|
Database formats include a Database Connection parameter that defines and stores authentication information. For general information about sharing database connections, please see Using Database Connections. Note that Database Connection parameters differ slightly, depending on context and/or database format. |
|
Connection From the Connection parameter in a database format, you can do one of the following:
|
Connection Parameters
The connection string for the database to which you are connecting. The precise format depends on the JDBC driver being used, but a connection string will always start with:
jdbc:<subprotocol>:
See the FME Community for information about the compatibility of various JDBC drivers with FME, and to view FME Workbench examples.
If not specified in the JDBC Connection String, enter the username and password to access the database.
In most cases, this parameter is not required for well-behaved JDBC 4.0+ drivers. However, in order for the connection string to be processed only by the desired driver, we recommend specifying the name of the Java class of the desired driver.
This parameter is required for drivers that do not self-register.
Yes – Connection strings and properties for database connections are masked in translation and error logs. Connection details may contain sensitive information, such as passwords. A masked connection string appears as:
jdbc:<subprotocol>:************
While masked connection properties appear as:
{<property_name1>=************, <property_name2>=************, ...}
Warning Connection strings for connections whose parameters are embedded in the workspace are not masked, regardless of this setting.
No – Connection strings and properties are logged in plain text.
Advanced
The number of features that FME places in each transaction before a transaction is committed to the database.
If the parameter is set to 0, then the entire write operation occurs in a single transaction.
Default: 1000
This parameter defines the time, in seconds, after which a query will be terminated if it has not yet returned a result.
If set to 0, there is no timeout. The default is 30.
This parameter defines how many times in succession will FME attempt to recover from a dropped connection.
- If set to 0: If a connection is dropped, the writer will fail the translation.
- If set to 1 or more: If a connection is dropped, the writer will make n attempts to reconnect. (The default is 0.) The writer will also keep a cache of features that have not yet been committed. After recovering from a dropped connection, the writer will continue writing from its cache, so that no features are dropped along with the connection. Due to the extra step in writing to the cache, overall writing speeds may be slower in this mode.
The counter for reconnection attempts is reset when a connection is successfully recovered.
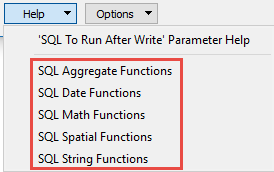
This parameter allows for the execution of SQL statements before writing to a table. For example, it may be necessary to clean up a table before attempting to write to it. The statements will be executed only when the first feature arrives at the writer.
For detailed information about SQL functions, click the corresponding menu item in the .
 to open the editor.
to open the editor.Available menu options depend on the format.
Multiple SQL commands can be delimited by a character specified using the FME_SQL_DELIMITER directive, embedded at the beginning of the SQL block. The single character following this directive will be used to split the SQL block into SQL statements, which will then be sent to the database for execution. Note: Include a space before the character.
For example:
FME_SQL_DELIMITER ; DELETE FROM instructors ; DELETE FROM people WHERE LastName='Doe' AND FirstName='John'
Multiple delimiters are not allowed and the delimiter character will be stripped before being sent to the database.
Any errors occurring during the execution of these SQL statements will normally terminate the reader or writer (depending on where the SQL statement is executed) with an error. If the specified statement is preceded by a hyphen (“-”), such errors are ignored.
This parameter allows for the execution of SQL statements after a set of tables has been written. For example, it may be necessary to clean up a temporary view after creating it.
For detailed information about SQL functions, click the corresponding menu item in the .
 to open the editor.
to open the editor.Available menu options depend on the format.
Multiple SQL commands can be delimited by a character specified using the FME_SQL_DELIMITER directive, embedded at the beginning of the SQL block. The single character following this directive will be used to split the SQL block into SQL statements, which will then be sent to the database for execution. Note: Include a space before the character.
For example:
FME_SQL_DELIMITER ; DELETE FROM instructors ; DELETE FROM people WHERE LastName='Doe' AND FirstName='John'
Multiple delimiters are not allowed and the delimiter character will be stripped before being sent to the database.
Any errors occurring during the execution of these SQL statements will normally terminate the reader or writer (depending on where the SQL statement is executed) with an error. If the specified statement is preceded by a hyphen (“-”), such errors are ignored.