FME Transformers: 2025.2
Reads features from any FME-supported format.
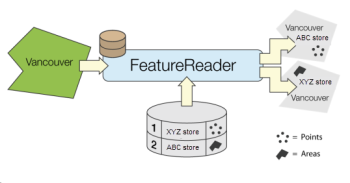
The features to be read are determined either by specifying feature types and optional constraints or, if the format supports it, by a custom query using the format’s query language.
When reading without a custom query, the features read can be constrained by specifying a WHERE clause or a spatial filter for formats that support them. Most reader settings and constraints can be configured dynamically from attribute values on the input features.
Additionally, a schema feature representing the feature type definition is output for each encountered feature type. The schema features can be used to configure feature type definitions for dynamic writing.
Optional Initiator Port
This transformer has two modes, depending on whether a connector is attached to the Initiator input port or not:
- Input-driven: When input features are connected, the transformer runs once for each feature it receives in the Initiator port.
- Run Once: When no input features are connected, the transformer runs one time.
When the Initiator input port is in use, the Initiator output port is also enabled.
Example
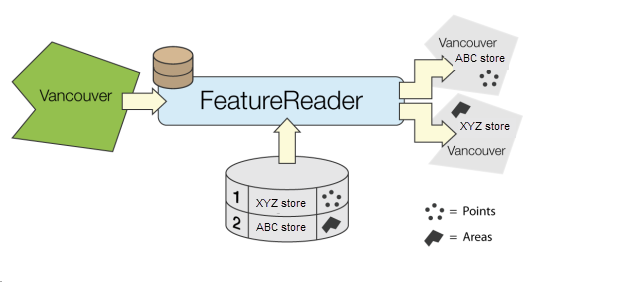
Configuration
Input Ports
This transformer accepts any feature.
Output Ports
Output port for schema features. If connected, a schema feature is produced for each unique feature type encountered during read. The schema feature is guaranteed to be output before any data features of the same feature type and is output only once per translation.
Note that schema features receive a new attribute fme_schema_handling with the value schema only. This attribute is used in writers to indicate that the feature should be used to define a schema only and then discarded, and so care should be taken if subsequently merging with other features.
Schema reading may affect performance. If the schema feature output port is not connected or Features to Read is set to Data Features, then schema reading will not occur and there will be no performance penalty. If a list of feature types to read was specified then schema reading will stop as soon as schemas for all the listed feature types have been output. If no feature types to read were listed, then schema reading will occur on every Initiator feature.
Performance can be improved when only reading schemas by configuring the transformer to not read data features. This is done by setting Features to Read to Schema Features or by ensuring that the <Generic>, the <Initiator>, and the named feature type output ports are not connected.
Parameters for Constraints or for Attribute and Geometry Handling do not apply to schema features.
Generic output port for features that do not have a corresponding named output port and features that result from a custom query.
When input Initiator features are used, they are output here with a (_matched_records) attribute containing the number of features read for that feature.
Upon reader error, outputs the original Initiator feature with the addition of the _reader_error attribute which contains the last error message from the reader.
Output Ports can be optionally generated for all or a subset of the feature types available to read.
Parameters
|
Reader |
Select the Reader format and dataset, including any reader-specific parameters. |
||||||||||||
|
Define Read Criteria By |
For formats that support query languages like SQL and Cypher, there are two options for reading:
|
||||||||||||
|
Query |
Only enabled if Custom Query was selected. Executes query statements against the database and returns resulting features through the <Generic> output port. |
||||||||||||
|
Constraints |
Only enabled if Constraint Parameters was selected.
|
||||||||||||
|
Schema/Data Features |
|
||||||||||||
|
Enable Data Feature Cache |
The FeatureReader reads the source data every time an Initiator feature is received. When enabled, Enable Cache creates a preprocessed cache to improve performance when rereading the data. Subsequent Initiator features or subsequent runs of the same workspace (on the same machine or engine) will use the contents of the cache. The cache expires after the specified time interval, or if the original data file is modified.
Note that:
|
|
Output Order |
Select an option for the ordering of output features:
|
||||||||||
|
Only enabled if Constraint Parameters was selected.
|
|
Accumulation Mode |
When input Initiator features are used for input-driven mode, select an attribute handling method:
|
|
Conflict Resolution |
|
|
Ignore Nulls |
Enabled when Accumulation Mode is set to Merge Initiator and Result. If Yes, where there are attributes with the same name on both Initiator and Result feature, if one has a value of <null> then the other attribute value will be used. If No, the Conflict Resolution selection will be strictly observed, including keeping null values. |
|
Prefix |
If the Accumulation Mode parameter is set to Prefix Initiator, this value will prefix attributes from the Initiator feature. |
|
Geometry |
When input Initiator features are used for input-driven mode, select a geometry handling method:
|
<Generic> Port
|
Attributes to Expose |
Enter the names of attributes to expose on the <Generic> output port. The attributes will be ordered in the same sequence as specified in the list. |
Editing Transformer Parameters
Transformer parameters can be set by directly entering values, using expressions, or referencing other elements in the workspace such as attribute values or user parameters. Various editors and context menus are available to assist. To see what is available, click  beside the applicable parameter.
beside the applicable parameter.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more.
When setting values - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors - strings and expressions containing String, Math, Date/Time or FME Feature Functions will have those functions evaluated. Therefore, the names of these functions (in the form @<function_name>) should not be used as literal string values.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
|
Special Characters |
A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| Date/Time Functions | Date and time functions are available in the Text Editor. |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Creating and Modifying User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Table Tools
Transformers with table-style parameters have additional tools for populating and manipulating values.
|
Row Reordering
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
|
|
Cut, Copy, and Paste
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
Cut, copy, and paste may be used within a transformer, or between transformers. |
|
Filter
|
Start typing a string, and the matrix will only display rows matching those characters. Searches all columns. This only affects the display of attributes within the transformer - it does not alter which attributes are output. |
|
Import
|
Import populates the table with a set of new attributes read from a dataset. Specific application varies between transformers. |
|
Reset/Refresh
|
Generally resets the table to its initial state, and may provide additional options to remove invalid entries. Behavior varies between transformers. |
Note: Not all tools are available in all transformers.
For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
No |
| Dependencies | None |
| Aliases | Querier OracleQuerier RasterReader |
| History |
FME Online Resources
The FME Community and Support Center Knowledge Base have a wealth of information, including active forums with 35,000+ members and thousands of articles.
Search for all results about the FeatureReader on the FME Community.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver, Open Government Licence - British Columbia, and/or Open Government Licence – Canada.