Accesses the Amazon Simple Storage Service (S3) file storage service to upload, download, or delete files and folders or list file/folder information from an S3 account.
Typical Uses
- Manage datasets on S3 by uploading, downloading, and deleting files and folders
- Transfer a file's contents (such as XML or raster) into or out of an attribute in FME
- Read downloaded S3 data using the FeatureReader, or upload data written by the FeatureWriter to S3
- Retrieve file and folder names, paths, links and other information from S3 to use elsewhere in a workspace.
How does it work?
The S3Connector uses your Amazon S3 account credentials (either via a previously defined FME web connection, or by setting up a new FME web connection right from the transformer) to access the file storage service.
Depending on your choice of actions, it will upload or download files, folders, and attributes; list information from the service; or delete items from the service. On uploads, link attributes can be added to the output features. On List actions, file/folder information are added as attributes.
Examples
In this example, the S3Connector is used to download an Esri Geodatabase from S3. After creating a valid web connection to an S3 account (which can be done right in the Account parameter), and browsing to the geodatabase folder, the Bucket and Path to the object are retrieved, and a destination for the download is selected.
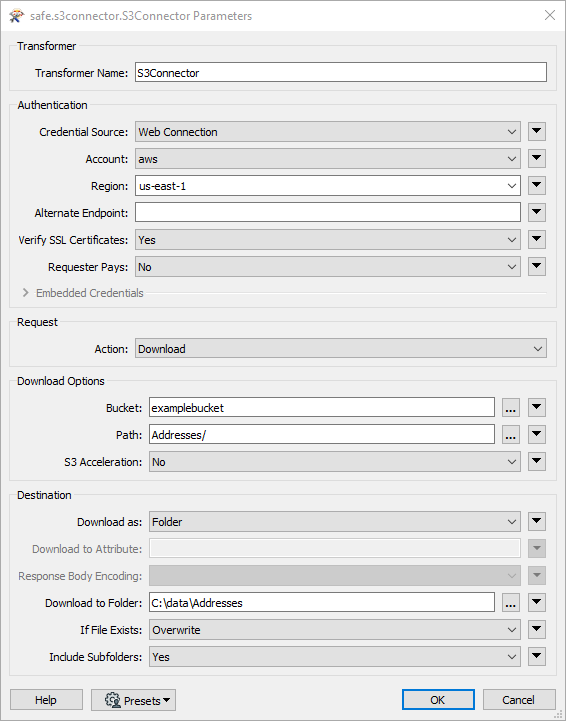
A FeatureReader is added to read the newly downloaded dataset. Here, the PostalAddress feature type will be further processed elsewhere in the workspace.


By executing the download here in the workspace, the geodatabase will be refreshed every time the workspace is run.
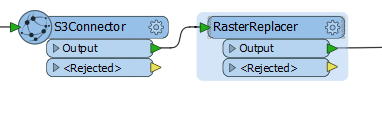
In this example portion of a workspace, the S3Connector is used to download a raster orthoimage from S3 into an attribute.

The file is read from S3, and the contents stored as a blob attribute. Then a RasterReplacer is used to interpret the blob into a usable raster format.

The combination of these two transformers avoids having to download the image to local storage and re-read it. A similar technique can be used for point cloud files, using the PointCloudReplacer transformer.
Usage Notes
- This transformer cannot be used to directly move or copy files between different S3 locations. However, multiple S3Connectors can be used to move or copy files with an intermediate download.
- The FeatureReader can access S3 directly, without using the S3Connector. In this case, a local copy of the dataset will not be created.
Configuration
Input Ports
This transformer accepts any feature.
Output Ports
The output of this transformer will vary depending on the S3 Action performed.
- After an Upload action, URLs to the file may be saved to the Direct Link attribute, and the bucket and path to the object will saved to the Full Path attribute.
- A Download action will output a new feature and can save to either a file, folder or attribute.
- A Delete action will output a new feature.
- A List action will output a new feature for each file/folder found in the path specified. Each of these new features will have attributes listing various pieces of information about the object.
Features that cause the operation to fail are output through this port. An fme_rejection_code attribute, having the value ERROR_DURING_PROCESSING, will be added, along with a more descriptive fme_rejection_message attribute which contains more specific details as to the reason for the failure.
Note: If a feature comes in to the S3Connector already having a value for fme_rejection_code, this value will be removed.
Rejected Feature Handling: can be set to either terminate the translation or continue running when it encounters a rejected feature. This setting is available both as a default FME option and as a workspace parameter.
