Open topic with navigation
.NET Quick Start
Setting Up a .NET Project Using Visual Studio
- Start Visual Studio.
- Choose File > New Project.
In this example, we'll create a Visual C# project with the Console Application template and name it FMEServerAPIDemo.
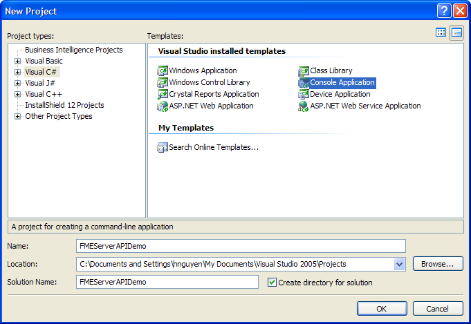
-
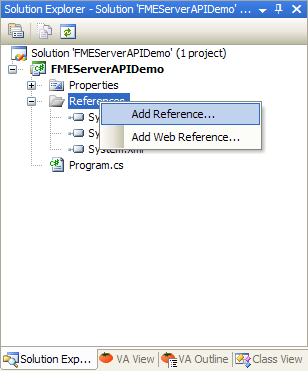
On the References folder in the Solution Explorer, click on Add Reference … to add a reference to the FME Server .NET API.
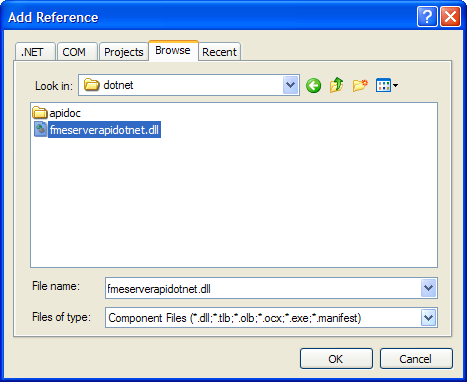
- The file name for the FME Server .NET API assembly is fmeserverdotnetapi.dll and is located at <FMEServerDir>\Server\sdk\dotnet\fmeserverapidotnet.dll. Browse to the location of the fmeserverapidotnet.dll and select it.
-
The namespace for the FME Server .NET API is Safe.FMEServer.API. Before developing your .NET application you may wish to import the types defined in the Safe.FMEServer.API namespace. In the C# language, the using keyword is for example used as follows:
using Safe.FMEServer.API;
Running the API Sample demo...
A sample command-line demo application illustrating the use of the FME Server API is available in C++, .Net,
and Java versions.
This demo can be used to ensure that everything has been setup properly, and contains code that may be useful
for your development process. (More in-depth coverage can be found in the later sections.)
If security is enabled for FME Server, your application must provide a client ID that has been registered
with FME Server. The client ID for the demo application is app_apidemo. By default,
the demo's client ID is not registered with FME Server, and you must register the client ID.
(See Resources for more information.)
The command-line application requires two parameters: the FME Server host and FME Server port.
Note: <fmeServerHost> represents the name of the host on which the FME Server is running.
<fmeServerPort> represents the TCP/IP port number the FME Server is listening on for requests. The default value is 7071 and this is usually correct for most FME Server installations.
The C# .NET source code was developed using Microsoft Visual Studio 2005 and is located in:
<FMEServerDir>\Server\sdk\samples\apidemo\dotnet\FMEServerAPIDemo.cs
...using the new project from the previous section
Add the source code to your project, and run.
...independently or with another IDE
Please reference the following file in your program:
<FMEServerDir>\Server\sdk\dotnet\fmeserverapidotnet.dll


