AreaOnAreaOverlayer
Performs an area-on-area overlay (intersection of polygons) so that all input areas are intersected against each other and resultant area features are created and output. The resultant areas can accumulate attribute from any overlapping polygons.
Typical Uses
- Deconstructing overlapping polygons to produce the intersections and differences
- Comparing multiple datasets for area overlaps
- Performing area calculations based on overlapping area data
How does it work?
The AreaOnAreaOverlayer takes in area features. All polygons are considered against each other, and where they overlap, new polygons are created that represent both the overlapping area and the original areas with the overlap removed.
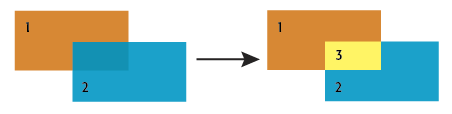
The new polygons can retain attributes from all original relevant features (performing a spatial join), and a count of the number of overlaps encountered during the overlay. This count starts at 1 for all features, as they are considered to overlap themselves.
Aggregates can either be deaggregated before processing or rejected.
Examples
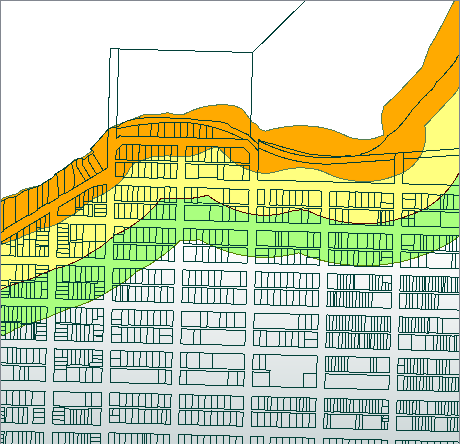
In this example, coastal zone polygons are overlaid with a parcel dataset, perhaps to identify where parcels may be subject to restrictions due to proximity to the coast. The original data looks like this:
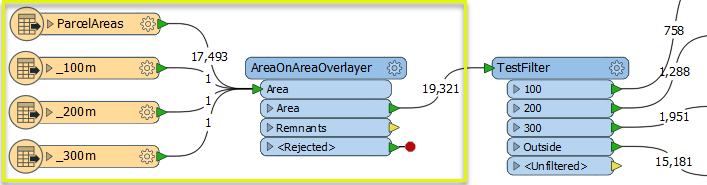
In this segment of a workspace, the input features - three polygons representing different setbacks from the coast and the parcel fabric - are routed into the Area input port.
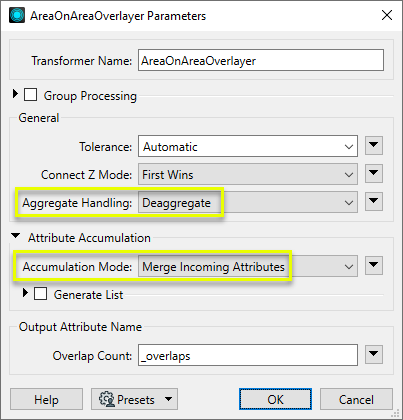
In the parameters dialog, we make the following selections:
- Aggregate Handling: Deaggregate, to ensure all areas will be processed
- Attribute Accumulation: Accumulation Mode is set to Merge Incoming Attributes.
As the overlay is processed, new area features are created, with the merged attributes of their source features. Some parcels are divided if they partially intersect a zone polygon, and areas representing the space between the parcels that falls within a zone polygon are also created (in this example, generally representing roads and laneways).
As we are interested in the parcels themselves, we have added a TestFilter to route the parcel polygons by zone and discard the non-parcel features.
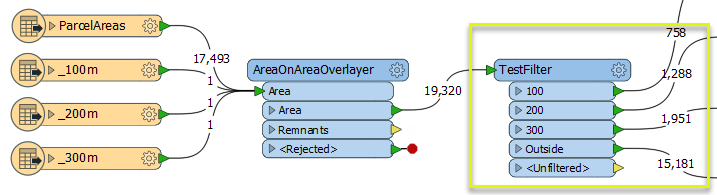
By creating test clauses that check for the existence of the ParcelA_ID attribute, non-parcel areas are output via the <Unfiltered> port, and discarded.
