Civil 3D Schema Mode
This option specifies the types of AutoCAD drawing entities which will be included in schema generation and data retrieval.
Civil 3D Entities Only
The reader will use FME feature types to represent types of Civil 3D specific entities such as pipes.
Civil 3D and CAD Entities
In addition to FME feature types representing types of Civil 3D specific entities, the AutoCAD Civil 3D reader will use additional FME feature types to represent layers.
All of the CAD entities in the AutoCAD drawing will be read according to the layer on which they are located. Although Civil 3D specific entities also belong to layers, they will only be read according to their object types.
Entity Options
When checked, this parameter explodes blocks and return the entities that form the components of the block as separate features.
When the reader resolves blocks, it outputs a feature for each of the AutoCAD entities that are part of the block definition. The original insert is not output. This results in the full graphical representation of the block transferred through FME, but the exact insertion point of the block is lost.
Each block member feature is given the attribute autocad_block_number which is set to the same value for each block so that the features comprising each block may be combined in subsequent processing. Arbitrary deep block nesting is permitted, however, the autocad_block_number attribute is only updated for each block at the outermost level. By default, all block members will be on the same layer as that of the original block.
Usual AutoCAD-to-AutoCAD translation setting: Unchecked
Use Block Feature Type for Components
Specifies how the reader sets the feature type of block component entities when resolving (or exploding) insert entities. This parameter applies only if Explode Blocks into Entities is checked.
When the reader resolves blocks, it outputs a feature for each of the AutoCAD entities that are part of the block definition. If this parameter is checked, all block members will be on the same layer-based feature type as that of the original block. If this parameter is unchecked, the block members will appear on their respective layer-based feature types.
This parameter is useful when resolving components and using a layer-based schema, and you want block component features to share a layer-based feature type. To change the layer information on the component features to match their layer-based feature type, use the Use Block Layer Information for Components parameter.
Usual AutoCAD-to-AutoCAD translation setting: Unchecked
Use Block Layer Information for Components
Specifies how the reader sets the layer information attributes of the block component entities when resolving (or exploding) insert entities. This parameter applies only if Explode Blocks into Entities is checked.
When the reader resolves blocks, it outputs a feature for each of the AutoCAD entities that are part of the block definition.
If this parameter is checked, all block members will have the same layer information as that of the original block. If this parameter is unchecked, the block members will have the layer information of their respective layers.
Examples of layer specific attributes are autocad_layer, autocad_layer_hidden, and autocad_layer_color. This parameter also affects related symbology attributes such as autocad_lineweight and autocad_color which may have ByLayer values.
Usual AutoCAD-to-AutoCAD translation setting: Unchecked
Store Insert Location on Components
When checked, the reader adds the insert point location as attributes to the block component entities when resolving (or exploding) inserts entities.
When the reader resolves blocks, it outputs a feature for each of the AutoCAD entities that are part of the block definition. The original insert is not part of the block definition, but this parameter allows the insert location to still be represented.
Each block member feature will include the attribute autocad_block_insert_[xyz].
Usual AutoCAD-to-AutoCAD translation setting: Unchecked
If the parameter Explode Blocks Into Entities is checked, and this parameter is also checked, then the insert points of exploded blocks are output as point features.
Explode Selected Blocks – This parameter is a space-delimited list of the block names that are to be exploded, and is processed only when Explode Blocks into Entities is checked.
Read as Geometry Instances
If the parameter Explode Blocks Into Entities is checked and this parameter is also checked, then blocks will be read as Geometry Definitions and Instances. In this way, a block definition will be stored as a geometry definition and each block insert point will become a geometry instance.
Specifies whether the reader should return visible attributes as separate text features or whether they should be returned as attributes of an insert feature.
State:
- Checked – Each visible attribute is returned as a single text feature.
Usual AutoCAD-to-AutoCAD translation setting: Unchecked
Specifies whether the reader will explode the mtext entities into separate text entities.
State:
- Checked – The resulting text features represent fragments of text with the same mtext properties such as style and location.
- Unchecked – The mtext entity will be read as a single text feature.
Usual AutoCAD-to-AutoCAD translation setting: Unchecked
Determines whether polylines should have their elevation attribute treated as a Z coordinate (applies to light-weight polylines and 2D polylines).
AutoCAD-to-AutoCAD translation setting: This option should not be checked when performing AutoCAD-to-AutoCAD translations as the elevations converted to Z coordinates when read in will not be converted back to elevation attributes when written out.
Determines whether the Civil 3D reader should attempt to represent Pipe and Structure parts of Pipe Networks as 3D solid geometries rather than as lines and points.
Determines whether the Civil 3D reader should attempt to represent Pressure Pipe and Structure parts of Pressure Pipe Networks as 3D solid geometries rather than as lines and points.
When this parameter is checked, the reader will add Esri MSC attributes to features that it finds on entities in the file.
When checked, multiview blocks will be read in the specified selected views. These views may include:
- Non Orthographic
- Back
- Bottom
- Front
- Left
- Right
- Top
When unchecked, multiviews will be read from the same view from which the file was last saved.
Model and Paper Space Options
When checked, this parameter instructs FME to read the entities from the model space.
If this parameter and Read Selected Paper Spaces are both checked, entities from the model space and paper space may be read. These entities are from spaces that represent distinct views and may overlap or be greatly separated (which may reduce visibility during inspection).
Specifies which paper spaces should be read if Read Paper Space is checked.
If this parameter and Read Model Space are both checked, entities from the model space and paper space may be read. These entities are from spaces that represent distinct views and may overlap or be greatly separated (which may reduce visibility during inspection).
If multiple paper spaces are checked, entities may overlap (which may reduce visibility during inspection).
Usual AutoCAD-to-AutoCAD translation setting: Unchecked
Attribute Options
Determines whether FME will read the extended entity data associated with AutoCAD entities in the Interpreted representation. By default, FME will not read extended entity data in this representation. See Extended Entity Data for details on these representations.
Determines whether FME will read the extended entity data associated with AutoCAD entities in the List representation.
By default, FME will read extended entity data in this representation. See Extended Entity Data for details on these representations.
Determines whether FME will read the Attribute entity information commonly associated with Insert entities.
By default, FME will read extended entity data in this representation.
This information consists of the fme_attrib_info attributes as a structured list. This is the same information that can be added to features as attributes with the Read Visible Attributes as Text Entities, though in a list representation. See Inserts for details.
Instructs the reader regarding reading of XRecord entries in the extension dictionaries of entities. These XRecord entries may become FME feature attributes accordingly.
State:
- Unchecked (default) – Any XRecord entries will not be read.
- Checked – The XRecord data will become FME feature attributes similar to the list form of Extended Entity Data, but with attributes with names of the form autocad_xrecord_data*.
Instructs the reader regarding reading of data fields on pipe network parts, known as Pipe and Structure entities.
State:
- Unchecked – Any data fields are not read.
- Checked (default) – The data fields become FME feature attributes on features representing Pipe or Structure entities.
Data Field Attribute Naming
When the Read Pipe and Structure Data Fields parameter is enabled, the Data Field Attribute Naming parameter becomes active. This parameter controls the names of the data field attributes. Data fields have three possible naming schemes:
- Original – The original name, which was used until this parameter was added.
- Description – The description value for the attribute, also set as the <name>_desc attribute.
- Context – The context value for the attribute, also set as the <name>_context attribute.
Instructs the reader regarding reading of user-defined properties on Parcel entities.
State:
- Unchecked (default) – Any user-defined properties on Parcel entities are not read.
- Checked – User-defined properties become FME feature attributes on features representing Parcel entities.
Instructs the reader regarding reading of user-defined properties on CoGo Point entities.
State:
- Unchecked (default) – Any user-defined properties on CoGo Point entities are not read.
- Checked – User-defined properties become FME feature attributes on features representing CoGo Point entities.
Schema Attributes
Use this parameter to expose Format Attributes in FME Workbench when you create a workspace:
- In a dynamic scenario, it means these attributes can be passed to the output dataset at runtime.
- In a non-dynamic scenario, this parameter allows you to expose additional attributes on multiple feature types. Click the browse button to view the available format attributes (which are different for each format) for the reader.
Spatial
Coordinate systems may be extracted from input feature data sources, may come predefined with FME, or may be user-defined. FME allows different output and input coordinate systems, and performs the required coordinate conversions when necessary.
If a coordinate system is specified in both the source format and the workspace, the coordinate system in the workspace is used. The coordinate system specified in the source format is not used, and a warning is logged. If a source coordinate system is not specified in the workspace and the format or system does not store coordinate system information, then the coordinate system is not set for the features that are read.
If a destination coordinate system is set and the feature has been tagged with a coordinate system, then a coordinate system conversion is performed to put the feature into the destination system. This happens right before the feature enters into the writer.
If the destination coordinate system was not set, then the features are written out in their original coordinate system.
If a destination coordinate system is set, but the source coordinate system was not specified in the workspace or stored in the source format, then no conversion is performed. The features are simply tagged with the output system name before being written to the output dataset.
For systems that know their coordinate system, the Coordinate System field will display Read from Source and FME will read the coordinate system from the source dataset. For most other input sources, the field will display Unknown (which simply means that FME will use default values). In most cases, the default value is all you'll need to perform the translation.
