Authentication
Source Type ArcGIS Online (default) – The feature server is hosted on ArcGIS Online. Select the feature services through your ArcGIS Online account.
Web Connection
If the Authentication Type is Web Connection, specify the Web Connection to use.
- Esri ArcGIS Online (AGOL) Feature Service Reader/Writer (ARCGISONLINEFEATURES)
- Esri ArcGIS Portal Feature Service Reader/Writer (ARCGISPORTALFEATURES)
Source Type Standalone Server – The feature server URL will be specified directly.
Authentication Type
|
Web Connection (default) – Use a web connection to authenticate access. Several types of web services are supported:
|
|
None – Access the feature service anonymously. |
|
Kerberos – Also known as Integrated Windows Authentication (IWA). Authenticates as the current Windows user. This option is supported only on Windows systems connected to a domain. |
Source Type Enterprise – The feature server is hosted on an organization’s ArcGIS Enterprise instance. Feature services accessible through a user’s ArcGIS Enterprise account can be selected.
Site URL
The host URL of the ArcGIS Enterprise Installation. This is expected to include the Web Adaptor name. For example:
https://YOUR_HOST_NAME.com/portal
Authentication Type
|
Web Connection (default) – Use a web connection to authenticate access. Several types of web services are supported:
|
|
None – Access the feature service anonymously. |
|
Kerberos – Also known as Integrated Windows Authentication (IWA). Authenticates as the current Windows user. This option is supported only on Windows systems connected to a domain. |
Feature Service
URL
Specify the fully-qualified URL for the Feature Service to read. For example
https://services1.arcgis.com/organizationID/arcgis/rest/services/featureservicename/FeatureServer
Item Source
Determines whether the feature service to write to will be specified using a user folder or a group:
- User Content (default) – Select this option when selecting this feature service from a user folder.
- Group – Select this option when selecting a feature service from a Group.
Folder
Specifies the name of the folder in which the feature service is contained.
The default value of / (forward slash) represents the root user folder. Clicking the Browse button will display a list of a user’s folders.
Group
Specifies the ID of a group for an existing feature service. Clicking the Browse button will display a list of the groups a user belongs to, as well as all the groups in their organization.
Feature Service
This parameter is used to specify a single feature service. Clicking the Browse button will display a list of all the feature services in the selected group or user folder. Once selected, the Feature Service Item ID will be appended to the name of the feature service.
Assuming the correct user folder is selected, these are all valid ways to specify an existing feature service with name My Feature Service and ID 567aba67c25cb60ee159d3fbe2b16eff:
- My Feature Service(567aba67c25cb60ee159d3fbe2b16eff)
- (567aba67c25cb60ee159d3fbe2b16eff)
- My Feature Service
Constraints
After you have entered a valid Feature Service, click the Browse button to select layers or tables for import. A connection window appears while the system retrieves a list of layers and tables from the selected Feature Service.
Once the list appears, you can select one or more layers or tables, and then click OK to dismiss the window. Their name(s) will appear in the Layers parameter.
Specifies whether to add a label attribute for each coded domain attribute on the layer. For instance, the coded domain attribute foo would result in an extra attribute foo_resolved that contains the label corresponding to the coded value of the foo attribute. Coded domains defined as part of layer subtypes are supported.
Esri ArcGIS Feature Service writers automatically recognize label attributes when working with existing Feature Services. If a valid label value is provided, and no value was provided for the corresponding coded domain attribute, then the coded domain attribute is set based on the label value. If there is no corresponding coded domain attribute, then the label attribute is treated as a regular attribute.
Values: Yes or No
Default: No
Attribute Format
Specifies how Global ID attribute values should be formatted.
- Use Server Value (default) – Values will be returned as-is from the server.
- GUID Format ({GUID}) – Values that are not enclosed in curly braces (that is, UUID-formatted) will be returned in uppercase text and enclosed in curly braces. For example:
- A server Global ID value of acd3d567-6547-4b1e-a90e-3d5c6f2dd9b would be returned as {ACD3D567-6547-4B1E-A90E-3D5C6F2DD9B}.
- A value of {0ca14a58-ca12-47bb-98aa-d3a7fbe4d93f}, which is already enclosed in curly braces, will not be modified.
Specifies how Date attribute values should be formatted. The Date attribute type is used to store datetime values without a timezone offset.
- FME Default (default) – Values will be converted to the FME default datetime format.
- Unix time in milliseconds – Values will be returned as-is from the server. The server value represents the milliseconds since Unix epoch.
Branch Versioning
Check this option to work with the Version Management Server.
Version Name
The name of the Branch Version to write against. If the version does not exist, it will be created.
Data to Read
The type of versioned data to read. Select one of:
- Features (default) – Read the features on the selected Branch Version.
