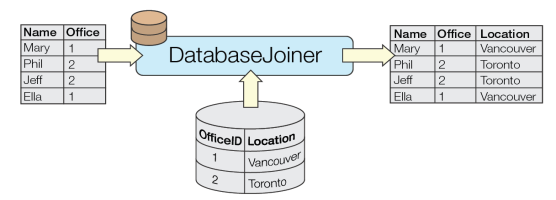
Joins attributes from an external table to features already in a workspace, based on a common key or keys.
The DatabaseJoiner queries an external table to retrieve attributes associated with a feature. One or more feature attributes (primary keys) are matched to one or more columns (foreign keys) in a table in the database, and the values from the matching table row(s) are added to the feature as attributes.
A number of matching methods (Cardinality) are available - Match All (1:M), First (1:0..1+), Exactly One (1:1), or Zero or One (1:0..1). Features that do not fulfill the matching conditions are output via the <Rejected> port.
The _matched_records attribute specifies how many records in the database the feature matched to. Multiple matches can create multiple features or add a list attribute to a single feature.

The DatabaseJoiner allows simple join relationships based on multiple attribute keys and requires no knowledge of SQL – this is often very effective for simple lookup tables.
In this example, we want to retrieve attributes from a table in a PostGIS database, and add those attributes to park polygons stored in a shapefile. The parks have an ID number which will be used to do the joining.
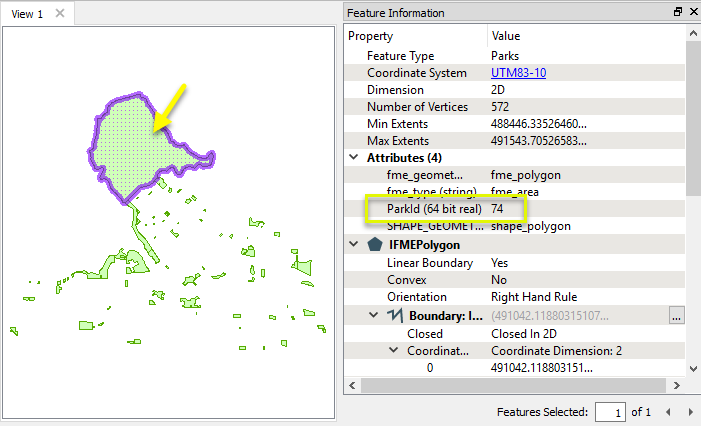
In this workspace, we start by reading the Parks shapefile, and then routing the park features into a DatabaseJoiner, where we will retrieve the rest of the attributes we want.
In the parameters dialog, the first step is to define the external database - much like configuring a regular database format reader.
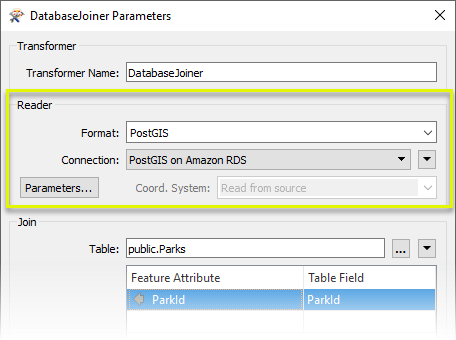
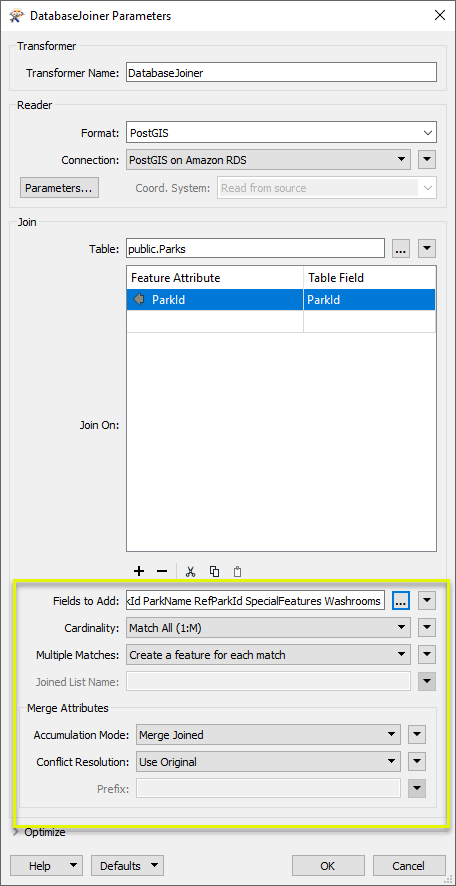
With the database connection made, we now select the desired table (public.Parks) via the browse button next to Table. This will load a list of available table to choose from. We then choose the attribute from both the incoming parks (Feature Attribute) and joined table (Table Field) to join on. In both cases, the attribute is called ParkId.
