FME Transformers: 2025.0
Adds vertices to linear features at regular intervals.
Typical Uses
- Preserving geometry shapes through reprojection
- Adding vertices for more even feature chopping
How does it work?
The Densifier receives features with line or area geometry and adds additional vertices to them at regular intervals.
Spacing is specified in ground units, and the placement is guided by Mode:
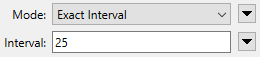
- Exact Interval: Vertices are added at the specified interval after each existing vertex.
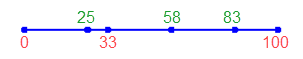
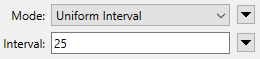
- Uniform Interval: Each segment of the feature is considered individually. The segment receives new vertices dividing it into equal parts. The number of parts is guided by the Interval value, and the distance between vertices can vary between segments.
|
|
Settings |
Result |
|---|---|---|
|
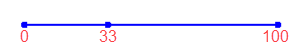
Input Feature |
|
|
|
Exact Interval |
|
|
|
Uniform Interval |
|

|
Examples
In this example, we have a set of polygons representing mapsheet boundaries across Canada. They are in a lat/long geographic coordinate system, and they are rectangles with points only at each corner.
Provincial boundaries are also displayed for reference.
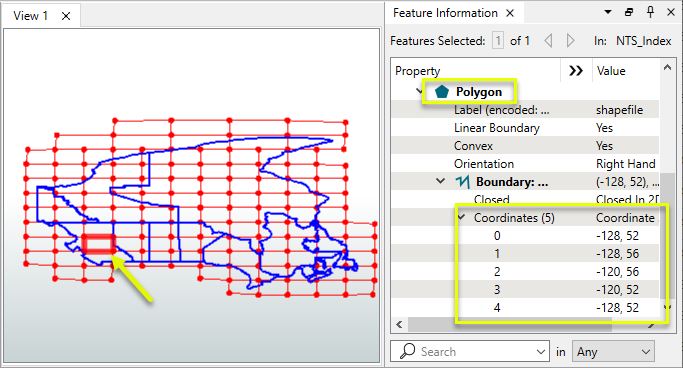
We want to work in British Columbia, at the far west end, and so reproject to a suitable coordinate system for that area.
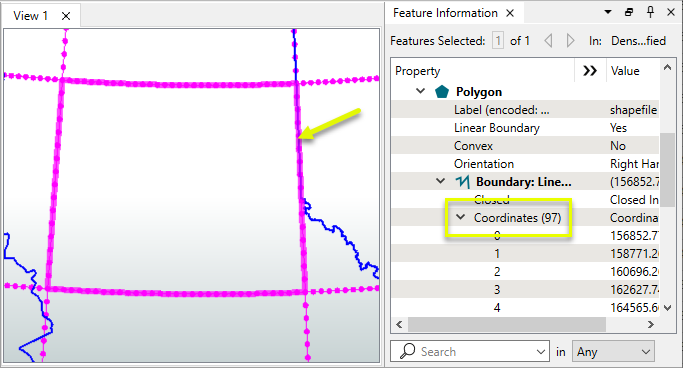
The straight edges of the polygons are still straight - which does not accurately represent where they fall in this UTM projection. The lines of latitude should curve.
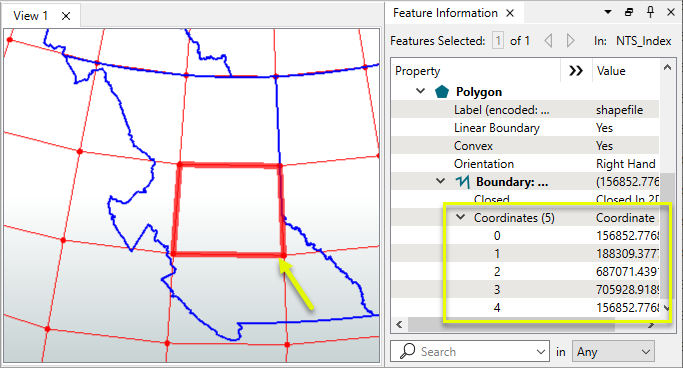
The features are routed into a Densifier prior to reprojecting.
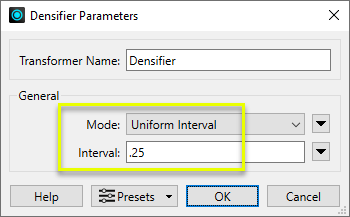
In the parameters dialog, an interval is set to add additional vertices along the feature. This is in ground units - in this case, degrees.
The reprojected feature is much more accurate.
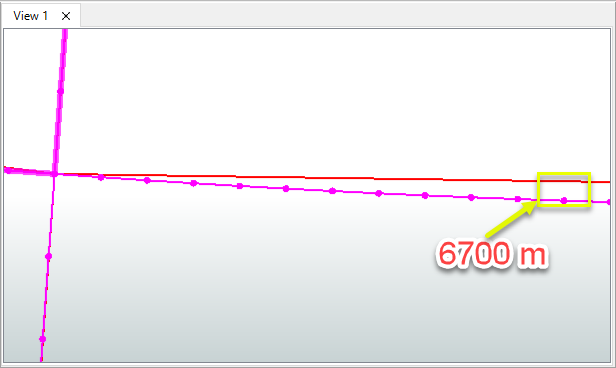
The positional difference between a two-point line and the densified line can be substantial.
Usage Notes
- To add a single vertex at a known position, use a VertexCreator.
- Use an ArcStroker to densify arcs or arcs within paths.
- The Generalizer may be useful for reversing densification.
- To densify a raster, use a RasterResampler.
Configuration
Input Ports
This transformer accepts any feature but will only densify line, path, or area geometry.
Output Ports
Features with added vertices as specified in parameters.
Parameters
|
Mode |
Select a method for determining added vertex positions:
|
|
Interval |
Specify the interval distance in ground units. |
Editing Transformer Parameters
Transformer parameters can be set by directly entering values, using expressions, or referencing other elements in the workspace such as attribute values or user parameters. Various editors and context menus are available to assist. To see what is available, click  beside the applicable parameter.
beside the applicable parameter.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more.
When setting values - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors - strings and expressions containing String, Math, Date/Time or FME Feature Functions will have those functions evaluated. Therefore, the names of these functions (in the form @<function_name>) should not be used as literal string values.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
|
Special Characters |
A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| Date/Time Functions | Date and time functions are available in the Text Editor. |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Creating and Modifying User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Table Tools
Transformers with table-style parameters have additional tools for populating and manipulating values.
|
Row Reordering
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
|
|
Cut, Copy, and Paste
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
Cut, copy, and paste may be used within a transformer, or between transformers. |
|
Filter
|
Start typing a string, and the matrix will only display rows matching those characters. Searches all columns. This only affects the display of attributes within the transformer - it does not alter which attributes are output. |
|
Import
|
Import populates the table with a set of new attributes read from a dataset. Specific application varies between transformers. |
|
Reset/Refresh
|
Generally resets the table to its initial state, and may provide additional options to remove invalid entries. Behavior varies between transformers. |
Note: Not all tools are available in all transformers.
For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
No |
| Dependencies | None |
| Aliases | |
| History |
FME Community
The FME Community has a wealth of FME knowledge with over 20,000 active members worldwide. Get help with FME, share knowledge, and connect with users globally.
Search for all results about the Densifier on the FME Community.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver, Open Government Licence - British Columbia, and/or Open Government Licence – Canada.