Advanced
Generators of vector files will typically create geometries with a small buffer beyond the tile extent so that geometries intersecting several tiles can be unioned back.
This option allows clipping of the geometries of input vector features to the tile extent.
Default: Yes (Any buffer geometries are removed and geometries are clipped to the tile extent.)
Allows specification of an explicit metadata.json file from which to read layer schemas and dataset bounds. If the dataset is structured tileset and a metadata.json file exists at the root directory above the tileset/zoom level folders, then it should be picked up automatically.
Although this is an optional parameter in most cases, it is recommended that a metadata file is specified when reading an entire tileset from the web, especially at higher zoom levels. If this parameter is not specified or the metadata file is not found, the driver scans the tiles in the dataset to determine the schema for each layer.
Identifies how many tiles will be read for schema information (that is, attribute names and types as well as geometry). If no metadata file can be found, the driver scans the tiles in the dataset to determine the schema. This option is applicable only when opening an entire zoom level, and is not used when reading a single tile.
Default: 1000
Identifies the individual tile file extension when reading either a local tileset directory or a URL tileset that may contain one or more individual tile files. All tiles in a given tileset are assumed to have the same file extension.
Default: mvt
|
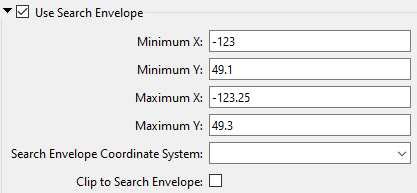
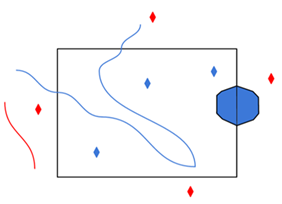
A search envelope (also known as a bounding box) is a rectangular area that defines a geographic area. In FME, the easiest way to define a search envelope is to use search envelope parameters. Defining a search envelope is the most efficient method of selecting an area of interest because FME will read only the data that is necessary – it does not have to read an entire dataset. Search Envelope parameters apply to both vector and raster datasets and can be particularly efficient if the source format has a spatial index. Most FME readers have parameters to define the search envelope of data that is being read:
The parameters include the x and y coordinates of the bounding box as well as a parameter that defines the coordinate system. How to Define the Bounding Box Using the minimum and maximum x and y parameters, define a bounding box that will be used to filter the input features. Only features that intersect with the bounding box are returned. Note that the bounding box intersection is not a full geometry intersection (based on spatial relationships) that would be returned by a transformer like the SpatialFilter. Note If all four coordinates of the search envelope are left at 0, the search envelope will be disabled even if this option is checked.
|
|||||||
|
Search Envelope Coordinate System |
Specifies the coordinate system of the search envelope if it is different than the coordinate system of the data. The coordinate system associated with the data to be read must always be set if this parameter is set. If this parameter is set, the minimum and maximum points of the search envelope are reprojected from the Search Envelope Coordinate System to the reader’s coordinate system prior to applying the envelope. |
||||||
|
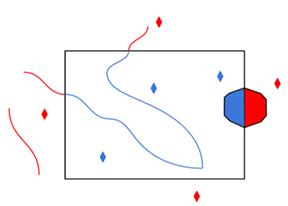
Clip to Search Envelope |
The underlying function for Use Search Envelope is an intersection; however, when Clip to Search Envelope is checked, a clipping operation is also performed.
|
||||||