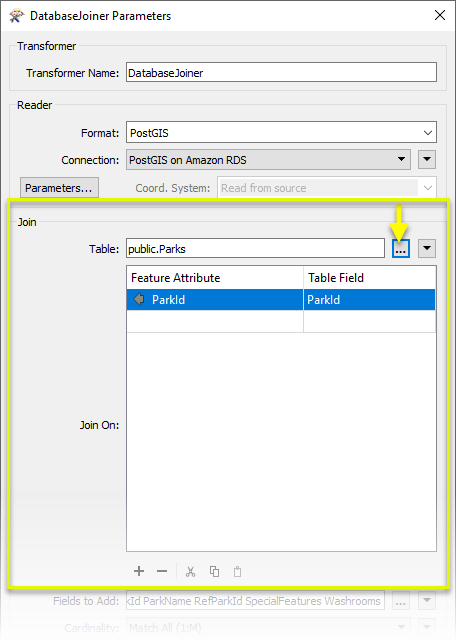
Fields to Add determines which attributes from the external database table are added to the Park features. We Select All of them.
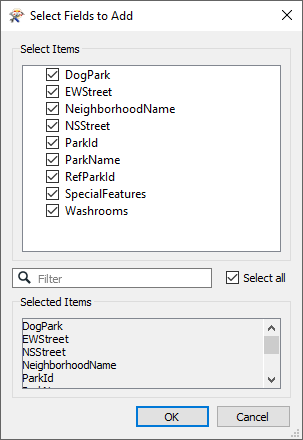
The default values for Cardinality, Multiple Matches, and attribute merging will provide the results we want.
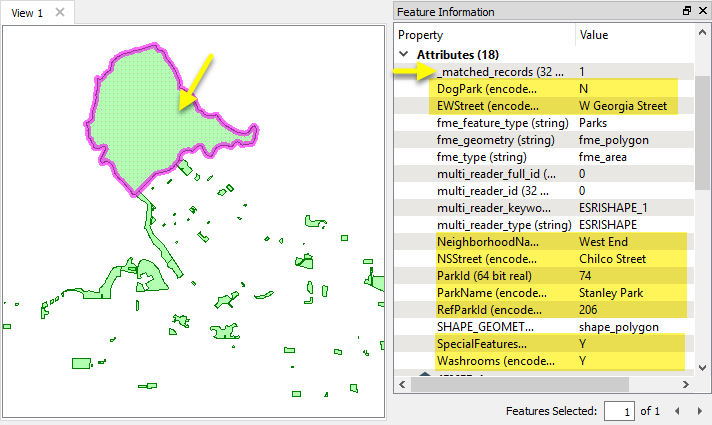
The output features from the Joined port now have additional attributes that were retrieved from the external database table. Note that the _matched_records attribute shows how many matches were encountered - in the case, one.
Many transformers can perform data joining based on matching attributes, expressions and/or geometry. When choosing one for a specific joining task, considerations include the complexity of the join, data format, indexing, conflict handling, and desired results. Some transformers use SQL syntax, and some access external databases directly. They may or may not support list attribute reading and creation.