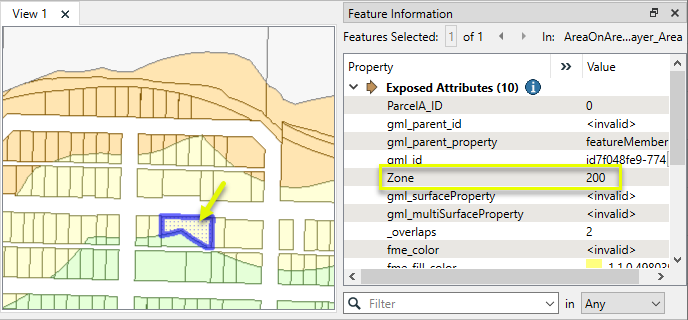
The results, viewed in the FME Data Inspector, with color coding by Zone.
Usage Notes
Choosing a Spatial Transformer
Many transformers can assess spatial relationships and perform spatial joins - analyzing topology, merging attributes, and sometimes modifying geometry. Generally, choosing the one that is most specific to the task you need to accomplish will provide the optimal performance results. If there is more than one way to do it (which is frequently the case), time spent on performance testing alternate methods may be worthwhile.
To correctly analyze spatial relationships, all features should be in the same coordinate system. The Reprojector may be useful for reprojecting features within the workspace.
|
Transformer |
Can Merge Attributes |
Alters Geometry |
Counts Related Features |
Creates List |
Supported Types* |
Recommended For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SpatialFilter | Yes | No | No | No |
|
|
| SpatialRelator | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
|
|
| AreaOnAreaOverlayer | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
|
| LineOnAreaOverlayer | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
|
| LineOnLineOverlayer | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
|
| PointOnAreaOverlayer | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
|
|
| PointOnLineOverlayer | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
|
| PointOnPointOverlayer | Yes | No | Yes | Yes |
|
|
| Intersector | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
|
|
| Clipper | Yes | Yes | No | No |
|
|
| NeighborFinder | Yes | In some cases | No | Yes |
|
|
| TopologyBuilder | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
|
|
* Note that Curve includes Lines, Arcs, and Paths. Area includes Polygons, Donuts, and Ellipses.
Spatial analysis can be processing-intensive, particularly when a large number of features are involved. If you would like to tune the performance of your workspace, this is a good place to start.
When there are multiple ways to configure a workspace to reach the same goal, it is often best to choose the transformer most specifically suited to your task.
If performance is an issue in your workspace, look for alternative methods, guided by geometry.
Configuration
Input Ports
This transformer accepts area features as input. Area features are expected to be non-self-intersecting.
Tip: If input areas are self-intersecting, first use the GeometryValidator’s Self-Intersection in 2D rule to remove self-intersections.
Output Ports
Area features resulting from the intersection of input areas are output through this port.
Geometries and attributes that are not part of the overlayed output. If the remnant feature has a geometry, this geometry was not used in any output area. If the remnant feature does not have a geometry, this feature contains attributes that were not used in any output area.
Features with invalid geometries will be rejected and output via this port.
Rejected features will have an fme_rejection_code attribute with one of the following values:
INVALID_POLYGON_GEOMETRY_TYPE
INVALID_POLYGON_GEOMETRY_VERTICES
INVALID_POLYGON_GEOMETRY_DEGENERATE
Rejected Feature Handling: can be set to either terminate the translation or continue running when it encounters a rejected feature. This setting is available both as a default FME option and as a workspace parameter.
Parameters
|
Group By |
The default behavior is to use the entire set of features as the group. This option allows you to select attributes that define which groups to form. |
||||
|
Complete Groups |
Select the point in processing at which groups are processed:
There are two typical reasons for using When Group Changes (Advanced) . The first is incoming data that is intended to be processed in groups (and is already so ordered). In this case, the structure dictates Group By usage - not performance considerations. The second possible reason is potential performance gains. Performance gains are most likely when the data is already sorted (or read using a SQL ORDER BY statement) since less work is required of FME. If the data needs ordering, it can be sorted in the workspace (though the added processing overhead may negate any gains). Sorting becomes more difficult according to the number of data streams. Multiple streams of data could be almost impossible to sort into the correct order, since all features matching a Group By value need to arrive before any features (of any feature type or dataset) belonging to the next group. In this case, using Group By with When All Features Received may be the equivalent and simpler approach. Note: Multiple feature types and features from multiple datasets will not generally naturally occur in the correct order. As with many scenarios, testing different approaches in your workspace with your data is the only definitive way to identify performance gains. |
|
Tolerance |
The minimum distance between geometries in 2D before they are considered equal, in ground units. If the tolerance is Automatic, a tolerance will be automatically computed based on the location of the input geometries. Additionally, a custom tolerance may be used. | ||||||||||||||||||
|
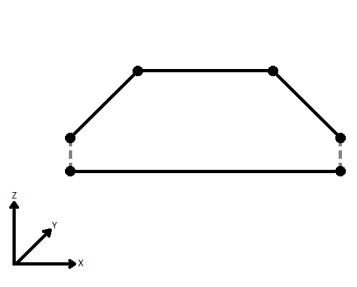
Connect Z Mode |
If applicable, select a method for handling z values. When viewed in 2D (ignoring Z), a path (which may define the border of a polygon) may appear to be closed as shown in the left figure below. This same path, when viewed in 3D, may appear to be open as shown in the right figure below.
To specify how (and if) paths should be closed in 3D, select one of the listed modes.
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
Aggregate Handling |
Choose how aggregate geometries are to be handled. Deaggregate: Decompose aggregates into their individual components. With this setting, the transformer might output more features than were given as inputs. Reject: Do not process aggregates and output them via the <Rejected> port. |
|
Accumulation Mode |
Specifies how attributes should be accumulated. Drop Incoming Attributes: All incoming attributes are removed from the features Merge Incoming Attributes: Merges all attributes from overlapping areas Use Attributes From One Feature: Takes all attributes from one representative feature |
||||||
| Generate List |
When enabled, adds a list attribute to the output features, retaining attribute values for multiple overlay matches. This allows later inspection of overlapping area attributes.
|
|
Overlap Count |
Name the attribute to contain the number of features that the resultant feature overlapped, which will be at least one. |
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters. There are a number of tools and shortcuts that can assist in constructing values, generally available from the drop-down context menu adjacent to the value field.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more.
When setting values - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors - strings and expressions containing String, Math, Date/Time or FME Feature Functions will have those functions evaluated. Therefore, the names of these functions (in the form @<function_name>) should not be used as literal string values.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
|
Special Characters |
A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| Date/Time Functions | Date and time functions are available in the Text Editor. |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Creating and Modifying User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Dialog Options - Tables
Transformers with table-style parameters have additional tools for populating and manipulating values.
|
Row Reordering
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
|
|
Cut, Copy, and Paste
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
Cut, copy, and paste may be used within a transformer, or between transformers. |
|
Filter
|
Start typing a string, and the matrix will only display rows matching those characters. Searches all columns. This only affects the display of attributes within the transformer - it does not alter which attributes are output. |
|
Import
|
Import populates the table with a set of new attributes read from a dataset. Specific application varies between transformers. |
|
Reset/Refresh
|
Generally resets the table to its initial state, and may provide additional options to remove invalid entries. Behavior varies between transformers. |
Note: Not all tools are available in all transformers.
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
Yes |
| Dependencies | |
| Aliases | |
| History |
FME Community
The FME Community is the place for demos, how-tos, articles, FAQs, and more. Get answers to your questions, learn from other users, and suggest, vote, and comment on new features.
Search for all results about the AreaOnAreaOverlayer on the FME Community.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver and/or the Open Government Licence – Canada.