Database Connection
This parameter must contain the name of the source CartoDB account. The account name is the same as the username that is used to log into the account on the CartoDB website.
For CartoDB Multiuser Enterprise accounts, note that this is not the same as the organization name.
CartoDB accounts are protected by API keys, which can be found in Your API keys in the CartoDB web interface. By default, the API key parameter is left blank.
- If the API key is left blank, FME can read public tables associated with the CartoDB account.
- If the API key is specified, FME can read both public and private tables associated with the CartoDB account.
When using CartoDB Multiuser Enterprise, multiple users can be associated with one account.
If you are Multiuser Account user, enter your username here. FME will access the associated CartoDB Multiuser Account.
Constraints
After you have specified the database connection, click the Browse button to select tables for import. A connection window appears while the system compiles a table from the database.
Once the table list appears, you can select one or more tables, and then click OK to dismiss the window. The table name(s) will appear in the Table List field in the parameter box.
Advanced
This parameter specifies the number of features to be retrieved from the server for each request.
If not specified, the default value is 500.
CartoDB has a SQL API, which allows FME to read and write data to CartoDB tables. This API is normally located at https://[account_name].cartodb.com/api/v2/sql.
However, if you are running your own instance of the open source CartoDB software, this API location may be different. If you are not running your own instance of CartoDB, leave this parameter blank.
- If the API URL is left blank, then FME will use the default API URL to access your CartoDB account.
- If the API URL is specified, then FME will use a URL in the form of:
https://[account_name].[API_URL_value]
Schema Attributes
Use this parameter to expose Format Attributes in Workbench when you create a workspace:
- In a dynamic scenario, it means these attributes can be passed to the output dataset at runtime.
- In a non-dynamic scenario where you have multiple feature types, it is convenient to expose additional attributes from one parameter. For example, if you have ten feature types and want to expose the same attribute in each one, it is easier to define it once than it is to set each feature type individually in the workspace.
Using the minimum and maximum x and y parameters, define a bounding box that will be used to filter the input features. Only features that intersect with the bounding box are returned.
If all four coordinates of the search envelope are specified as 0, the search envelope will be disabled.
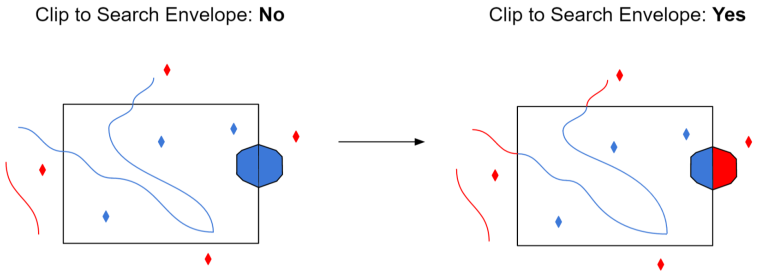
Select this parameter to remove any portions of exported features outside the area of interest.
The illustration below shows the results of the Search Envelope when Clip to Search Envelope is set to No on the left side and Yes on the right side.
- No: Any features that cross the search envelope boundary will be read, including the portion that lies outside of the boundary.
- Yes: Any features that cross the search envelope boundary will be clipped at the boundary, and only the portion that lies inside the boundary will be read. The underlying function for the Clip to Search Envelope function is an intersection; however, when Clip to Search Envelope is set to Yes, a clip is also performed in addition to the intersection.