Adds new components with constant values to a point cloud.
Typical Uses
- Adding standard or custom components to point cloud features to meet processing or format requirements.
How does it work?
The PointCloudComponentAdder receives point cloud features and adds one or more new components to them, with each new component set to a specified constant value. The components may be either standard named components that are not already in use on the feature, or user-specified components with non-standard names.
Each component definition consists of three parts - Component name, Data Type, and Value. A selection of data types is available, including various numeric types and strings. Values may be entered directly or obtained from an attribute or expression. The value will be applied as a constant value to all points in the point cloud feature.
Examples
In this example, we are preparing a LiDAR point cloud dataset for use in creating a Minecraft world. The source dataset has a number of standard point cloud components. To prepare for Minecraft world building, we need to separate different classification types and add some new Minecraft-specific components.
The point cloud is first routed into a PointCloudFilter, and then on to a PointCloudComponentAdder.

In the PointCloudFilter parameters dialog, we create one Expression/Output Port pair, which filters points with a classification value of 2 (meaning ground) into a single output feature, which is output via the defined Class 2 Ground output port.

The filtered feature is then sent to the PointCloudComponentAdder, where in the parameters dialog we add two new custom components - blockID and blockData. Both are set to a Data Type of UInt8 and have constant values assigned to them - 3 and 0, respectively.

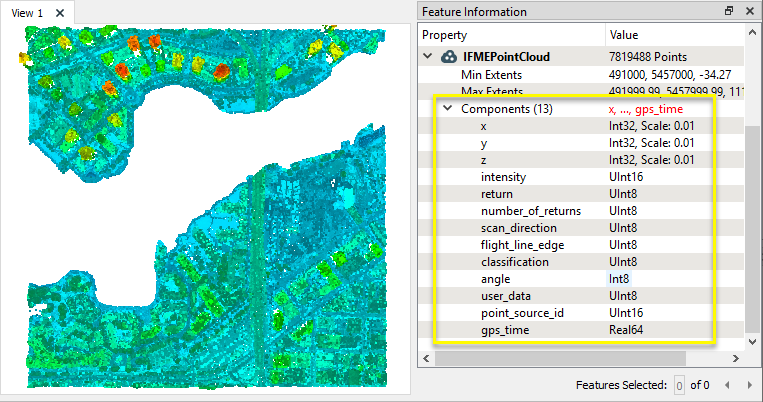
The output point cloud feature, as viewed here in the FME Data Inspector, contains only points of classification type 2. Those points now have the additional blockID and blockData components and values, and are passed along for further processing.

Usage Notes
- The PointCloudExpressionEvaluator can also add components in a similar fashion, however, it does not support string values.
- To update the values of components that already exist on a point cloud, use the PointCloudExpressionEvaluator.
- To set individual point component values, including values derived from expressions using existing point component values, use the PointCloudExpressionEvaluator.
- To convert attributes and values to components when converting other data types to point clouds, use the Attributes to Preserve as Components parameter in the PointCloudCombiner.
Choosing a Point Cloud Transformer
FME has a selection of transformers for working specifically with point cloud data.
For information on point cloud geometry and properties, see Point Clouds (IFMEPointCloud).
|
Converts point clouds to point or multipoint geometries, optionally retaining attribute and component values. |
|
|
Combines features into a single point cloud. Point cloud and non-point cloud geometries are supported. |
|
|
Adds new components with constant values to a point cloud. |
|
|
Copies selected component values onto either a new or existing component |
|
|
Keeps only specified point cloud components, discarding all others. |
|
|
Removes specified components from a point cloud. |
|
|
Renames an existing component. |
|
|
Alters the data type of point cloud components, and converts component values if required. |
|
|
Reads point cloud features for testing purposes, including any accumulated point cloud operations. No additional operations are performed, and nothing is done with the features. |
|
|
Creates a point cloud of specified size and density, with default component values. |
|
|
Evaluates expressions on each point in a point cloud feature, including algebraic operations and conditional statements, and sets individual point cloud component values. |
|
|
Serializes the geometry of a point cloud feature into a Blob attribute, encoding the contents according to a choice of common binary point cloud formats. |
|
|
Separates point clouds into multiple features, based on evaluating expressions including component values, and creates a separate output port for each expression defined. |
|
|
Merges component values from one point cloud to another. Features that contain the desired components are connected through the Supplier port, and the features that will receive the components are connected through the Requestor port. |
|
|
Sets point cloud component values by overlaying a point cloud on a raster. The component values for each point are interpolated from band values at the point location. |
|
|
Extracts the geometry properties of a point cloud feature and exposes them as attributes, optionally checking for their existence, retrieving component properties, and finding minimum and maximum values. Extents may also be recalculated and updated. |
|
|
Decodes a binary attribute containing encoded point clouds stored as Blobs, replacing the feature’s geometry with the decoded point cloud. |
|
|
Reduces the number of points in a point cloud by selectively keeping points based on the shape of the point cloud. The simplified and removed points are output as two discrete point clouds. |
|
|
Sorts a point cloud by the values of components. |
|
|
Separates point clouds into multiple features based on component values, color, or first/last return. |
|
|
Calculates statistics on point cloud components and adds the results as attributes. |
|
|
Takes an input point cloud and reconstructs it into an output mesh. |
|
|
Reduces the number of points in (thins) a point cloud by keeping points at a fixed interval, a maximum number of points, or a set quantity of first or last points. Remaining points are discarded. |
|
|
Applies transformations on a point cloud. Applying a transformation is primarily done for compatibility with other processing and writers that cannot support the transformation natively. For example, the LAS reader produces Int32 coordinates with a scale and offset. However, the POINTCLOUDXYZ writer cannot support component scale/offsets, so the transformation will be applied. The resulting coordinates will be Real64 with no transformation. Note that processing and writers that cannot support transformations will apply them automatically, but this transformer can be used to manually apply the transformation if desired. |
Configuration
Input Ports
This transformer accepts only point cloud features.
Output Ports
Point cloud features with added components and values as specified.
Non-point cloud features will be routed to the <Rejected> port, as well as invalid point clouds.
Rejected features will have an fme_rejection_code attribute with one of the following values:
INVALID_GEOMETRY_TYPE
INVALID_FEATURE_COMPONENTS
Rejected Feature Handling: can be set to either terminate the translation or continue running when it encounters a rejected feature. This setting is available both as a default FME option and as a workspace parameter.
Parameters
Add one line per added component in this table, consisting of a set of Component name, Data Type, and Value. All three columns must exist for each component entry.
| Component | The name of the component to add. Names may be entered directly, or choose Select Component from the drop-down menu to access standard component names. |
| Type |
Select the desired type of the added component. Choices include:
|
| Value |
The value of the added component. This value will be assigned to all points. Values may be entered directly, or set from attribute values or expressions. |
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters. There are a number of tools and shortcuts that can assist in constructing values, generally available from the drop-down context menu adjacent to the value field.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more.
When setting values - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors - strings and expressions containing String, Math, Date/Time or FME Feature Functions will have those functions evaluated. Therefore, the names of these functions (in the form @<function_name>) should not be used as literal string values.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
|
Special Characters |
A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| Date/Time Functions | Date and time functions are available in the Text Editor. |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Creating and Modifying User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Dialog Options - Tables
Transformers with table-style parameters have additional tools for populating and manipulating values.
|
Row Reordering
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
|
|
Cut, Copy, and Paste
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
Cut, copy, and paste may be used within a transformer, or between transformers. |
|
Filter
|
Start typing a string, and the matrix will only display rows matching those characters. Searches all columns. This only affects the display of attributes within the transformer - it does not alter which attributes are output. |
|
Import
|
Import populates the table with a set of new attributes read from a dataset. Specific application varies between transformers. |
|
Reset/Refresh
|
Generally resets the table to its initial state, and may provide additional options to remove invalid entries. Behavior varies between transformers. |
Note: Not all tools are available in all transformers.
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
No |
| Dependencies | None |
| FME Licensing Level | FME Professional Edition and above |
| Aliases | |
| History |
FME Community
The FME Community is the place for demos, how-tos, articles, FAQs, and more. Get answers to your questions, learn from other users, and suggest, vote, and comment on new features.
Search for all results about the PointCloudComponentAdder on the FME Community.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver
Keywords: point "point cloud" cloud PointCloud LiDAR sonar