FME Transformers: 2025.2
Combines feature geometries into heterogeneous or homogeneous aggregates. Alternatively, combines feature attributes without any geometry.
Features are aggregated in the order they are received by this transformer. If the order of individual geometry parts within the resulting aggregate is important, you can first route the features through a Sorter.
Feature geometries and attributes can also be deaggregated using a similar transformer, the Deaggregator.
Example
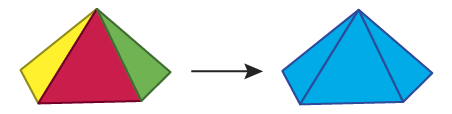
Geometric Representation
The example below illustrates a geometric feature of diverse attributes on the left and its aggregated output on the right.

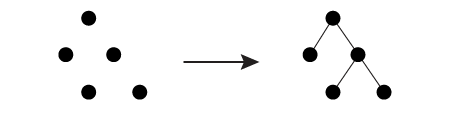
Data Structure Representation
The example below illustrates a set of points representing a non-aggregated data structure on the left and its corresponding aggregated output on the right.
Usage Notes
-
This transformer will not dissolve adjacent area boundaries – it simply creates a collection of all that it is given. Use the Dissolver if adjacent areas are to be merged into a single area.
Configuration
Parameters
|
Group By |
If you do not select Group By attributes, then all features fall into the same group. When you select Group By attributes, this transformer will aggregate the geometries of the input features, based on the selection in the Group By parameter. Each group of features that have the same values for the Group By attributes will be processed independently of other groups. |
||||
|
Complete Groups
|
Select the point in processing at which groups are processed:
There are two typical reasons for using When Group Changes (Advanced) . The first is incoming data that is intended to be processed in groups (and is already so ordered). In this case, the structure dictates Group By usage - not performance considerations. The second possible reason is potential performance gains. Performance gains are most likely when the data is already sorted (or read using a SQL ORDER BY statement) since less work is required of FME. If the data needs ordering, it can be sorted in the workspace (though the added processing overhead may negate any gains). Sorting becomes more difficult according to the number of data streams. Multiple streams of data could be almost impossible to sort into the correct order, since all features matching a Group By value need to arrive before any features (of any feature type or dataset) belonging to the next group. In this case, using Group By with When All Features Received may be the equivalent and simpler approach. Note Multiple feature types and features from multiple datasets will not generally naturally occur in the correct order.
As with many scenarios, testing different approaches in your workspace with your data is the only definitive way to identify performance gains. |
|
Aggregation Mode |
Select a mode:
|
|
Accumulation Mode |
If Drop Incoming Attributes is chosen, the output feature will not preserve any input attributes. If Merge Incoming Attributes is chosen, the output feature will merge all input attributes. If Use Attributes From One Feature is chosen, the output feature will get attributes from only one input feature. |
||||||
|
Attributes to Concatenate |
Attributes can be concatenated so that the resulting Aggregate feature preserves multiple source attribute values under the same attribute name. For example, if input feature 1 has an “id” attribute of 1 and input feature 2 has an “id” attribute of 2, specifying “id” for this parameter together with a separate character of “,” will cause the output Aggregate feature to have an “id” with value “1, 2”. |
||||||
|
Separator Character |
The Separator Character is used to separate elements within an attribute value string. For example, if features with attribute values of “River Rd”, “Marine Dr” and “HWY 1” for the attribute named “Road Name” respectively, and the Separator Character is “, ” (a comma followed by a space) on the output aggregate feature, the attribute “Road Name” will contain “River Rd, Marine Dr, HWY 1” as a value. The separator character can be expressed as a regular character but it can also reference parameters and contain special characters. |
||||||
|
Attributes to Sum |
Any attributes specified in this field will undergo statistical accumulation. For example, if two input polygons have an attribute “salary” set to 30000 and 50000, then summing them would result in a “salary” of 80000 on the aggregate output. |
||||||
|
Attributes to Average |
Any attributes specified in this field will undergo statistical accumulation. For example, if two input polygons have an attribute “salary” set to 30000 and 50000, then averaging them would result in a “salary” of 40000 on the aggregate output. |
||||||
|
Attributes to Average, Weighted by Area |
Any attributes specified in this field will undergo statistical accumulation. For example, if two input polygons have an attribute “salary” set to 30000 and 50000, and the second polygon was 3 times larger than the first polygon, then the weighted average would be 45000. Attributes to Average, Weighted by Area may produce non-numeric results if some input features have zero, or no area. |
||||||
|
Generate List |
When enabled, adds a list attribute to the output Aggregate feature.
