FME Transformers: 2025.2
Overlays points on lines, splitting lines and sharing attributes.
Typical Uses
- Splitting lines where they overlay points
- Identifying lines that intersect with a point
- Identifying points that fall on a line
How does it work?
The PointOnLineOverlayer compares points and lines, splitting the lines where a point falls on (or within a specified distance of) the lines. Each resulting new line may receive the attributes of the points that matched the original line, and points may receive attributes from the lines (a spatial join). Features (points and lines) also receive a count of the number of matches encountered.
Aggregates can either be deaggregated before processing or rejected. Intersections between linear features are not computed.
Z Values and Measures
If the input Line features have measures and/or 3D coordinates, measures and elevations (z values) are interpolated and assigned to points according to the selections made in the Attribute Accumulation parameters.
If Attribute Accumulation Mode is set to Drop Overlaid Attributes, the measures and z values will be ignored. If it is set to Merge, Prefix, or Replace with Single Overlaid, the appropriate values will be calculated and assigned to the points. If a z value is added to a 2D point, it will become 3D.
Examples
In this example, we perform an overlay of rapid transit stations points on rapid transit lines. The source data, as seen here, contains three individual transit routes, each one a single line feature.
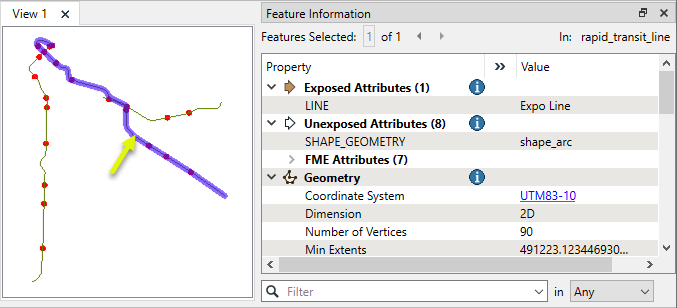
The station points are close to the lines, but not right on them - generally within a meter.
The stations are connected to the Point input port, and the routes are connected to the Line input port.
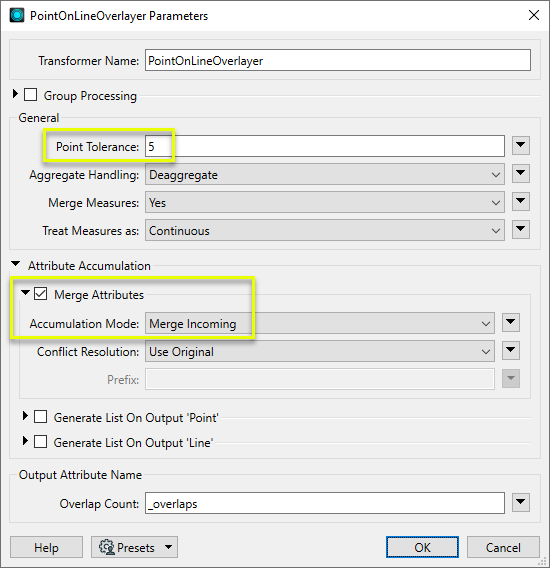
In the parameters dialog, we enter a tolerance of “5” - meaning 5 meters, as these datasets are in a UTM projection, with ground units in meters. We also choose to merge attributes.
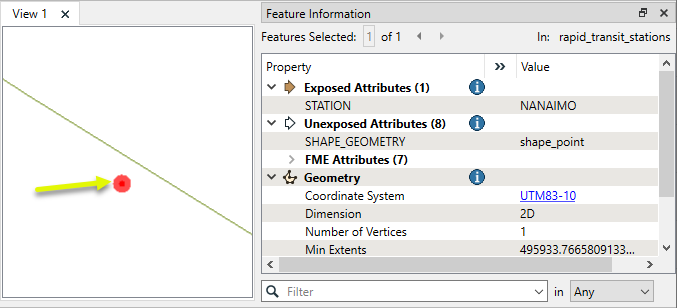
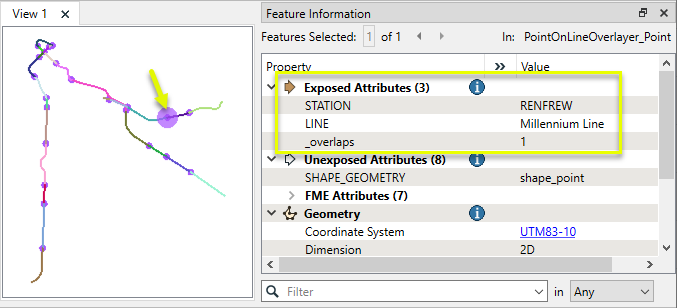
The transit lines are split where they encounter a station within the specified tolerance, as shown here by randomly coloring the output line features. Attributes are shared between the points and lines, as in these point attributes for Renfrew Station, which now has a new attribute indicating that it overlaid the Millennium Line.