Generally, choosing the one that is most specific to the task you need to accomplish will provide the optimal performance results. If there is more than one way to do it (which is frequently the case), time spent on performance testing alternate methods may be worthwhile. Performance may vary greatly depending on the existence of key indexes when reading external tables (as opposed to features already in the workspace).
|
Transformer |
Match By |
Uses SQL Statements |
Can Create List |
Input Type |
Notable |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FeatureJoiner | Attributes | No | No | Features |
|
Joins features by combining the attributes and/or geometry of features based on common key attribute values. Performs the equivalent of Inner, Left, and Full SQL joins. |
| FeatureMerger | Attributes | No | Yes | Features |
|
Merges the attributes and/or geometry of one set of features onto another set of features, based on matching key attribute values and expressions. |
| ListBasedFeatureMerger | List Attribute to Single Attribute | No | Yes | Features |
|
Merges the attributes and/or geometry of one set of features onto another set of features, based on matching list attribute values with key attribute values and expressions. |
| InlineQuerier | SQL query | Yes | No | Features |
|
Creates a set of SQLite database tables from incoming features, executes SQL queries against them, and outputs the results as features. |
| SQLCreator | SQL query | Yes | No | External DB |
|
Generates FME features from the results of a SQL query executed once against a database. One FME feature is created for each row of the results of the SQL query. |
| SQLExecutor | SQL query | Yes | No | External DB |
|
Executes SQL queries against a database. One query is issued to the database for each initiating feature that enters the transformer. Both the initiating features and the results of the query may be output as features. |
| DatabaseJoiner | Attributes | No | Yes | External DB and Features |
|
Joins attributes from an external table to features already in a workspace, based on a common key or keys. SQL knowledge not required. Non-blocking transformer. |
| Matcher | Geometry and/or Attributes | No | Yes | Features |
|
Detects features that are matches of each other. Features are declared to match when they have matching geometry, matching attribute values, or both. A list of attributes which must differ between the features may also be specified. If matching on attributes only (not geometry), using the FeatureMerger or another method will give better performance. |
Features to be joined with attributes from an external table.
Features that successfully matched.
Features that had no matches.
If Cardinality is set to Must Match Exactly One or Must Match Zero or One, then features that do not meet the criteria are rejected.
Rejected Feature Handling: can be set to either terminate the translation or continue running when it encounters a rejected feature. This setting is available both as a default FME option and as a workspace parameter.
The DatabaseJoiner is a very powerful transformer with many performance-related settings.
| Format | Select the format of the external dataset, or allow it to be guessed from the dataset selected. |
| Dataset or Connection | Select the dataset to be read. Depending upon the format, this may be a file, folder, or database connection. |
| Parameters | Access reader parameters specific to the chosen reader and dataset. |
| Table | Specify the table to join. Click the Browse button to select the table from a list. Note that you can only select this after you have completely specified the reader format, dataset, and format-specific parameters. | ||||||||
| Join On |
Select the attribute(s) from the incoming feature and their corresponding table field(s) that will be used to find matches. Matches are made when the values of all the attributes equal the values of their corresponding table fields. There is one row for each attribute and column pair in the table entry widget. You can add more pairs by clicking the plus (+) button located to the right of the table. Similarly, you can remove pairs by pressing the minus (-) button. A minimum of one pair must be specified for the join to work. Select attributes from a drop-down list in the Feature Attributes column. (You can type directly in the corresponding table fields or select from a list by clicking the Browse button.) For the Browse button to list available table fields, all the information needed to read from the table needs to be specified. Join Row Tools:
These tools may be used to Add, Delete, Cut, Copy, and Paste rows. |
||||||||
| Fields to Add |
Specify a list of fields from the matching table rows to join onto the incoming feature. To select the fields from a list, click the Browse button. A dialog showing the list of possible fields will appear. Place a check next to each field you wish to add, and click OK. If no fields are specified, all the fields from the matching rows will be added. |
||||||||
| Cardinality |
Indicate the type of relationship between the database rows and each feature. This will describe how many rows will match to each feature and what action the DatabaseJoiner will take if the expected number is not found. Choices include:
The Must Match rules are very strict. When in doubt, use Match First or Match All. |
||||||||
| Multiple Matches |
Specify how results of multiple matches will be given. Create a feature for each match: Each row matched is added to a copy of the incoming feature. In this scenario, for each feature in, there will be matched features out. If there are no matches, the feature exits the Unjoined output port. Add fields on a list attribute: Each row matched is added to a list attribute on the feature. If there are no matches, the feature exits the Unjoined output port. |
||||||||
| Joined List Name |
The name of the list attribute to append multiple matches. Note: List attributes are not accessible from the output schema in Workbench unless they are first processed using a transformer that operates on them, such as ListExploder or ListConcatenator. All list attribute transformers are displayed in the Contents pane of the Transformer Help under Lists. Alternatively, AttributeExposer can be used. |
| Accumulation Mode |
If Merge Joined is chosen, attributes from the feature and table will be merged, and in case of conflicts the value specified in the Conflict Resolution parameter will be used. If Prefix Joined is chosen, then all incoming attributes will be presented with a prefix set in the Prefix parameter. |
| Conflict Resolution |
This parameter is enabled when Accumulation Mode is set to Merge Joined. Use Original and Use Joined will give priority to original and incoming attributes respectively in case of attribute conflicts. |
| Prefix | The specified value is used as a prefix for incoming attributes when Accumulation Mode is Prefix Joined. |
Tip:
| Prefetch Query |
For Database formats only. For formats that support SQL, the DatabaseJoiner cache can be preloaded (that is, filled with a specific set of data before matching takes place) by issuing a prefetch query. This prefetch query can select an entire table or selected parts of a table most likely to be matched by the feature attributes. For example, a number of FME features of type "highways" require a database match. The database table (myrecords) has a field (record_type) with a number of values; road, highway, avenue, street. The FME features will only ever be matched to where record_type=highway so the overall join process would be much more efficient if the following prefetch was issued: SELECT * from myrecords where record_type = 'highway' Note: Unless the prefetch query is exhaustive, cache size limits apply. See Prefetch Exhaustive to learn what constitutes an exhaustive prefetch query |
| Prefetch Exhaustive |
For Database formats only. A prefetch query which is known to retrieve all possible matches is called an exhaustive query. In this case the database is never further consulted for a match. When a match cannot be found within the cached results of an exhaustive query, it is assumed that no match exists. If Prefetch Exhaustive is set to Yes, this indicates whether a prefetch is exhaustive (and the user doesn’t want to query the database any further). Even when it is set to No, however, any prefetch query is assumed to be exhaustive when it does not contain a WHERE clause, and is of the form: SELECT * from TableName Note: When FME considers a prefetch query to be exhaustive, the cache size limit will be ignored. This is because the cache must contain all results from the query. |
| Cache Size |
For Database formats only. Specify the number of rows to cache locally if you do not want to accept the default of 5000. You can optionally specify a SQL query to preload the cache. Note that cache size is ignored if the prefetch query is exhaustive. |
| Trim Key Fields |
Appears for character fields. Engaging trimming of key fields may significantly reduce performance and should only be done if key column values in the database are known to contain trailing spaces. It has no effect if an exhaustive prefetch query is used (see above for an explanation of Prefetch Exhaustive). Note: This parameter is included for backwards compatibility and most users will have no need to use it. The parameter can only be accessed using the pane of the Workbench. |
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters. There are a number of tools and shortcuts that can assist in constructing values, generally available from the drop-down context menu adjacent to the value field.
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
| A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. | |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Working with User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
No |
| Dependencies | Format-dependent - may require third-party drivers for some formats |
| FME Licensing Level | FME Base Edition and above |
| Aliases | Joiner |
| History | |
| Categories |
The FME Knowledge Center is the place for demos, how-tos, articles, FAQs, and more. Get answers to your questions, learn from other users, and suggest, vote, and comment on new features.
Search for all results about the DatabaseJoiner on the FME Knowledge Center.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver