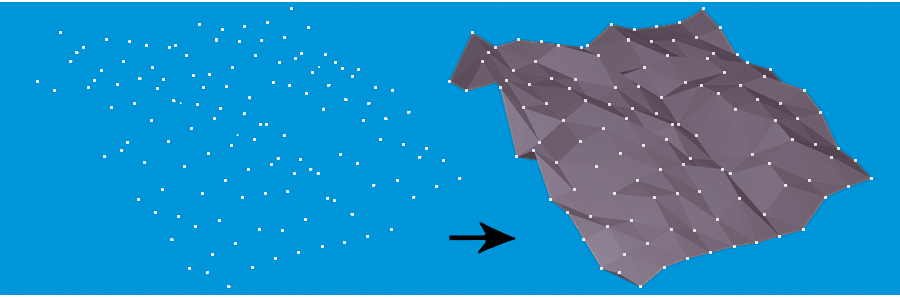
Constructs a Delaunay triangulation based on input points and breaklines. The surface model may be output in a number of representations: a triangulated irregular network (TIN), TIN vertices, TIN edges, and triangles.
SurfaceModel.vertex1_id and SurfaceModel.vertex2_id, which identify the vertices to which it is connected.| SurfaceModel.vertex1_id, SurfaceModel.vertex2_id, and SurfaceModel.vertex3_id | identify the vertices that define the triangle |
| SurfaceModel.slope | the slope of the plane defined by the triangle, in degrees, relative to the horizontal plane |
| SurfaceModel.percentageSlope | the slope expressed as ( rise / run ) * 100%, or equivalently tan( SurfaceModel.slope ) * 100% |
| SurfaceModel.aspect | the aspect angle, in degrees, measured by the angle between nx and ny, where nx and ny are are the x and y components of the normal vector of the triangle |
SurfaceModel.vertex_id which uniquely identifies the vertex.This parameter allows groups to be formed by attribute values. Zero or more attributes may be specified.
Input features with the same attribute values are placed into the same group. The transformer then operates independently on each group of input features.
If this parameter is left blank, the transformer will treat the entire set of input features as one group.
How parallel processing works with FME: see About Parallel Processing for detailed information.
This parameter determines whether or not the transformer should perform the work across parallel processes. If it is enabled, a process will be launched for each group specified by the Group By parameter.
| Parameter | Number of Processes |
|---|---|
| No Parallelism | 1 |
| Minimal | coresThe processor, or CPU, is the physical part of the computer that performs mathematical calculations. It is the most important part of a computer system. Traditional processors have only one core on the processor, meaning that at any given time, only one set of calculations is being performed. If a processor is dual-core, this means the single chip contains hardware for two processors, now called cores to distinguish them from the single chip, running simultaneously, side by side. (Source: http://www.ehow.com/facts_5730257_computer-core-processors_.html) / 2 |
| Moderate | exact number of cores |
| Aggressive | cores x 1.5 |
| Extreme | cores x 2 |
For example, on a quad-core machine, minimal parallelism will result in two simultaneous FME processes. Extreme parallelism on an 8-core machine would result in 16 simultaneous processes.
You can experiment with this feature and view the information in the Windows Task Manager and the Workbench Log window.
This parameter is used to determine which input points to add to the surface model as vertices. Specifying a value of 0 turns off vertex filtering.
Tip: A larger value will speed up surface model construction. The larger the value, the more input points will be filtered out. For input files with millions – or even billions – of points, it becomes essential to increase this value.
When a positive value for surface tolerance is specified, it works as follows. For each vertex that is being added to the model:

FME Professional edition and above
About Transformer Parameter Options
Search for samples and information about this transformer on FMEpedia.
Keywords: breakline morphology tessellate tessellation "surface model" TIN