Parameters
| Credential Source |
The S3Connector can use credentials from different sources. Using a web connection integrates best with FME, but in some cases, you may wish to use one of the other sources.
|
| Account |
Available when the credential source is Web Connection. To create an S3 connection, click the 'Account' drop-down box and select 'Add Web Connection...'. The connection can then be managed via Tools -> FME Options... -> Web Connections. |
| Region | The AWS Region in which the specified Bucket resides. If the default value, US East, N. Virginia (us-east-1), is specified, and the specified Bucket does not reside there, the operation will still succeed. However, to optimize latency, it is best practice to specify the correct region. |
| Alternate Endpoint | If specified, use an alternate S3-compatible API. These are typically object storage services from providers other than AWS, or on-premises solutions. |
| Verify SSL Certificates |
|
|
AWS CA Bundle |
The AWS CA Bundle specifies the path to a certificate bundle to use for certificate validation. If set, this has precedence over the value of the AWS_CA_BUNDLE environment variable. |
| Requester Pays | Some public buckets require the requester to pay the cost of operations performed. Setting this parameter to Yes will allow AWS to charge the account associated with the provided credentials to be charged. |
| Access Key ID and Secret Access Key | Available when the credential source is Embedded. An access key ID and secret access key can be specified directly in the transformer instead of in a web connection. |
| Session Token | Optional. Available when the credential source is Embedded. If specified, use the temporary security credentials to connect to S3. |
| Action |
The type of operation to perform. Choices are:
|
The remaining parameters available depend on the value of the Request > Action parameter. Parameters for each Action are detailed below.
Delete Options
|
Bucket |
The bucket the file or folder is in. If valid credentials have been provided as a web connection, you may browse for a bucket. |
|
Path |
The full path of a file or folder on S3 to delete. If valid credentials have been provided as a web connection, you may browse for a location. |
Download Options
|
Bucket |
The bucket the file or folder is in. If valid credentials have been provided as a web connection, you may browse for a bucket. |
|
Path |
The full path of a file or folder on S3 to download. If valid credentials have been provided as a web connection, you may browse for a location. |
|
S3 Acceleration |
If Yes, allows Amazon S3 Transfer Acceleration on the bucket, if enabled. To enable acceleration, see https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/UG/enable-bucket-transfer-acceleration.html. When allowing S3 Acceleration, keep in mind the following:
|
Destination
| Download as |
Select whether to store the downloaded data in a File, Folder or Attribute.
|
| Download to Attribute |
Specify the attribute that will store the contents of the downloaded file. Valid for Download as Attribute only. |
| Response Body Encoding |
For Download as Attribute, you can specify a character set encoding to ensure the output is in a human-readable form. If Auto Detect from HTTP Header is specified but there is no encoding in the Content-Type metadata associated with the data, the output will be returned as raw bytes. |
| Download to Folder | Specify the path to the folder that will store the downloaded file. Valid for Download as File or Folder. |
| If File Exists |
Specify what to do if the file already exists locally. Valid for Download as File or Folder.
|
| Include Subfolders |
Choose whether to download subfolders of the S3 Source or not. Valid for Download as Folder only. Default: No. |
Output Attributes
The selected attributes will be added to the output feature.
|
_download_path |
Path of the downloaded object on the local file system. This attribute will not be added for Download as Attribute. |
List Options
|
Bucket |
The bucket the folder is in. If valid credentials have been provided as a web connection, you may browse for a bucket. |
|
Path |
The full path to the folder on S3 to list. If valid credentials have been provided as a web connection, you may browse for a location. |
|
Include Subfolders |
If set to Yes, then subfolders are recursively traversed, and their contents are included in the result. Default: No. |
Output Attributes
Default attribute names are provided, and may be overwritten.
|
File or Folder Name |
Specify the attribute to hold the name of an object on S3. |
|
Bucket Name |
Specify the attribute to hold the ID of an object on S3. |
|
Full Path |
Specify the attribute to hold the full path to an object on S3. |
|
URL |
Specify the attribute to hold the URL of an object on S3. |
|
File Size |
Specify the attribute to hold the size of a file object on S3. |
|
Last Modified |
Specify the attribute to hold the last modified date of an object on S3. |
|
File or Folder Flag |
Specify the attribute to hold the type (file or folder) of an object on S3. |
|
Relative Path |
Specify the attribute to hold the relative path to an object on S3. |
Data Source
|
Upload |
The type of data to be uploaded.
