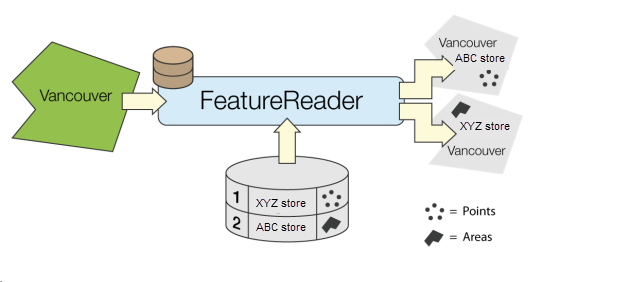
Receives features that initiate feature reading.
Reads features from any FME-supported format. A complete read is done for each feature that enters the Initiator port. The features resulting from the read are output either through named output ports or through the generic output port.
The features read can be constrained by specifying a WHERE clause or a spatial filter for formats that support them. Most reader settings and constraints can be configured dynamically from attribute values on the input features.
Additionally, a schema feature representing the feature type definition is output for each encountered feature type. The schema features can be used to configure feature type definitions for dynamic writing.
Receives features that initiate feature reading.
Output port for schema features. If connected, a schema feature is produced for each unique feature type encountered during read. The schema feature is guaranteed to be output before any data features of the same feature type and is output only once per translation.
Schema reading may affect performance. If the schema feature output port is not connected or Features to Read is set to Data Features, then schema reading will not occur and there will be no performance penalty. If a list of feature types to read was specified then schema reading will stop as soon as schemas for all the listed feature types have been output. If no feature types to read were listed, then schema reading will occur on every Initiator feature.
Performance can be improved when only reading schemas by configuring the transformer to not read data features. This is done by setting Features to Read to Schema Features or by ensuring that the <Generic>, the <Initiator>, and the named feature type output ports are not connected.
Parameters for Constraints or for Attribute and Geometry Handling do not apply to schema features.
Generic output port for features that do not have a corresponding named output port.
Upon read success, outputs the original Initiator features with the addition of the _matched_records attributes which holds the number of data features read for that Initiator feature.
Upon reader error, outputs the original Initiator feature with the addition of the _reader_error attribute which contains the last error message from the reader.
Note: <Rejected> features are accessible only if the workspace is run with feature inspection, or if the <Generic> or <Initiator> port connects to another transformer (such as a Junction).
Output Ports can be optionally generated for all or a subset of the feature types available to read.
Select the Reader format and dataset, including any reader-specific parameters.
Enter the feature types that will be read. Feature types can be selected from a list generated by the reader by clicking the Browse button. For some formats, the parameter can be left empty to indicate all feature types should be read.
When published, this parameter can be represented as a fixed list, a fixed list with aliases, or left as a dynamic list that determines the feature types at runtime.
Feature types can also come from an existing attribute or generated from an expression. To specify the feature types, separate each feature type with a space. If a feature type name contains a space or a double quote, then quote the whole feature type name with double quotes and escape any internal double quotes with an additional double quote. For example, a feature type named 'my "special" table' would become '"my ""special"" table"'.
Note: Older versions of the FeatureReader using colon as a separator will work as before, but can be updated (see Feature Type Separator).
This option allows older versions of the FeatureReader to change the separator for multiple feature types in an attribute to be a space instead of a colon. The colon separator is deprecated; once space has been selected, colon cannot be re-selected.
This option is only available to versions 4 and older of the FeatureReader that had been upgraded to version 5 or newer and that were specifying feature types to read from an attribute.
For formats that support it, only features that fulfill the WHERE clause will be read.
A WHERE clause is used to filter the results and takes the form:
column_name operator value
FME attributes can be used to substitute values in the WHERE clause using the syntax
@Value(<attribute>)
For example, "ID" = @Value(road_id)
User Parameters can be used to substitute values in the WHERE clause with the syntax
$(User Parameter)
For example, "PATHID" =$(ROAD_DID)
Select only features that fulfill the specified spatial relationship with the Initiator feature. See Spatial Relations Defined for a description of the permitted spatial relations. Select <No Spatial Filter> when no spatial filtering is desired. Select Envelope Intersects to read only those features whose envelope intersects the Initiator feature’s envelope.
The performance of the Spatial Filter can vary depending on the spatial filter being applied and whether the reader supports a Spatial Index. Spatial Filtering is done in two steps: first the candidate features are read, then the more costly filter is applied. For readers that support a Spatial Index, the candidate features are fetched by performing a search envelope on the reader which can greatly improve performance as not all features are read. For readers that do not support a Spatial Index or when the relationship Disjoint is selected, all features are considered candidate features and so all features are read. Check the format’s Quick Facts section to see if the reader supports a Spatial Index.
Note that when setting the Spatial Filter from an attribute, the attribute value can be any of the options found in the drop down list.
Limits the number of data features on each read. If left empty or set to a number less than one, all features are read.
Schema and Data Features: Schema features and data features are read and output based on whether their corresponding output ports are connected. For data features, this includes the <Initiator>, <Generic>, and named feature type output ports. For schema features, it is the <Schema> output port.
Schema Features: Only schema features are read and output. Data features are not read.
Data Features: Only data features are read and output. Schema features are not read.
By default, this transformer rereads the original source data for each Initiator feature. To improve performance (for example, with web services, databases, or URLs), you can choose to create a preprocessed cache to improve speed when rereading the original source data.
The cache expires after the specified time interval, or if the original data file is modified.
Note: The Cache Timeout value is also a component of the preprocessed cache. This means that different values of Cache Timeout correspond to different versions of the cached dataset. For example, if the FeatureReader is set with a Cache Timeout of 1 hour, then set a second time with the same dataset, but with a Cache Timeout of 2 hours, there will be two cached copies of this dataset.
Output ports can be optionally generated for all or a subset of the feature types available to read. Features that do not have a generated output port will exit the generic output port. In order for output ports to be generated, the reader must be fully specified and accessible.
An output port is generated for each feature type to read.
No additional output ports are generated. All feature types will exit out of the generic output port
Enter a list of feature types that will be used to generate the output ports. Feature types can also be selected from a list generated by the reader by clicking the Browse button.
Merge Initiator and Result: Output features will contain all of the un-conflicted attributes from the results of the read as well as any un-conflicted attributes from the Initiator feature. This mode will handle conflicted attributes based on the Conflict Resolution parameter.
Only Use Result: Output features will contain only attributes resulting from the read.
Only Use Initiator: Output features will contain all of the attributes from the Initiator feature, but none of the attributes resulting from the read.
Prefix Initiator: Output features will contain attributes resulting from the read, as well as attributes from the Initiator feature but with the Initiator attribute names prefixed with the Prefix parameter.
Use Result: If a conflict occurs, the values resulting from the read will be used.
Use Initiator: If a conflict occurs, the values of the Initiator will be used.
If the Accumulation Mode parameter is set to Prefix Initiator, this value will prefix attributes from the Initiator feature.
Result: The feature geometry from the results of the read is used.
Initiator: The feature geometry from the Initiator feature is used.
Aggregate Initiator and Result: The feature geometry is an aggregate of the geometry from the Initiator feature followed by the geometry from the result of the read. The aggregate geometry will be tagged with the coordinate system from the result of the read. The Initiator geometry will not be reprojected. This can create unexpected results if it is in a different coordinate system. For best results, ensure the Initiator geometry has the same coordinate system as the geometry being read.
Enter the names of attributes to expose on the <Generic> output port. The attributes will be ordered in the same sequence as specified in the list.
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Associated FME function or factory: QueryFactory
Search for samples and information about this transformer on the FME Knowledge Center.
Tags Keywords: query Querier OracleQuerier RasterReader