If you choose either Scripted (Python) or Scripted (Tcl) from the Type menu, you can write a script that assigns the value of a parameter to the workspace at runtime. This script will compute a value and assign it to a global parameter before the data is even read (for example, you might want to open a database, extract a value, and then run the workspace).
You can also use these parameters in a custom transformer.
Templates that contain Scripted (Python) parameters are available for download from FMEpedia. To download:
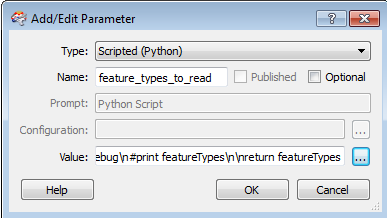
You can use the Scripted (Python) parameter to allow grouping of feature types (layers) in a workspace. In this example, taken from one of the templates described above, the parameter allows you to choose to group by different layers when you run the workspace.
In the Workbench Add/Edit Parameter dialog, the parameter is defined using the following options:

Click the browse button beside the Value field to display the source code editor. The code in the editor is described here:
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
|
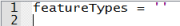
Initially set featureTypes variable to empty. |

|
If you choose Bus Information for global parameter Layers, set the feature types to Bus Routes and BusStops. |

|
If you choose Road and Rail for global parameter Layers, set the feature types to metrorail and Roads. |

|
If you choose All Transit for global parameter Layers , set the feature types to metrorail, Roads, BusRoutes, BusStops and Labels. |

Note: For both Python and Tcl, your code must contain a |
Return the The |
Note the style of code block indentation. FME's source code editor uses tab stops for indenting blocks, whereas other Python development environments (like IDLE) substitute tab stops by four spaces (by default). Mixed styles in the same block are not allowed. To avoid errors, you may have to replace tabs or spaces in code copied from another environment.
To run the workspace, select File > Prompt and Run Translation, press Ctrl+R, or click the  button.
button.
Prompt and Run will display a Translation Parameters dialog. The translation will pause until you choose which layers to group.
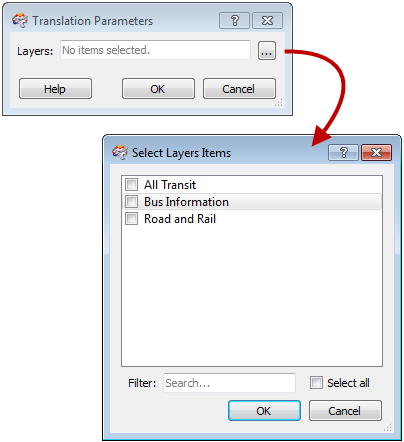
If you Select All, the features are set to all feature types:
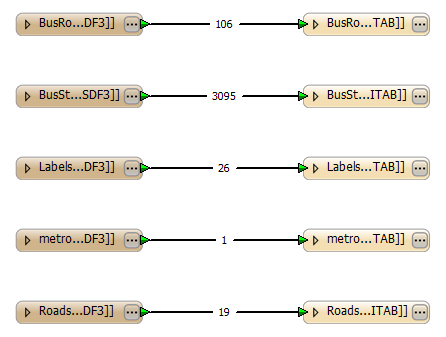
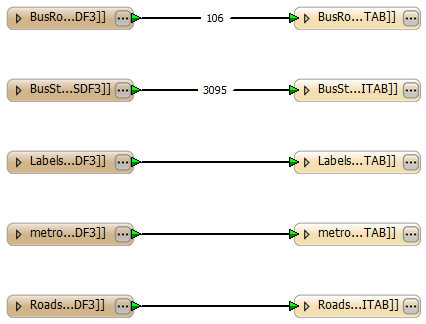
If you select Bus Information only, for example, the feature types are set to Bus Routes and BusStops only:
This table gives examples of actions you might want to include in your Python or Tcl script.
| Action | Python | Tcl |
|---|---|---|
| Access other parameters |
FME_MacroValues['MacroName']
|
In neither case will changing the value of a macro in the dictionary take effect outside the scope of your code. |
| Set other parameters | Not applicable |
puts Note this will set that parameter in the FME_MacroValues dictionary after your code has executed. Change |
| Write to the log file. The message will appear in the log window in Workbench in execution context with the color indicated by the error level. | Not applicable |
puts {Tcl2 FME_LogMessage fme_fatal {message message}} |
| To write to the end of the log file. The message will appear in the log at the end in the ‘info’ level. |
If you have multiple print or |
puts {Tcl2 error {my message}} See FME Factories and Functions help for the complete description of the |