You are here: Popular Formats > Google KML Reader/Writer > Feature Representation > Common Element Attributes > LookAt Example
To set the LookAt element in Workbench for a KML document written by FME, you need to write a "document" feature that overrides the root document. To do this, follow these steps:
- Open a blank workspace.
- Place a Creator transformer, and create a new feature.
- Route the new feature through an AttributeCreator transformer to the writer feature type (you might have to create a new writer feature type when prompted).
- Create the following attributes in the AttributeCreator:
| Attribute | Value | AttributeCreator Example |
|---|---|---|
| kml_id | The value must match the filename of the destination dataset (that is, if you are writing to mydoc.kml, the id should be mydoc.kml) . If the kml_id does not match, a second document will be created. |
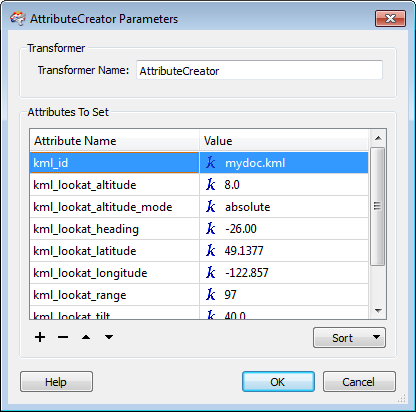
|
| kml_lookat_longitude (required) | Maps to the <longitude> element of <LookAt> | |
| kml_lookat_latitude (required) | Maps to the <latitude> element of <LookAt> | |
| kml_lookat_altitude | Maps to the <altitude> element of <LookAt> | |
| kml_lookat_altitude_mode | maps to the <altitudeMode> element of <LookAt> | |
| kml_lookat_heading | Maps to the <heading> element of <LookAt> | |
| kml_lookat_tilt | Maps to the <tilt> element of <LookAt> | |
| kml_lookat_range | Maps to the <range> element of <LookAt> |
Note: See the KML Documentation for LookAt for more information about the values for the above attributes.
The finished workspace should look like this example:
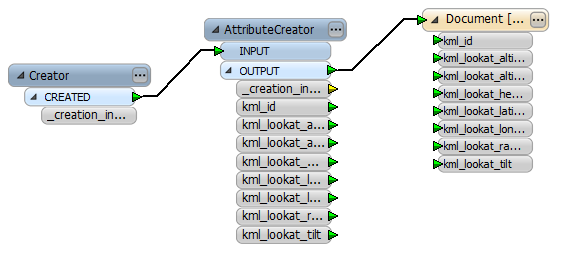
Save and run the workspace to generate the mydoc.kml file.