FME Flow: 2025.2
WebSocket Server
The FME Flow WebSocket Server allows fast, real-time communication with client web applications that execute on WebSocket-supported browsers.
You can communicate with the WebSocket Server in the following ways:
Notification Mode
WebSocket support is provided through Automations (preferred) and Notification Service publishers and subscribers. Use Notification Mode for WebSocket communication that is low-volume, or when your application requires added flexibility.
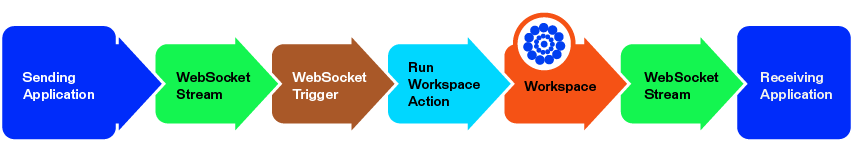
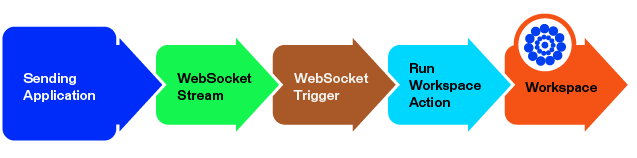
In the following example, a WebSocket trigger receives a named WebSocket stream, and sends it to a Run Workspace action, which runs an FME workspace equipped with a WebSocketConnector transformer.
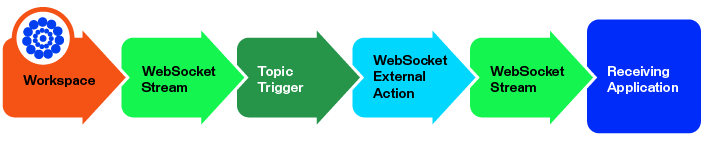
In this example, an FME workspace equipped with a WebSocketConnector transformer sends a named WebSocket stream to a FME Flow Topic trigger. A WebSocket external action receives the message stream from the topic and sends it to a WebSocket-supported client.
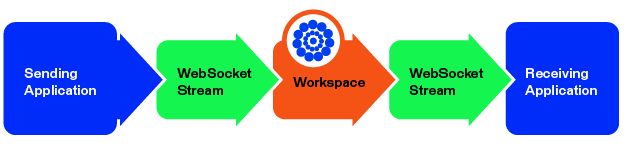
Message Streaming Mode
In message streaming mode, an FME workspace equipped with a WebSocketConnector transformer receives messages via the WebSocket Server, processes a job, and sends the resulting WebSocket message stream to a client, via the WebSocket Server. This mode works well when you can dedicate an FME Engine to running a workspace continuously, receiving and sending messages, until you explicitly cancel it.
Hybrid Mode
You can combine elements of Notification Mode and Message Streaming Mode, depending on your requirements. For example, you may want to use a WebSocket trigger to receive WebSocket message streams and send them to a Run Workspace action, while your FME workspace sends WebSocket message streams directly through the WebSocket Server. This design is useful when there are few requests, but you still want the server to respond without the overhead of polling from the client, or you do not want to dedicate a continuously running FME Engine to the job.