FME Server and N-Tier Architecture
When you install FME Server, you can package all the components, or layers, of the FME Server Architecture onto a single machine. This "Express" installation option is the quickest and easiest way to get started with FME Server, because all the components are provided for you. You only need to provide a single server on which to host the installation.
Alternatively, you can physically distribute these layers to achieve an n-tier architecture. Both 3-tier and 2-tier configurations are supported:
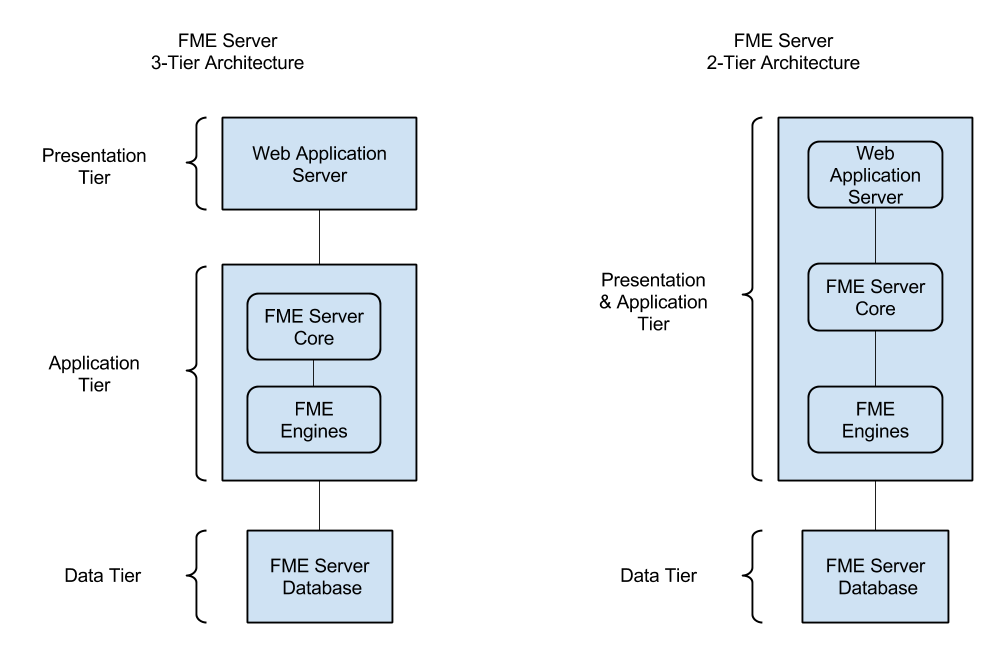
A 3-tier architecture distributes the FME Server Web Services, FME Server application (including the FME Server Core and FME Engines), and the FME Server Database across three physically separate servers. In this scenario, you must provide and manage the following additional components:
- A web application server to run the FME Server Web Services. You can run the FME Server Web Services on your own servlet (Apache Tomcat and Oracle WebLogic are supported), or use an Apache Tomcat servlet provided with the installation.
- A database server to host the FME Server Database (Oracle, PostgreSQL, and SQL Server are supported).
- A remote file system to host Resources.
In a 2-tier architecture, an Apache Tomcat servlet is provided to run the FME Server Web Services, and is installed along with the FME Server Core and Engines. Only the FME Server Database is installed separately, on a server you provide, along with a remote file system.
Benefits of an N-Tier Architecture
Implement an n-tier architecture for any of the following reasons:
- You want to keep components separate so that each can be managed by the appropriate expert team.
- You want to implement an Active-Passive system for failover.
Implementing an N-Tier Architecture
You can implement an n-tier architecture of FME Server in one of two ways:
- At installation time, by choosing one of the Distributed Installation options.
- After an Express installation, by performing one or both of the following reconfigurations: