|
About Database Connections |
|---|
|
Database formats include a Database Connection parameter that defines and stores authentication information. For general information about sharing database connections, please see Note that Database Connection parameters differ slightly, depending on context and/or database format. |
|
Connection From the Connection parameter in a database format, you can do one of the following:
|
| Adding a Database Connection for Intergraph GeoMedia Access Warehouse and GeoMedia SQL Server Warehouse |
|---|
|
Note that parameter selection may vary, depending on the format and Authentication method. Entering a descriptive name allows you to easily find the connection in future workspaces. The following characters are not allowed in connection names: ^ \ / : * ? " < > | & = ' + % # Specifies the name of the server hosting the Microsoft SQL Server that stores the GeoMedia warehouse. The name of the database to connect to. When connecting through a Windows user account, select Windows Authentication. The database can validate the account name and password using the Windows principal token in the operating system. The user account is retrieved by Windows, so if you choose Windows Authentication, the Username and Password parameters are ignored. Select SQL Server Authentication to proceed with specifying login credentials through the Username and Password parameters. When Authentication is set to SQL Server Authentication, enter the username and password to access the database. |
Constraints
After specifying the database connection, click the Browse button (...) to select tables for import. A connection window appears while the system retrieves the tables from the database.
Once the Select Tables dialog appears, you can select one or more tables. Click OK to dismiss the window and add the selected table name(s) to the Tables parameter.
Any SQL where clause can be applied to the columns of a table to limit the resulting features.
Text Options
GeoMedia can store text in two variations: plain text and rich text. Since FME supports plain text only, the GeoMedia reader will convert all rich text to plain text and set the text size to the default (1 ground unit).
Schema Attributes
Additional Attributes to Expose
Use this parameter to expose Format Attributes in FME Workbench when you create a workspace:
- In a dynamic scenario, it means these attributes can be passed to the output dataset at runtime.
- In a non-dynamic scenario, this parameter allows you to expose additional attributes on multiple feature types. Click the browse button to view the available format attributes (which are different for each format) for the reader.
|
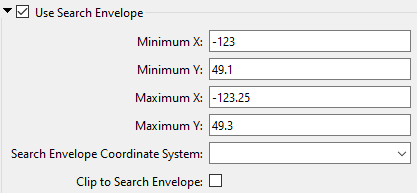
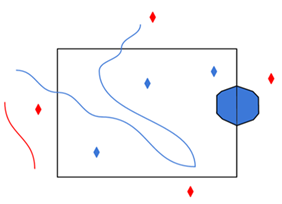
A search envelope (also known as a bounding box) is a rectangular area that defines a geographic area. In FME, the easiest way to define a search envelope is to use search envelope parameters. Defining a search envelope is the most efficient method of selecting an area of interest because FME will read only the data that is necessary – it does not have to read an entire dataset. Search Envelope parameters apply to both vector and raster datasets and can be particularly efficient if the source format has a spatial index. Most FME readers have parameters to define the search envelope of data that is being read:
The parameters include the x and y coordinates of the bounding box as well as a parameter that defines the coordinate system. How to Define the Bounding Box Using the minimum and maximum x and y parameters, define a bounding box that will be used to filter the input features. Only features that intersect with the bounding box are returned. Note that the bounding box intersection is not a full geometry intersection (based on spatial relationships) that would be returned by a transformer like the SpatialFilter. Note If all four coordinates of the search envelope are left at 0, the search envelope will be disabled even if this option is checked.
|
|||||||
|
Search Envelope Coordinate System |
Specifies the coordinate system of the search envelope if it is different than the coordinate system of the data. The coordinate system associated with the data to be read must always be set if this parameter is set. If this parameter is set, the minimum and maximum points of the search envelope are reprojected from the Search Envelope Coordinate System to the reader’s coordinate system prior to applying the envelope. |
||||||
|
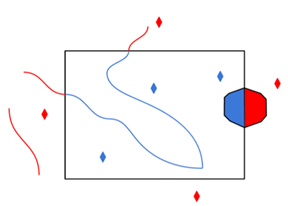
Clip to Search Envelope |
The underlying function for Use Search Envelope is an intersection; however, when Clip to Search Envelope is checked, a clipping operation is also performed.
|
||||||
Advanced
How the GeoMedia oriented points will be read. If Yes, all GeoMedia oriented points are returned with orientation information. If No, all GeoMedia-oriented points are returned as normal points without orientation information.
If this parameter is set to Yes, feature geometry will be read into an aggregate. A directive is set on the aggregate to indicate that each part of the aggregate is independent from the others, and its own geometry.
Geometry parts of the aggregate are named and contain geometry according to their respective column in the table.