You can always choose to override the defaults and choose a new coordinate system. Select More Coordinate Systems from the drop-down menu to open the Coordinate System Gallery.
Changing a Reprojection
To perform a reprojection, FME typically uses the CS-MAP reprojection engine, which includes definitions for thousands of coordinate systems, with a large variety of projections, datums, ellipsoids, and units. However, GIS applications have slightly different algorithms for reprojecting data between different coordinate systems. To ensure that the data FME writes matches exactly to your existing data, you can use the reprojection engine from a different application.
To change the reprojection engine, Select Workspace Parameters > Spatial > Reprojection Engine. In the example shown, you can select Esri (but the selection here depends on your installed applications):
- The coordinate systems file coordsys.db in the FME installation folder contains the names and descriptions of all predefined coordinate systems.
- Some users may wish to use coordinate systems that do not ship with FME, and in those cases, FME also supports custom coordinate systems.
- Learn more about Working with Coordinate Systems in FME.
A search envelope (also known as a bounding box) is a rectangular area that defines a geographic area. In FME, the easiest way to define a search envelope is to use search envelope parameters.
Defining a search envelope is the most efficient method of selecting an area of interest because FME will read only the data that is necessary – it does not have to read an entire dataset. Search Envelope parameters apply to both vector and raster datasets and can be particularly efficient if the source format has a spatial index.
Most FME readers have parameters to define the search envelope of data that is being read:
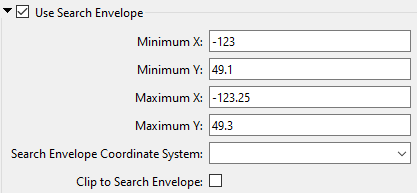
The parameters include the x and y coordinates of the bounding box as well as a parameter that defines the coordinate system.
How to Define the Bounding Box
Using the minimum and maximum x and y parameters, define a bounding box that will be used to filter the input features. Only features that intersect with the bounding box are returned. Note that the bounding box intersection is not a full geometry intersection (based on spatial relationships) that would be returned by a transformer like the SpatialFilter.
|
Search Envelope Coordinate System |
Specifies the coordinate system of the search envelope if it is different than the coordinate system of the data. The coordinate system associated with the data to be read must always be set if this parameter is set. If this parameter is set, the minimum and maximum points of the search envelope are reprojected from the Search Envelope Coordinate System to the reader’s coordinate system prior to applying the envelope. |
||||||
|
Clip to Search Envelope |
The underlying function for Use Search Envelope is an intersection; however, when Clip to Search Envelope is checked, a clipping operation is also performed.
|
Advanced
Determines whether to resolve the entity's color, or keep it as ByLayer. When checked (default), the autocad_color attribute will contain the actual color by value (an integer between 0 and 255 inclusive) therefore preserving the original attributes.
For example, if you have an entity on a "rivers" layer, with its color set to ByLayer, and the layer color set to "blue":
- If you check this option, then the autocad_color attribute will be set to "blue" (its equivalent integer value).
- If you do not check this option, then the autocad_color attribute will remain set to ByLayer (an integer value of 256) or ByBlock (an integer value of 0), and the components will all be assigned the same layer color or block color, respectively.
Usual AutoCAD-to-AutoCAD translation setting: Unchecked
This parameter can be used to toggle purging of unused objects or entities after the target dataset has been loaded into FME, but before reading features. This will not modify the target dataset.
Unused objects are those which are not referenced by other objects in the drawing. For example, for a layer to be eligible to be purged, there must be no entities on that layer.
If this option is checked, the reader will attempt to purge the following object types:
- Blocks
- Layers
- Detail View Styles
- Dimension Styles
- Groups
- Linetypes
- Materials
- MLine Styles
- MLeader Styles
- Registered Applications
- Section View Styles
- Table Styles
- Text Styles
- Visual Styles
Usual AutoCAD-to-AutoCAD translation setting: Unchecked
Specifies whether or not to read hatches and MPolygons in a way that preserves their complex properties.
State:
- Checked – The loops will be aggregated together as polygons, and ordered such that any enclosing loop will be stored before any enclosed loop. Attributes may be added to store polyline bulge arc information.
- Unchecked – The loops of each hatch entity will be converted to areas and aggregated together, and polyline bulge arcs will be interpolated into lines.
Usual AutoCAD-to-AutoCAD translation setting: Checked
Specifies whether the reader should leave a raster unclipped and only store the clipping information as attributes, or whether it should apply the clipping.
State:
- Checked – The raster will not be clipped and the clipping information may be retrieved from the feature attributes, this allows clipped raster features to pass through FME with no loss of data.
- Unchecked (default) – Clipped rasters being read will have their clipping information applied, and anything outside the clipping bounds will be lost.
Usual AutoCAD-to-AutoCAD translation setting: Checked
Specifies whether or not to resolve (explode) dimensions into their individual pieces.
State:
- Checked – Each geometric piece of the dimension will be output as a separate feature, as well as a non-geometric
autocad_dimension_deffeature. - Unchecked – An aggregate containing all the pieces of the original dimension will be output (i.e., an
autocad_dimension).
Usual AutoCAD-to-AutoCAD translation setting: Unchecked
Determines how multi-line entities are read.
State:
- Unchecked (default) – Multi-line geometry is constructed of lines containing only the explicit vertexes of the base line and the relative vertexes of additional lines.
- Checked – Additional evaluation of multi-line properties is performed, which may result in additional vertexes and gaps in the geometry. The evaluated geometry form is a more complete geometric representation of a multi-line entity, but cannot be written without loss by the AutoCAD writer.
When checked, the reader, in addition to vectorizing the splines, stores the spline coefficients as attributes.
See the description of Splines for the attribute names used to store the spline definition.
Usual AutoCAD-to-AutoCAD translation setting: Checked
Specifies whether a zero-length arc should be converted into a point feature (that is, autocad_point).
If the feature becomes a point, it will still retain all the attributes it had while it was an arc.
Usual AutoCAD-to-AutoCAD translation setting: Never checked
Determines whether or not AutoCAD groups will be read.
Default: FME will not read groups.
Determines whether or not AutoCAD xrecord data will be read from the dictionaries in a drawing.
Default: FME will not read these XRecords.
This option creates non-geometric autocad_xrecord features with attributes similar to those created with the Entity XRecord Data Reading option.
See also XRecord Data
Determines whether FME will read AutoCAD entities that represent External References.
Default: FME will not read External References.
If you select this option, the reader will add additional attributes describing the layer properties for the layer of each feature. These include autocad_layer_linetype, autocad_layer_color, and autocad_layer_lineweight.
Specifies whether the reader will ignore all features on layers that are in a frozen state.
- Unchecked (default) – Features are read from frozen layers.
- Checked – Features located on frozen layers are not read from the input dataset.
Specifies whether the reader will ignore all features on layers that are in a frozen state from the perspective of a Paper Space Viewport.
- Unchecked (default) – Features are read from frozen layers.
- Checked – Features located on frozen layers are not read from the input dataset.
Specifies whether the reader will ignore all features on layers that are in a hidden state.
- Unchecked (default) – Features are read from hidden layers.
- Checked – Features located on hidden layers are not read from the input dataset.
Determines whether FME will attempt to read a graphical representation of Proxy entities which are placeholders for certain unsupported objects.
Default: FME will read Proxy Graphics.
Determines whether FME will attempt to read certain AutoCAD System Variables that are stored within the drawing.
Default: FME will not read Drawing System Variables.
Determines whether the reader will attempt to read Region entities as Area geometries rather than as Surface geometries.
Default: FME will read region entities as Areas.
Determines whether FME will attempt to read raster entities stored in the drawing.
Default: FME will read raster entities.
Determines whether FME will output layer definitions as features.
Default: FME will not output layer definition features.
DXF Header File
When reading DXF files, this parameter instructs the reader to use the specified DXF header file as the header for the file being read. This option is used in situations where organizations produce headerless DXF files to save storage space.
Specify the full pathname to the DXF header file.
This parameter controls which storage type the reader will look at first when trying to read a coordinate system from the file:
- Esri - The reader will first look for an ESRI PRJ coordinate system on read.
- Native – The reader will first look for a natively stored coordinate system on read. In the event the preferred storage method does not have a coordinate system that FME can use, FME will attempt to read the coordinate system from the other method as a fallback.
Check this parameter if you have an Esri World file (*.wld or *.wld3) that you want FME to use when determining the coordinates for features in your dataset.
FME will search the folder of the dataset for a file with the same name as your dataset but with a .wld or .wld3 extension. If it cannot find a file with that name, it will then look for the file esri_cad.wld or esri_cad.wld3 within the dataset folder. If either of those files exists, FME will use the information in the files to translate the coordinates of the features in the dataset to their new geospatial coordinates.
If the files cannot be found, then the translation will continue, using the coordinate information found in the dataset and without performing any additional transformation.
Instructs FME to ignore the user-defined coordinate system of the file being read.
Default: FME applies the UCS when reading the coordinate data.
Usual AutoCAD-to-AutoCAD translation setting: Always checked