This is the version number of the LAS file to be written.
Different LAS versions have support for different components. See Fixed Components below.
Version 1.4 also adds support for having more than 4294967296 points in a file.
Version 1.4 (Legacy-Compatible) writes a 1.4 file that may be compatible with other applications that do not have full 1.4 support. This setting forces use of a "legacy" point format, a GeoTIFF-based coordinate system, and restricts the file to a maximum 4294967296 points.
This parameter enables or disables compression when writing an LAS file. There are two types of compression:
- LAZ (by LASzip) – The output file has an .laz extension
- zLAS (by Esri) – The output file has a .zlas extension (Windows only)
Compression significantly decreases file size; compressed files are often only 10-20% of the original size. However, compressed files take longer to read than uncompressed files.
Note that LAZ compression is currently not supported for some point formats when writing version 1.4 files. To enforce compression when writing a version 1.4 file, set the ASPRS LAS Version to 1.4 (Legacy-Compatible).
| Point Cloud Component | Data Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| x | Int32 | |
| y | Int32 | |
| z | Int32 | |
| intensity | UInt16 | |
| returns | UInt8 | |
| number_of_returns | UInt8 | |
| scan_direction | UInt8 | |
| flight_line_edge | UInt8 | |
| classification | UInt8 | |
| angle | Int8 | |
| file_marker | UInt8 | Allows for LAS flight-line based files to be combined into single files with more than one flight-line. Only supported in version 1.0. |
| user_data | UInt8 (version 1.0) or UInt16 (version 1.1+) | |
| point_source_id | UInt16 | Only supported in version 1.1+ |
| gps_time | Real64 | Only supported in version 1.1+ |
| color_red | UInt16 | Only supported in version 1.1+ |
| color_green | UInt16 | Only supported in version 1.1+ |
| color_blue | UInt16 | Only supported in version 1.1+ |
| classification_flags | UInt8 |
Indicates special characteristics associated with each point. This is a bit flag with the following values:
Only supported in version 1.4. |
| scanner_channel | UInt8 | Indicates the channel (scanner head) of a multi-channel system. Only supported in version 1.4. |
| nir | UInt16 | The NIR (near infrared) value. Only supported in version 1.4. |
LAS supports storing additional components (not part of the fixed component set) for each point through an "extra bytes" Variable Length Record. This parameter specifies a list of components that should be written for each point.
Note that the String data type is not supported for user components.
LAS supports "list" components with up to three elements. To write a list component, add the list suffix {} to the end of a component name. Note that each member of a list component must have the same data type.
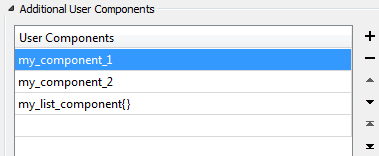
You can add, remove, or re-order the list to change the order in which the components are stored in the output dataset.
Spatial
Coordinate systems may be extracted from input feature data sources, may come predefined with FME, or may be user-defined. FME allows different output and input coordinate systems, and performs the required coordinate conversions when necessary.
If a coordinate system is specified in both the source format and the workspace, the coordinate system in the workspace is used. The coordinate system specified in the source format is not used, and a warning is logged. If a source coordinate system is not specified in the workspace and the format or system does not store coordinate system information, then the coordinate system is not set for the features that are read.
If a destination coordinate system is set and the feature has been tagged with a coordinate system, then a coordinate system conversion is performed to put the feature into the destination system. This happens right before the feature enters into the writer.
If the destination coordinate system was not set, then the features are written out in their original coordinate system.
If a destination coordinate system is set, but the source coordinate system was not specified in the workspace or stored in the source format, then no conversion is performed. The features are simply tagged with the output system name before being written to the output dataset.
For systems that know their coordinate system, the Coordinate System field will display Read from Source and FME will read the coordinate system from the source dataset. For most other input sources, the field will display Unknown (which simply means that FME will use default values). In most cases, the default value is all you'll need to perform the translation.
You can always choose to override the defaults and choose a new coordinate system. Select More Coordinate Systems from the drop-down menu to open the Coordinate System Gallery.
Changing a Reprojection
To perform a reprojection, FME typically uses the CS-MAP reprojection engine, which includes definitions for thousands of coordinate systems, with a large variety of projections, datums, ellipsoids, and units. However, GIS applications have slightly different algorithms for reprojecting data between different coordinate systems. To ensure that the data FME writes matches exactly to your existing data, you can use the reprojection engine from a different application.
To change the reprojection engine, Select Workspace Parameters > Spatial > Reprojection Engine. In the example shown, you can select Esri (but the selection here depends on your installed applications):
- The coordinate systems file coordsys.db in the FME installation folder contains the names and descriptions of all predefined coordinate systems.
- Some users may wish to use coordinate systems that do not ship with FME, and in those cases, FME also supports custom coordinate systems.
- Learn more about Working with Coordinate Systems in FME.
Advanced
LAS Dataset File
You must install and license both ArcGIS 10.1 (or newer) and the 3D Analyst extension.
Identifies the name of the Esri ArcGIS LAS dataset file to create. If specified, the writer will produce one .lasd file that references all the LAS files created by the FME LAS writer during the translation.
An .lasd file is required to work with LAS files in the Esri ArcGIS environment. By default, the .lasd file will be written to the same folder as the .las files to which it refers. To write the .lasd to a different folder, use a fully qualified path.
When an ArcGIS LAS Dataset is written, this parameter determines whether to calculate statistics for the LAS files referenced by the ArcGIS LAS Dataset.
zLAS Parameters
This parameter specifies whether to rearrange point records when applying zLAS compression.
When set to Yes, points are re-ordered to optimize data access and minimize file I/O. This is beneficial when using the compressed LAS data directly.
When applying zLAS compression, the optimizer builds a spatial index to make direct use of the compressed data more efficient. In order to do this, the average point spacing of the data is needed.
This option specifies where that data should be found.
- Scan Points – Scan through point data to calculate an accurate spacing
- From Header – Estimate the spacing based on the extents and number of points. This may be faster but less accurate than Scan Points.
- Specify Value – Explicitly specify the spacing value. Enables the zLAS Point Spacing Value parameter.
This parameter specifies the point spacing for zLAS compression. This is only used when zLAS Point Spacing Source is set to Specify Value.