Output Lines receive attributes from all of the points that the original unchopped line encountered - see Usage Notes for more detail.
Usage Notes
- Where point geometries are expected, Point Cloud geometries are not supported.
- Chopped Lines output via the Line output port receive the attributes of all points that matched the original input line (if a list is enabled). All points that the original line encountered are included - not only the endpoints of the new line segment.
To obtain attributes from points matching only the ends of the new line features, use a second transformer (consider another PointOnLineOverlayer, or a NeighborFinder).
Choosing a Spatial Transformer
Many transformers can assess spatial relationships and perform spatial joins - analyzing topology, merging attributes, and sometimes modifying geometry. Generally, choosing the one that is most specific to the task you need to accomplish will provide the optimal performance results. If there is more than one way to do it (which is frequently the case), time spent on performance testing alternate methods may be worthwhile.
To correctly analyze spatial relationships, all features should be in the same coordinate system. The Reprojector may be useful for reprojecting features within the workspace.
|
Transformer |
Can Merge Attributes |
Alters Geometry |
Counts Related Features |
Creates List |
Supported Types* |
Recommended For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SpatialFilter | Yes | No | No | No |
|
|
| SpatialRelator | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
|
|
| AreaOnAreaOverlayer | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
|
| LineOnAreaOverlayer | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
|
| LineOnLineOverlayer | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
|
| PointOnAreaOverlayer | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
|
|
| PointOnLineOverlayer | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
|
| PointOnPointOverlayer | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
|
|
| Intersector | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
|
| Clipper | Yes | Yes | No | No |
|
|
| NeighborFinder | Yes | In some cases | No | Yes |
|
|
| TopologyBuilder | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
|
|
* Note that Curve includes Lines, Arcs, and Paths. Area includes Polygons, Donuts, and Ellipses.
Spatial analysis can be processing-intensive, particularly when a large number of features are involved. If you would like to tune the performance of your workspace, this is a good place to start.
When there are multiple ways to configure a workspace to reach the same goal, it is often best to choose the transformer most specifically suited to your task.
If performance is an issue in your workspace, look for alternative methods, guided by geometry.
Configuration
Input Ports
Point features against which the lines will be compared.
Line features against which the points will be compared.
Output Ports
Point features, with attributes added according to transformer parameter configuration. Geometry is unmodified, unless z-values have been extracted from lines.
Line features which have been split at the location closest to matching points, with attributes added according to transformer parameter configuration.
Features with invalid geometries will be rejected and output via this port.
Rejected features will have an fme_rejection_code attribute with one of the following values:
INVALID_POINT_GEOMETRY_TYPE
INVALID_LINE_GEOMETRY_TYPE
INVALID_LINE_GEOMETRY_VERTICES
INVALID_GEOMETRY_DEGENERATE
Rejected Feature Handling: can be set to either terminate the translation or continue running when it encounters a rejected feature. This setting is available both as a default FME option and as a workspace parameter.
Parameters
|
Group By |
The default behavior is to use the entire set of features as the group. This option allows you to select attributes that define which groups to form. |
||||
|
Complete Groups |
Select the point in processing at which groups are processed:
There are two typical reasons for using When Group Changes (Advanced) . The first is incoming data that is intended to be processed in groups (and is already so ordered). In this case, the structure dictates Group By usage - not performance considerations. The second possible reason is potential performance gains. Performance gains are most likely when the data is already sorted (or read using a SQL ORDER BY statement) since less work is required of FME. If the data needs ordering, it can be sorted in the workspace (though the added processing overhead may negate any gains). Sorting becomes more difficult according to the number of data streams. Multiple streams of data could be almost impossible to sort into the correct order, since all features matching a Group By value need to arrive before any features (of any feature type or dataset) belonging to the next group. In this case, using Group By with When All Features Received may be the equivalent and simpler approach. Note Multiple feature types and features from multiple datasets will not generally naturally occur in the correct order.
As with many scenarios, testing different approaches in your workspace with your data is the only definitive way to identify performance gains. |
|
Point Tolerance |
The Point Tolerance value is compared to the distance from the lines to the points, and the lines will be segmented if the distance is less than or equal to the Point Tolerance value. When such a match occurs, the attributes of the segmented lines are merged with the points and the attributes of the points are merged with the lines. |
|
Aggregate Handling |
Choose how aggregate geometries are to be handled. Deaggregate: Decompose aggregates into their individual components. Reject: Do not process aggregates and output them via the <Rejected> port. |
|
Merge Measures
|
If Yes, any measures that exist on a line will be added to matching points. Measure values are determined according to the Treat Measures As parameter. If both point and line have measures of the same name, the point's values will be overwritten by the line's values. If No, no measures will be copied, and any existing measures (on points or lines) will be output unchanged. |
|
Treat Measures As |
This parameter determines how measures are computed:
Continuous: The new measure value will be calculated, interpolating based on the nearest measures. Discrete: The new measure value will be copied from the nearest measure. |
If attributes on the overlaid and original feature share the same name, but are not geometry attributes that start with fme_, then they are deemed conflicted.
