Scales x, y, and/or z coordinate values to resize geometry.
Typical Uses
-
Scaling z values for emphasis or de-emphasis
-
Scaling z values when vertical and horizontal units are mismatched
-
Georeferencing
-
Sizing objects or labels
-
Mirroring objects
-
Changing units
How does it work?
The Scaler receives features with any type of geometry and applies a multiplier to their coordinates, resizing the features relative to either their center or the origin of their coordinate system.
X, y and/or z coordinates are multiplied by the provided X, Y, and Z Scale Factors. A scale factor of one (1) implies no change to a coordinate.
The origin for scaling may be either 0,0 in the feature’s own coordinate system, or the center of the feature itself.
When using the 0,0 origin, if the object being scaled is not on or near the 0,0 point of the coordinate system (as is usually the case with georeferenced data), using the Scaler will also introduce a shift.
When using the Center Point origin, each individual feature will be scaled around its own center, not the center of the dataset’s extents.
Additional parameters are provided for type-specific scaling, including text, raster, and point cloud. This transformer supports raster band and palette selection. The RasterSelector can be used to modify selection.
Examples
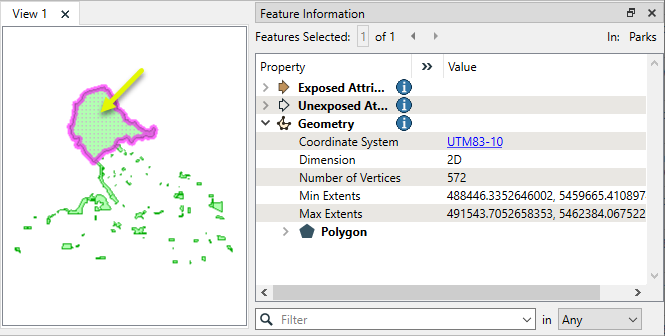
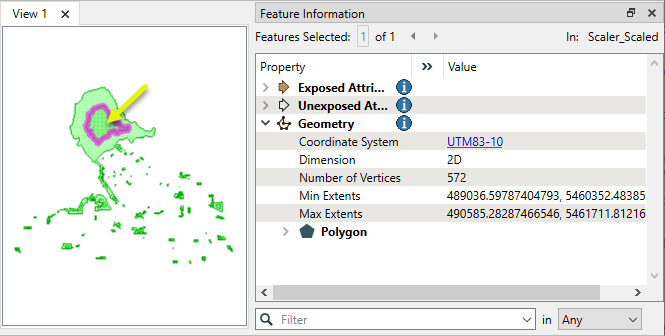
In this example, we have a set of park polygons, and want to scale them down.
The features are routed into a Scaler.
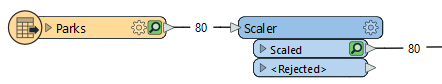
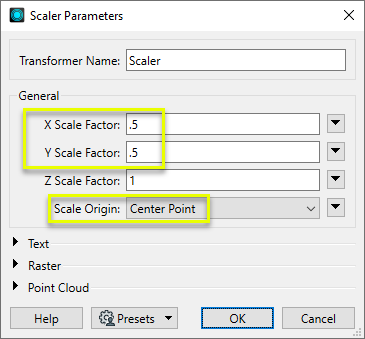
In the parameters dialog, the X and Y Scale Factors are set to 0.5. The Scale Origin chosen is Center Point.
The output features are half the size of the originals, and have been scaled around each feature’s center point.
Usage Notes
- The Aggregator and Deaggregator may be useful for scaling around a dataset’s center.
- Reprojecting to a local coordinate system may also be useful - see the CommonLocalReprojector and Reprojector (to local coordinate systems).
Configuration
Input Ports
Features with geometry to be scaled.
Output Ports
Features resized according to parameter selections.
Features that cannot be scaled will be output via this port. Rejected features will receive an explanatory fme_rejection_code attribute.
Rejected Feature Handling: can be set to either terminate the translation or continue running when it encounters a rejected feature. This setting is available both as a default FME option and as a workspace parameter.
Parameters
|
X Scale Factor |
Provide a multiplier for the feature’s x coordinates. Values may be entered directly or provided via an attribute, expression, user parameters, or conditional value. |
|
Y Scale Factor |
Provide a multiplier for the feature’s y coordinates. Values may be entered directly or provided via an attribute, expression, user parameters, or conditional value. |
|
Z Scale Factor |
Provide a multiplier for the feature’s z coordinates. Values may be entered directly or provided via an attribute, expression, user parameters, or conditional value. This parameter has no effect on two-dimensional vector features. On rasters, the multiplier is applied to the cell values of all selected bands. |
|
Scale Origin |
Select a scaling direction. Coordinates may be scaled relative to:
|
|
Text Scaling |
Select a method for scaling text features:
Note that text location is a point, and scaling a point from its own center will have no effect on position. |
|
Raster Scaling |
Select a method for scaling rasters:
|
Use this table to scale point cloud components other than x, y, and z.
|
Component |
Specify the component to scale. |
|
Scale Factor |
Provide a multiplier for the component. Note that more complex component value manipulations may be done with the PointCloudExpressionEvaluator. |
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters. There are a number of tools and shortcuts that can assist in constructing values, generally available from the drop-down context menu adjacent to the value field.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more.
When setting values - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors - strings and expressions containing String, Math, Date/Time or FME Feature Functions will have those functions evaluated. Therefore, the names of these functions (in the form @<function_name>) should not be used as literal string values.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
|
Special Characters |
A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| Date/Time Functions | Date and time functions are available in the Text Editor. |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Creating and Modifying User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Dialog Options - Tables
Transformers with table-style parameters have additional tools for populating and manipulating values.
|
Row Reordering
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
|
|
Cut, Copy, and Paste
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
Cut, copy, and paste may be used within a transformer, or between transformers. |
|
Filter
|
Start typing a string, and the matrix will only display rows matching those characters. Searches all columns. This only affects the display of attributes within the transformer - it does not alter which attributes are output. |
|
Import
|
Import populates the table with a set of new attributes read from a dataset. Specific application varies between transformers. |
|
Reset/Refresh
|
Generally resets the table to its initial state, and may provide additional options to remove invalid entries. Behavior varies between transformers. |
Note: Not all tools are available in all transformers.
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
No |
| Dependencies | None |
| Aliases | |
| History |
FME Community
The FME Community is the place for demos, how-tos, articles, FAQs, and more. Get answers to your questions, learn from other users, and suggest, vote, and comment on new features.
Search for all results about the Scaler on the FME Community.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver and/or the Open Government Licence – Canada.