FME Transformers: 2025.1
Filters features by test conditions to one or more output ports.
Typical Uses
- Replacing multiple Testers
- Dividing features into multiple streams
How does it work?
The TestFilter accepts any type of feature and evaluates them against any number of specified tests.
Features are output though a named port when they pass a test, and may be output at the first test they pass or for every test they pass.
Features that do not pass any tests are output as <Unfiltered>.
Creating Test Clauses
Each clause is composed of a value to test, and the method of testing it. Depending on the type of test, at a minimum the clause will consist of a Left Value and an Operator. If the chosen Operator needs more information (for example, testing for an attribute that is greater than a certain value), a Right Value field is provided.
The Test Clauses are created in a table, and numbered from the top down.
|
Left Value |
Operator |
Right Value |
Mode* |
|---|---|---|---|
| The value or expression to test | The type of test to perform | The value for comparison, if required by the operator | Test the values in a specific manner |
| Examples | |||
| Latitude | > | 49.000001 | Automatic |
| @Area() | In Range | (1,100) | Numeric |
| SnackType | Like | Kebabs | Case Sensitive |
| Traffic | Attribute Is Null | <Unused> | Automatic |
| Count | Type Is | Integer | Automatic |
* Note that Mode is only available for individual tests when Comparison Mode is set to Specify Per Test.
Test Clause Operators
These are the Operators available for constructing test clauses. They may be used to test attribute values, constructed expressions, constants, and published parameters.
Note that (unless otherwise specified) most operators can be used with both numeric values and strings. Strings may be compared with the =, !=, <, >, <=, and >= operators, and are evaluated by their character codes, so A < B.
|
Operator |
Description |
Right Value Configuration |
||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| = | Equal to | Enter a value for comparison. | ||||||||||||||||
| != | Not Equal to | Enter a value for comparison. | ||||||||||||||||
| < | Less than | Enter a value for comparison. | ||||||||||||||||
| > | Greater than | Enter a value for comparison. | ||||||||||||||||
| <= | Less than or equal to | Enter a value for comparison. | ||||||||||||||||
| >= | Greater than or equal to | Enter a value for comparison. | ||||||||||||||||
| In Range |
Tests if the value falls within the numeric range specified in set notation. Open-ended ranges may be defined by leaving either the lower or upper limit blank. |
Range values are separated by a comma and enclosed by brackets. Square brackets - [ ] - indicate inclusive limits (greater than or equal to, less than or equal to). Round brackets - ( ) - indicate exclusive limits (greater than, less than). Valid range examples: (1,9) Greater than 1 and less than 9 [1,9] Greater than or equal to 1 and less than or equal to 9 (1,9] Greater than 1 and less than or equal to 9 (1,) Greater than 1 [,9] Less than or equal to 9 Note This operator is not available when Mode is set to Case Sensitive or Case Insensitive, and those modes are not available when the operator is set to In Range.
|
||||||||||||||||
| In | Tests if the value may be found in the provided list of possible values and ranges. |
Enter any combination of comma-separated strings, numeric values, and/or ranges (in the form of x-y). Valid configuration examples: 1,10,100 1-99 cat cat,dog,cats and dogs dogs,1-9,7 String ranges (for example, a-d) can also be specified. To test for values that contain a hyphen, enclose the value in quotation marks: "LL-27","LL-83". To test for values that contain either single (') or double (") quotes, enclose the value in the opposing quotes: "Duncan's Lake" or 'Say "Hello"'. |
||||||||||||||||
| Like | Tests that the value matches a specified string pattern. |
Enter a string pattern. Wildcards are supported using the percentage symbol (%), rather than an asterisk (*). In Automatic mode, this operator is case insensitive. This operator is not available when Mode is set to Numeric. Example: If Right Value is %bc%: abcd: Passed bc: Failed |
||||||||||||||||
| Contains | Tests that the Right Value occurs somewhere in the Left Value. |
Enter a value to test for. In Automatic mode, this operator is case insensitive. This operator is not available in Numeric mode. Example: If Right Value is bc: abcd: Passed abde: Failed |
||||||||||||||||
| Begins With | Tests that the Left Value string begins with the Right Value string. |
Enter the string to be tested against. In Automatic mode, this operator is case insensitive. This operator is not available in Numeric mode. Example: If Right Value is Do: Dogs: Passed Cats: Failed |
||||||||||||||||
| Ends With | Tests that the Left Value string ends with the Right Value string. |
Enter the string to be tested against. In Automatic mode, this operator is case insensitive. This operator is not available in Numeric mode. Example: If Right Value is gs: Dogs: Passed Cats: Failed |
||||||||||||||||
| Contains Regex | Tests that the value contains a string that matches a pattern described by a Regular Expression. |
Enter a Regular Expression. The Regular Expression Editor is available via the ellipsis (...) button, and may be used to construct and test expressions. The regex to test may represent a string to be found anywhere within the value, or may represent the entire value (by creating a regex long enough to represent the extent of the desired value). Example: If regex is \d (Any digit) cats: Failed 9: Passed cats82: Passed |
||||||||||||||||
| Type Is |
Tests if the value is compatible with the chosen Type. You may test for multiple types by adding additional Test Clauses. |
Select the Type to test for.
|
||||||||||||||||
| Encodable In | Tests if the value is encodable in the specified encoding without data loss. |
Select from a list of standard encodings. Sample encodings:
|
||||||||||||||||
| Attribute has a value | Tests that the attribute has a value, and is not null, missing, or empty. | <Unused> | ||||||||||||||||
| Attribute Is Null | Tests that the attribute has a null value. |
<Unused> |
||||||||||||||||
| Attribute is Empty String | Tests that the value is an empty string. | <Unused> | ||||||||||||||||
| Attribute is Missing | Tests that the attribute is absent on the feature | <Unused> |
Cached Values and Data-Aware Test Clauses
If Feature Caching is enabled, valid attribute values from upstream features can be viewed to complete test clauses.
As shown here in the Tester, if the Left Value has been set to an Attribute Value and the features have been cached, the context menu provides access to the values available in those features. If there are only a few choices, they will be presented in a sub-menu.
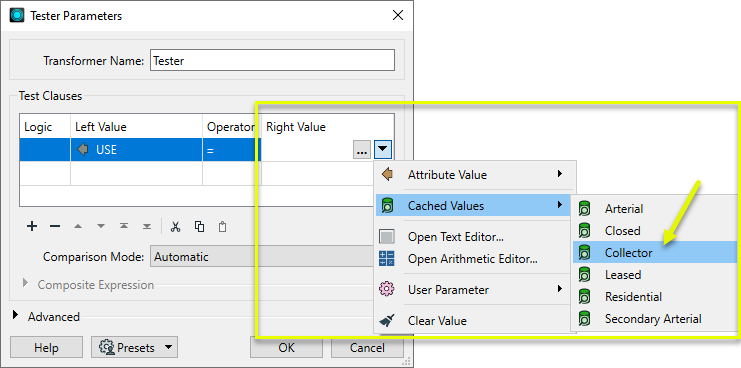
If there are a large number of choices, the values will be presented in a Select Value dialog, where the values may be sorted and searched with the Filter option.

Connecting Test Clauses: Logic
Multiple test clauses are connected with Logic, using AND, OR, and NOT in addition to parentheses to specify how the tests are evaluated to determine passing or failing.
Logic connectors can be edited by selecting options in the Logic column of the Test Clauses table, or may be edited directly using the Composite Expression parameter’s Edit button.
Configuration
Input Ports
This transformer accepts any type of feature.
Output Ports
Features that pass tests are output via named ports as specified in parameters.
Features that do not pass any test are output here. This port may be renamed in parameters.
Parameters
This table specifies the tests to perform and their associated output port names.
Each entry consists of a Test condition and port. The same Output Port name may be assigned to multiple entries.
Tests are performed in same order as the table entries.
Features that do not pass any tests are output via <Unfiltered>, which may be renamed.
|
Test Output
|
Select an option for feature output with multiple tests:
|
|
Preserve Feature Order
|
This parameter controls the order in which features exit a transformer. When a transformer has more than one output port, features usually exit one port at a time. At times, it may be useful to keep the order that features arrived in, switching from port to port as necessary. This allows feature order to be preserved, though at a potential cost in processing efficiency. Select a method for feature ordering.
|
|
Port Name |
Name the attribute to contain the name of the port the feature was output through. |
Editing Transformer Parameters
Transformer parameters can be set by directly entering values, using expressions, or referencing other elements in the workspace such as attribute values or user parameters. Various editors and context menus are available to assist. To see what is available, click  beside the applicable parameter.
beside the applicable parameter.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more.
When setting values - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors - strings and expressions containing String, Math, Date/Time or FME Feature Functions will have those functions evaluated. Therefore, the names of these functions (in the form @<function_name>) should not be used as literal string values.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
|
Special Characters |
A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| Date/Time Functions | Date and time functions are available in the Text Editor. |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Creating and Modifying User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Table Tools
Transformers with table-style parameters have additional tools for populating and manipulating values.
|
Row Reordering
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
|
|
Cut, Copy, and Paste
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
Cut, copy, and paste may be used within a transformer, or between transformers. |
|
Filter
|
Start typing a string, and the matrix will only display rows matching those characters. Searches all columns. This only affects the display of attributes within the transformer - it does not alter which attributes are output. |
|
Import
|
Import populates the table with a set of new attributes read from a dataset. Specific application varies between transformers. |
|
Reset/Refresh
|
Generally resets the table to its initial state, and may provide additional options to remove invalid entries. Behavior varies between transformers. |
Note: Not all tools are available in all transformers.
For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
No |
| Dependencies | None |
| Aliases | |
| History |
FME Community
The FME Community has a wealth of FME knowledge with over 20,000 active members worldwide. Get help with FME, share knowledge, and connect with users globally.
Search for all results about the TestFilter on the FME Community.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver, Open Government Licence - British Columbia, and/or Open Government Licence – Canada.