- Differences – Compare the selected Branch Version against the DEFAULT version. The resulting features will have an additional fme_db_operation format attribute with a value of insert, update, or delete, corresponding to the type of difference. On older versions of ArcGIS Enterprise, only object IDs may be returned.
Advanced
Specifies the maximum number of features that may be present in a single response from the server. Reduce this value if reads are failing due to timeouts.
The value for this parameter is capped to the maxRecordCount property on the Feature Service.
Default: 1000
Specifies whether the reader should verify HTTPS Certificates:
- Yes – Ensures that a URL's digital certificate is valid (signed by a trusted certificate authority), trusted, and belongs to the domain to which you are connecting.
- No – Verification will not be performed (that is, there is no verification that the URL’s certificate is valid or trusted).
- Use Web Connection Value – The parameter uses the Verify SSL Certificate parameter defined in the web connection.
Schema Attributes
Use this parameter to expose Format Attributes in FME Workbench when you create a workspace:
- In a dynamic scenario, it means these attributes can be passed to the output dataset at runtime.
- In a non-dynamic scenario, this parameter allows you to expose additional attributes on multiple feature types. Click the browse button to view the available format attributes (which are different for each format) for the reader.
This parameter controls how field aliases are used.
-
None – (default value) Field aliases are ignored.
-
Replace Attribute Names with Aliases – (only applicable when adding a Reader) Attributes on feature types will be named for their aliases rather than their official names. An arcgisfeatureservice_feature_type_alias attribute will be included on each feature. Use this mode when the target format should create feature types using the aliases as attribute names.
NoteTo change the alias mode after you select Replace Attribute Names with Aliases, remove the reader from the canvas and re-add it with your preferred alias mode setting.
- Expose Aliases as Metadata Attributes – For each attribute read, a second <name>_alias attribute will be added that stores the alias for the attribute in question. An arcgisfeatureservice_feature_type_alias attribute will also be included on each feature. Use this mode when the target format is a Feature Service format and the aliases should be preserved during feature type and table creation.
If you want to make changes after you select Expose Aliases as Metadata Attributes, you can only change the setting back to None. To change the alias mode to Replace Attribute Names with Aliases, remove the reader from the canvas and re-add it with your preferred alias mode setting.
Spatial
Coordinate systems may be extracted from input feature data sources, may come predefined with FME, or may be user-defined. FME allows different output and input coordinate systems, and performs the required coordinate conversions when necessary. To perform this reprojection, FME uses the CS-MAP reprojection engine, which includes definitions for thousands of coordinate systems, with a large variety of projections, datums, ellipsoids, and units.
For systems that know their coordinate system, this field will display Read from Source and FME will read the coordinate system from the source dataset. For most other input sources, the field will display Unknown (which simply means that FME will use default values). In most cases, the default value is all you'll need to perform the translation.
You can always choose to override the defaults and choose a new coordinate system. Select More Coordinate Systems from the drop-down menu to open the Coordinate System Gallery.
- The coordinate systems file coordsys.db in the FME installation folder contains the names and descriptions of all predefined coordinate systems.
- Some users may wish to use coordinate systems that do not ship with FME, and in those cases, FME also supports custom coordinate systems.
- Working with Coordinate Systems in FME.
A search envelope (also known as a bounding box) is a rectangular area that defines a geographic area. In FME, the easiest way to define a search envelope is to use search envelope parameters.
Defining a search envelope is the most efficient method of selecting an area of interest because FME will read only the data that is necessary – it does not have to read an entire dataset. Search Envelope parameters apply to both vector and raster datasets and can be particularly efficient if the source format has a spatial index.
Most FME readers have parameters to define the search envelope of data that is being read:
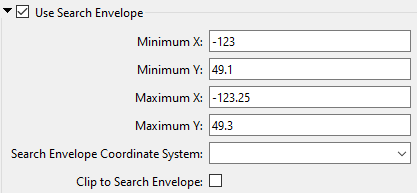
The parameters include the x and y coordinates of the bounding box as well as a parameter that defines the coordinate system.
How to Define the Bounding Box
Using the minimum and maximum x and y parameters, define a bounding box that will be used to filter the input features. Only features that intersect with the bounding box are returned. Note that the bounding box intersection is not a full geometry intersection (based on spatial relationships) that would be returned by a transformer like the SpatialFilter.
|
Search Envelope Coordinate System |
Specifies the coordinate system of the search envelope if it is different than the coordinate system of the data. The coordinate system associated with the data to be read must always be set if this parameter is set. If this parameter is set, the minimum and maximum points of the search envelope are reprojected from the Search Envelope Coordinate System to the reader’s coordinate system prior to applying the envelope. |
||||||
|
Clip to Search Envelope |
The underlying function for Use Search Envelope is an intersection; however, when Clip to Search Envelope is checked, a clipping operation is also performed.
|