FME Transformers: 2025.2
Calculates a circle containing all vertices of the input feature, output as either attribute values or geometry.
Typical Uses
-
Calculating circular boundaries around features
How does it work?
The transformer has two modes:
-
Replace Geometry - replace the input feature geometry with the circle
-
Set Attributes - add the center coordinates and radius as attribute values, keeping the input geometry intact.
One circle is generated for each feature or aggregate.
Features with 3D geometry such as 3D objects and point clouds will have a circle generated that encloses their footprint in 2D.
Point features are passed through unchanged (unless they are aggregated or multi-point).
Examples
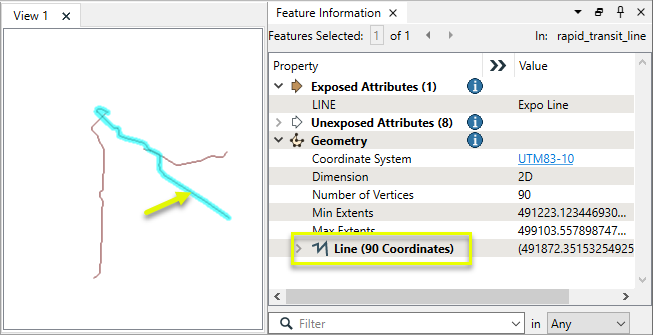
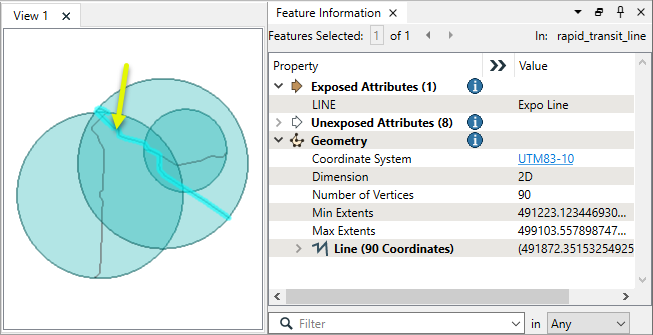
In this example, we have a set of transit lines containing three individual routes.
The features are routed into a MinimumSpanningCircleReplacer.
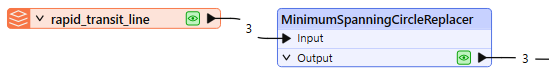
In the parameters dialog, Mode is set to Replace Geometry.
A circle is generated for each feature, as shown here layered over the original line geometry.
Usage Notes
-
To generate a circle around multiple features, use an Aggregator before the MinimumSpanningCircleReplacer.
Configuration
Input Ports
This transformer accepts any feature type.
Output Ports
Features with minimum spanning circles as either geometry or attribute values, as specified in parameters.
Parameters
|
Mode |
Select a method for handling the calculated circles:
|
|
Center X |
When Mode is Set Attributes, name the attribute to contain the center x coordinate. |
|
Center Y |
When Mode is Set Attributes, name the attribute to contain the center y coordinate. |
|
Radius |
When Mode is Set Attributes, name the attribute to contain the radius of the circle. |
Editing Transformer Parameters
Transformer parameters can be set by directly entering values, using expressions, or referencing other elements in the workspace such as attribute values or user parameters. Various editors and context menus are available to assist. To see what is available, click  beside the applicable parameter.
beside the applicable parameter.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more.
When setting values - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors - strings and expressions containing String, Math, Date/Time or FME Feature Functions will have those functions evaluated. Therefore, the names of these functions (in the form @<function_name>) should not be used as literal string values.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
|
Special Characters |
A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| Date/Time Functions | Date and time functions are available in the Text Editor. |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Creating and Modifying User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Table Tools
Transformers with table-style parameters have additional tools for populating and manipulating values.
|
Row Reordering
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
|
|
Cut, Copy, and Paste
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
Cut, copy, and paste may be used within a transformer, or between transformers. |
|
Filter
|
Start typing a string, and the matrix will only display rows matching those characters. Searches all columns. This only affects the display of attributes within the transformer - it does not alter which attributes are output. |
|
Import
|
Import populates the table with a set of new attributes read from a dataset. Specific application varies between transformers. |
|
Reset/Refresh
|
Generally resets the table to its initial state, and may provide additional options to remove invalid entries. Behavior varies between transformers. |
Note: Not all tools are available in all transformers.
For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
No |
| Dependencies | None |
| Aliases | |
| History |
FME Online Resources
The FME Community and Support Center Knowledge Base have a wealth of information, including active forums with 35,000+ members and thousands of articles.
Search for all results about the MinimumSpanningCircleReplacer on the FME Community.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver, Open Government Licence - British Columbia, and/or Open Government Licence – Canada.