corner Style. The value must be between 0 and 90 degrees. |
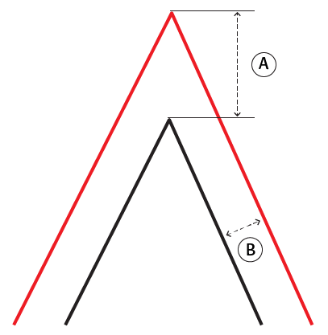
| Miter Limit |
Miter Limit This parameter controls how pointed a buffered corner can be before it is beveled. It is the highest value that the ratio of corner distance to offset is allowed to have before truncation occurs. A higher number allows for more extreme corner angles.
Miter Ratio = Corner distance / Offset
|
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters. There are a number of tools and shortcuts that can assist in constructing values, generally available from the drop-down context menu adjacent to the value field.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
| A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. | |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Working with User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
No |
| Dependencies | |
| FME Licensing Level | FME Professional Edition and above |
| Aliases | |
| History | |
| Categories |
FME Knowledge Center
The FME Knowledge Center is the place for demos, how-tos, articles, FAQs, and more. Get answers to your questions, learn from other users, and suggest, vote, and comment on new features.
Search for all results about the GeographicBufferer on the FME Knowledge Center.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver