To access feature type parameters, click the gear icon  on a feature type in the workspace to open the Feature Type Parameter Editor. To always display the editor in Workbench, you can select View > Windows > Parameter Editor.
on a feature type in the workspace to open the Feature Type Parameter Editor. To always display the editor in Workbench, you can select View > Windows > Parameter Editor.
General
All feature types share similar General parameters, which may include the Feature Type Name, Reader or Writer Name, and Geometry.
In most Writer Feature Type parameter dialogs, you can also control Dynamic Schema Definitions. Some database formats accept a Table Qualifier prefix on the output table feature type.
See Editing Writer Feature Types for more information.
Table Settings: General
This parameter specifies how features will be written into the destination table. Supported feature operations are described below. Note that the described behavior can be dependent on the selected options, as well as the underlying table properties.
|
Option |
Description |
If the Row Does Not Exist |
If the Row Exists |
|---|
| Insert | The writer appends a new row to a table using input feature attributes and/or geometries. | The writer creates a new row using input feature attributes and/or geometries. |
Not always applicable: if the table does not have a unique key or it has an automatically generated unique key, insertion is always possible. The database cannot violate its key constraints; therefore, errors can occur on row insertion. For example, if there is a unique key and a user specifies the value with the feature, and the feature already exists, then Workbench logs an error. This error might be in the form of a rejected feature, or the database may stop processing altogether. |
| Update |
The writer updates existing row(s) in a table using input feature attributes and/or geometries. A selection method must be specified in the Row Selection group. |
The writer rejects the input feature or logs an error if it is unable to continue. | Changes only values of the existing row(s) corresponding to the input feature that differ from the input feature. |
| Delete |
The writer deletes an existing row(s) in a table. A selection method must be specified in the Row Selection group. |
The writer rejects the input feature or logs an error if it is unable to continue. | The writer deletes existing row(s) corresponding to the input feature. |
| fme_db_ operation |
The feature operation will be determined by the attribute fme_db_operation on each input feature. A selection method must be specified in the Row Selection group. The value of fme_db_operation will be processed according to the steps below. Note: The processing steps listed below depend on a format's available Feature Operation options.
Note about earlier FME versions: To use fme_db_operation, you must set Feature Operation to this option. In previous versions of FME, you could set fme_db_operation when the destination feature type was set to Insert, Update, or Delete. Doing this now will cause feature rejection. |
The action depends on the operation; however, in general, if nothing is specified, the value is treated as Insert. | The value is treated as Insert. |
Controls how the feature type handles destination tables or lists. These options are available:
- Use Existing: Write to an existing table or list. If the destination table/list does not exist, the translation will fail.
- Create If Needed: Create destination table/list if it does not exist.
- Drop and Create: Drop destination table/list if it exists, and then create it. The writer will drop and re-create the table before writing any features to it. Tables will be overwritten when the first input feature is processed. If no features are sent to a feature type, then the corresponding table will not be overwritten.
- Truncate Existing: (This option is not available for all formats.) If destination table/list does not exist, the translation will fail. Otherwise, delete all rows from existing table or list.
When updating features, users have a choice to update, or skip, their spatial column(s). Possible options are:
- Yes: The spatial column(s) specified by the user will be updated. IFMENulls will be written as null values and replace existing spatial values.
- No: No spatial columns will be updated.
Row Selection
When inserting into a table, Row Selection is ignored. When updating and deleting from a table (if applicable, based on a format's available Feature Operation options), a condition needs to be specified for selecting which rows to operate on. This parameter group offers two methods to construct the selection condition:
The columns specified in the corresponding column picker dialog will be used for matching destination rows. All matching rows will be selected for update or delete. If any feature attributes corresponding to the specified match columns contain null or missing values, the feature will be rejected.
This parameter opens a WHERE Clause Builder. You can also type a WHERE clause inline, without launching the Builder. It is optional to start the clause with the word WHERE.
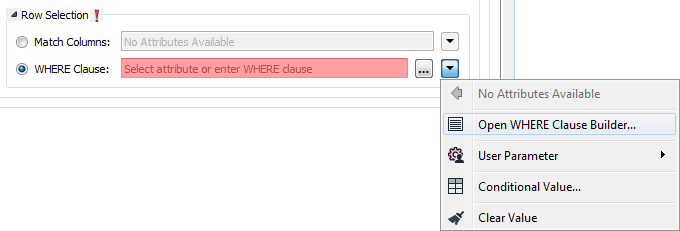
The WHERE Clause Builder makes it easy for users to reference feature attribute values, destination table columns, and invoke FME functions. The WHERE clause is first evaluated as an FME expression, before being passed onto the destination database.
If the WHERE clause is incorrect or if its evaluation results in failure, the translation will fail. Otherwise, if the WHERE clause passes FME evaluation but it is SQL invalid, the feature will be rejected or the translation will fail.
For advanced users, conditional FME expressions created through the Conditional Value editor can be used to create WHERE clauses.
Tip: You can set the WHERE Clause to an attribute. This supports workspace migration and existing workflows involving fme_where. (Direct support for fme_where has been deprecated.) To advanced users who are accustomed to using fme_where, if Feature Operation is set to Update, Delete, or fme_db_operation, an fme_where attribute that conflicts with Match Columns or WHERE Clause will result in feature rejection.
Table Creation Parameters
The parameters in this section take effect only when FME creates a table.
Specifies whether a system OID column should be created or not. OIDs are not guaranteed to be unique feature identifiers, and their use is deprecated outside of system tables. If set to No, then the OID column is not created.
This parameter determines whether or not a GiST index is created on the geometry column of the table (as long as one exists). This indexing of the geometry column is required for spatial query performance.
Table Settings: Spatial
Specifies the name of the column to be created that will hold the spatial data when creating a new PostGIS table. Valid values are geography and geometry. The default value is geometry.
Specifies the name of the column to be created that will hold the spatial data when creating a new PostGIS table. The default value is geom.
Specifies the spatial referencing information for the geometry in the table. By default, this value is not set, which causes the conversion of the FME coordinate system of the writer into an SRID to be used as the SRID for the given table.
Alternatively, a specific integer SRID value may be specified. Specified SRID values should correspond to an existing spatial reference identifier value stored in the (SRID) column in the global table spatial_ref_sys.
Note:
- All geometry within a given table must have the same spatial referencing.
- If postgis_srid is not specified, tables will be created with the SRID of the writer coordinate system.
- If no SRIDs are desired, the value for the SRID field can be set to -1, indicating no spatial reference system.
Table Settings: Advanced
Determines if the database function to vacuum and analyze the table is performed once the table is successfully written. This will build statistics for the table.
Allows the writer to overwrite the values of automatically populated serial columns specified on feature tables.
(Note that in PostgreSQL, serial columns are equivalent to a sequence.)