Field Separation
Choose the separator that will divide the fields in the file. By default, this parameter is set to auto; however, you can also select one of the following separators:
- , (comma)
- ; (semicolon)
- | (vertical bar)
- space
- tab
By default, each separator is treated as if it separates a different field.
When this parameter is checked, multiple contiguous separators are treated as a single separator.
Some CSV files place quotation marks around all values they contain. When checked, this parameter will strip quotation marks from column values.
If the field or column names of the table are specified in the file, check this parameter and the names will be extracted from the file. Otherwise, the columns of the table are given default names (for example, col0, col1, ... , colN).
Field Names Follow Header
If the column/field names is AFTER the header information instead of BEFORE, then you can set this option. Otherwise, by default, the first line of the file will be used as the column/field names.
Lines to Skip
This indicates the number of lines to skip at the top of the file. By default, 1 line is skipped. Each line skipped is logged to the log file. This is useful if the file contains a header line of field names or other descriptive material (like comments) that should be skipped.
This field indicates the number of footer lines to skip at the bottom of the file. By default, no footer lines are skipped. Each footer line skipped is logged to the log file. This is useful if the file contains a footer line of descriptive material that should be skipped.
Limits the number of lines read into the point cloud.
Component Map Generation
Indicates the number of rows in the file that should be read to generate the automatic mapping of the component map.
The default is 10000. If this parameter is set to 0, there will be no limit and all rows will be read.
File Preview
Displays a preview of the data, if available.
Point Cloud Component Map
Maps each data column in the Point Cloud XYZ file to a component of the point cloud. This table is automatically populated from the first Point Cloud XYZ file, if one is present. The component map is reset every time a parameter that affects the columns is changed.
If not specified, the point cloud will have one component for each column, with the component name equal to the column name, and where the type is determined by scanning the file.
Schema Attributes
Use this parameter to expose Format Attributes in FME Workbench when you create a workspace:
- In a dynamic scenario, it means these attributes can be passed to the output dataset at runtime.
- In a non-dynamic scenario, this parameter allows you to expose additional attributes on multiple feature types. Click the browse button to view the available format attributes (which are different for each format) for the reader.
Spatial
Coordinate systems may be extracted from input feature data sources, may come predefined with FME, or may be user-defined. FME allows different output and input coordinate systems, and performs the required coordinate conversions when necessary.
If a coordinate system is specified in both the source format and the workspace, the coordinate system in the workspace is used. The coordinate system specified in the source format is not used, and a warning is logged. If a source coordinate system is not specified in the workspace and the format or system does not store coordinate system information, then the coordinate system is not set for the features that are read.
If a destination coordinate system is set and the feature has been tagged with a coordinate system, then a coordinate system conversion is performed to put the feature into the destination system. This happens right before the feature enters into the writer.
If the destination coordinate system was not set, then the features are written out in their original coordinate system.
If a destination coordinate system is set, but the source coordinate system was not specified in the workspace or stored in the source format, then no conversion is performed. The features are simply tagged with the output system name before being written to the output dataset.
For systems that know their coordinate system, the Coordinate System field will display Read from Source and FME will read the coordinate system from the source dataset. For most other input sources, the field will display Unknown (which simply means that FME will use default values). In most cases, the default value is all you'll need to perform the translation.
You can always choose to override the defaults and choose a new coordinate system. Select More Coordinate Systems from the drop-down menu to open the Coordinate System Gallery.
Changing a Reprojection
To perform a reprojection, FME typically uses the CS-MAP reprojection engine, which includes definitions for thousands of coordinate systems, with a large variety of projections, datums, ellipsoids, and units. However, GIS applications have slightly different algorithms for reprojecting data between different coordinate systems. To ensure that the data FME writes matches exactly to your existing data, you can use the reprojection engine from a different application.
To change the reprojection engine, Select Workspace Parameters > Spatial > Reprojection Engine. In the example shown, you can select Esri (but the selection here depends on your installed applications):
- The coordinate systems file coordsys.db in the FME installation folder contains the names and descriptions of all predefined coordinate systems.
- Some users may wish to use coordinate systems that do not ship with FME, and in those cases, FME also supports custom coordinate systems.
- Learn more about Working with Coordinate Systems in FME.
A search envelope (also known as a bounding box) is a rectangular area that defines a geographic area. In FME, the easiest way to define a search envelope is to use search envelope parameters.
Defining a search envelope is the most efficient method of selecting an area of interest because FME will read only the data that is necessary – it does not have to read an entire dataset. Search Envelope parameters apply to both vector and raster datasets and can be particularly efficient if the source format has a spatial index.
Most FME readers have parameters to define the search envelope of data that is being read:
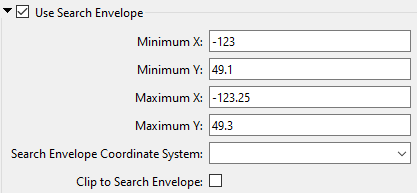
The parameters include the x and y coordinates of the bounding box as well as a parameter that defines the coordinate system.
How to Define the Bounding Box
Using the minimum and maximum x and y parameters, define a bounding box that will be used to filter the input features. Only features that intersect with the bounding box are returned. Note that the bounding box intersection is not a full geometry intersection (based on spatial relationships) that would be returned by a transformer like the SpatialFilter.
|
Search Envelope Coordinate System |
Specifies the coordinate system of the search envelope if it is different than the coordinate system of the data. The coordinate system associated with the data to be read must always be set if this parameter is set. If this parameter is set, the minimum and maximum points of the search envelope are reprojected from the Search Envelope Coordinate System to the reader’s coordinate system prior to applying the envelope. |
||||||
|
Clip to Search Envelope |
The underlying function for Use Search Envelope is an intersection; however, when Clip to Search Envelope is checked, a clipping operation is also performed.
|
Advanced
This parameter is applicable if you are working with extended (not basic ASCII) character sets. If your source data contains non-ASCII characters, using this parameter along with the encoding value ensures that the original data is preserved from the reader to the writer.
By default, the character encoding will be automatically detected from the local operating system. If you select any other character encoding, it will take precedence over the automatically detected character encoding.
FME supports most encodings.
Specifies whether string component data may contain separators.
This parameter must be set to Yes if the data contains separators, or the file may be read incorrectly.