When working with large objects, File is a better choice than Attribute as the data will be streamed directly from disk and not require that the object be stored entirely in memory on a feature. S3 treats file uploads of the same name, in a specific folder, as duplicates, but does not allow multiple instances in a specific folder. You must upload the file to a different folder than the existing one or the original will be overwritten. When wanting to upload content from a folder, it is better to upload as a folder instead of setting a fixed path and sending multiple features into the connector to upload as a file. |
|
File to Upload |
The file to be uploaded to S3 if Upload is set to File. |
|
Folder to Upload |
The folder to be uploaded to S3 if Upload is set to Folder. |
|
Include Subfolders |
Choose whether or not to upload subfolders of the Folder to Upload. |
|
Contents Only |
|
|
Attribute to Upload as File |
The data to be uploaded, supplied from an attribute if Upload is set to Attribute. |
Upload Options
| Bucket | The bucket the folder is in. If valid credentials have been provided as a web connection, you may browse for a bucket. |
| Path | The full path to the folder on S3 to upload to. If valid credentials have been provided as a web connection, you may browse for a location. |
| Upload with File Name | The name of the file created from the data supplied in Attribute to Upload as File. The name must include a filename extension (for example, .txt, .jpg, .doc). |
| If File Exists |
Specify what to do if the file already exists on S3.
|
|
S3 Acceleration |
If Yes, allows Amazon S3 Transfer Acceleration on the bucket, if enabled. To enable acceleration, see https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/UG/enable-bucket-transfer-acceleration.html. When allowing S3 Acceleration, keep in mind the following:
|
| Encryption |
|
| Permissions | The predefined set of grantees and permissions to store with each uploaded object. For more information, see https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/ACLOverview.html#CannedACL. |
| Generate Presigned URL | If enabled, a presigned URL is generated for the uploaded file, and stored in the _presigned_url attribute. This allows access to the file without credentials for the bucket. For more information, see https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonS3/latest/dev/ShareObjectPreSignedURL.html. |
| Expiry | When generating a presigned URL, optionally specify a number of seconds for which the link will remain valid. |
| Metadata | You can specify header fields in the HTTP upload request. Under Name, specify a header field. You can select from a drop-down list of predefined fields that include metadata and ACL permissions parameters. Alternatively, enter fields manually. Under Value, specify a field value. Custom metadata fields will automatically be prefixed with ‘x-amz-meta-’ by AWS. |
Output Attributes
| File or Folder Name |
Specify the output attribute that will store the name of the file or folder. For example, the attribute could contain ‘CityParks.gml’. |
| Full Path |
Specify the output attribute that will store the full path of the file/folder that was just uploaded. For example, the attribute could contain ‘city_data/GML/CityParks.gml’. |
|
Bucket Name |
Specify the output attribute that will store the name of the bucket to which the file was uploaded . |
|
URL |
Specify the output attribute that will store the URL to the file or folder on S3. |
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters. There are a number of tools and shortcuts that can assist in constructing values, generally available from the drop-down context menu adjacent to the value field.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more.
When setting values - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors - strings and expressions containing String, Math, Date/Time or FME Feature Functions will have those functions evaluated. Therefore, the names of these functions (in the form @<function_name>) should not be used as literal string values.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
|
Special Characters |
A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| Date/Time Functions | Date and time functions are available in the Text Editor. |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Creating and Modifying User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Dialog Options - Tables
Transformers with table-style parameters have additional tools for populating and manipulating values.
|
Row Reordering
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
|
|
Cut, Copy, and Paste
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
Cut, copy, and paste may be used within a transformer, or between transformers. |
|
Filter
|
Start typing a string, and the matrix will only display rows matching those characters. Searches all columns. This only affects the display of attributes within the transformer - it does not alter which attributes are output. |
|
Import
|
Import populates the table with a set of new attributes read from a dataset. Specific application varies between transformers. |
|
Reset/Refresh
|
Generally resets the table to its initial state, and may provide additional options to remove invalid entries. Behavior varies between transformers. |
Note: Not all tools are available in all transformers.
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
No |
| Dependencies | S3 account |
| Aliases | S3Deleter, S3Downloader, S3ObjectLister, S3Uploader |
| History | Released FME 2019.0 |
FME Community
The FME Community is the place for demos, how-tos, articles, FAQs, and more. Get answers to your questions, learn from other users, and suggest, vote, and comment on new features.
Search for all results about the S3Connector on the FME Community.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver and/or the Open Government Licence – Canada.