If measures on the point and line share the same name, then they are deemed conflicted.
The resolution of conflicted measures on points occurs in the same manner as the resolution of conflicted attributes on features. It is resolved according to the Accumulation Mode and Conflict Resolution values.
Merge Attributes
|
Accumulation Mode |
Merge Overlaid: The original feature will retain all of its own un-conflicted attributes, and will additionally acquire any un-conflicted attributes that the overlaid feature has. This mode will handle conflicted attributes based on the Conflict Resolution parameter. Prefix Overlaid: The original feature will retain all of its own attributes. In addition, the original will acquire attributes reflecting the overlaid feature’s attributes, with the name prefixed with the Prefix parameter. Replace with Single Overlaid: The original feature will have all of its attributes removed, except geometry attributes that start with fme_. Then, all of the attributes from one (arbitrary) overlaid feature will be placed onto the original. |
|
Conflict Resolution |
Use Original: If a conflict occurs, the original values will be maintained. Use Overlaid: If a conflict occurs, the values of the overlaid feature will be transferred onto the original. |
|
Prefix |
If the Accumulation Mode parameter is set to Prefix Overlaid, this value will prefix attributes and measures that are being added to the original feature from the overlaid feature. |
Generate List on Output ‘Point’
When enabled, adds a list attribute to the Point output features, and the attributes of each line matching an output point are added to that point's list.
|
‘Point’ List Name |
Enter a name for the list attribute. Note List attributes are not accessible from the output schema in FME Workbench until they are exposed with an AttributeExposer or processed with a transformer that operates on them, such as a ListExploder or ListConcatenator.
|
|
Add To 'Point' List |
All Attributes: All attributes will be added to the output Point features. Selected Attributes: Enables the Selected Attributes parameter, where specific attributes may be chosen for inclusion. |
|
Selected Attributes |
Enabled when Add To 'Point' List is set to Selected Attributes. Specify the attributes you wish to be included. |
Generate List on Output ‘Line’
When enabled, adds a list attribute to the Line output features, and the attributes of each point matching an original input line are added to each output line created from it.
|
‘Line’ List Name |
Enter a name for the list attribute. Note List attributes are not accessible from the output schema in FME Workbench until they are exposed with an AttributeExposer or processed with a transformer that operates on them, such as a ListExploder or ListConcatenator.
|
|
Add To 'Line' List |
All Attributes: All attributes will be added to the output Line features. Selected Attributes: Enables the Selected Attributes parameter, where specific attributes may be chosen for inclusion. |
|
Selected Attributes |
Enabled when Add To 'Line' List is set to Selected Attributes. Specify the attributes you wish to be included. |
|
Overlap Count |
The Overlap Count Attribute added to output linear features holds the number of point features that were near to it. The Overlap Count Attribute added to output point features holds the number of linear features that the point was near to. |
Editing Transformer Parameters
Transformer parameters can be set by directly entering values, using expressions, or referencing other elements in the workspace such as attribute values or user parameters. Various editors and context menus are available to assist. To see what is available, click  beside the applicable parameter.
beside the applicable parameter.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more.
When setting values - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors - strings and expressions containing String, Math, Date/Time or FME Feature Functions will have those functions evaluated. Therefore, the names of these functions (in the form @<function_name>) should not be used as literal string values.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
|
Special Characters |
A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| Date/Time Functions | Date and time functions are available in the Text Editor. |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Creating and Modifying User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Table Tools
Transformers with table-style parameters have additional tools for populating and manipulating values.
|
Row Reordering
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
|
|
Cut, Copy, and Paste
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
Cut, copy, and paste may be used within a transformer, or between transformers. |
|
Filter
|
Start typing a string, and the matrix will only display rows matching those characters. Searches all columns. This only affects the display of attributes within the transformer - it does not alter which attributes are output. |
|
Import
|
Import populates the table with a set of new attributes read from a dataset. Specific application varies between transformers. |
|
Reset/Refresh
|
Generally resets the table to its initial state, and may provide additional options to remove invalid entries. Behavior varies between transformers. |
Note: Not all tools are available in all transformers.
For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
Yes |
| Dependencies | |
| Aliases | |
| History |
FME Online Resources
The FME Community and Support Center Knowledge Base have a wealth of information, including active forums with 35,000+ members and thousands of articles.
Search for all results about the PointOnLineOverlayer on the FME Community.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver, Open Government Licence - British Columbia, and/or Open Government Licence – Canada.