|
|
Aggregate Type |
Heterogeneous Collection: the output geometry will be an IFMEAggregate. Homogeneous Collection (If Possible): if the output geometry can be made into a homogeneous collection without changing the geometry type of any of its parts, then this option will perform the conversion. |
|
Geometry Label Attribute |
If Geometry Label Attribute is specified, each incoming feature will store the value of this attribute as the label of the geometry it owns. This way, as the input geometries are combined to form the output Aggregate feature, we will have transferred the geometry labels onto the output features. |
|
ID Selection |
When the Mode is Geometry - Assemble Hierarchy, the user may reconstruct hierarchical geometries either using ID and Parent ID, ID and Child ID, or all three sets of ID information (All). If a hierarchical geometry were to be represented as a tree, then each tree node would have a unique ID. Each node would refer to its parent by Parent ID and its children by child IDs. |
|
ID Attribute |
The attribute that uniquely identifies each input node feature. This value must be unique across all input features for the Aggregator to function properly. |
|
Parent ID Attribute |
The attribute that identifies a node feature’s parent node. |
|
Child ID List Attribute |
The list attribute that identifies all child nodes of a node. |
|
Convert Attributes to Traits |
If set to Yes, then attributes on an input feature will be stored as traits on the geometry owned by the feature. This way as geometries are combined to form aggregates, the input attribute information is preserved. If set to No, then no input attributes are saved, except the input attributes of the root node feature. |
|
Preserve IDs |
IDs are used to reconstruct hierarchical geometries and may be removed after the reconstruction. Specify Yes to keep these IDs as traits. Specify No to remove these IDs. |
|
Cycle ID Error Attribute |
If specified, an attribute with this name will be added to each output feature if a cycle with no root node is detected, containing the ID of one of the features in the cycle. |
|
Number of Aggregated Features |
Name the attribute to contain the number of features that were combined to form the aggregate. |
Editing Transformer Parameters
Transformer parameters can be set by directly entering values, using expressions, or referencing other elements in the workspace such as attribute values or user parameters. Various editors and context menus are available to assist. To see what is available, click  beside the applicable parameter.
beside the applicable parameter.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more.
When setting values - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors - strings and expressions containing String, Math, Date/Time or FME Feature Functions will have those functions evaluated. Therefore, the names of these functions (in the form @<function_name>) should not be used as literal string values.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
|
Special Characters |
A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| Date/Time Functions | Date and time functions are available in the Text Editor. |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Creating and Modifying User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Table Tools
Transformers with table-style parameters have additional tools for populating and manipulating values.
|
Row Reordering
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
|
|
Cut, Copy, and Paste
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
Cut, copy, and paste may be used within a transformer, or between transformers. |
|
Filter
|
Start typing a string, and the matrix will only display rows matching those characters. Searches all columns. This only affects the display of attributes within the transformer - it does not alter which attributes are output. |
|
Import
|
Import populates the table with a set of new attributes read from a dataset. Specific application varies between transformers. |
|
Reset/Refresh
|
Generally resets the table to its initial state, and may provide additional options to remove invalid entries. Behavior varies between transformers. |
Note: Not all tools are available in all transformers.
For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
Yes |
| Dependencies | None |
| Aliases | AttributeAccumulator |
| History |
FME Online Resources
The FME Community and Support Center Knowledge Base have a wealth of information, including active forums with 35,000+ members and thousands of articles.
Search for all results about the Aggregator on the FME Community.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver, Open Government Licence - British Columbia, and/or Open Government Licence – Canada.