FME Transformers: 2025.1
Slices geometry along a specified plane.
Typical Uses
- Slicing solids, surfaces, and other 3D geometry with a plane.
How does it work?
The 3DSlicer accepts features with any geometry type and splits them along a specified 3D plane.
Both 3D and 2D geometries are accepted, including points clouds and aggregates. 2D features are handled as 3D with a Z coordinate of zero (0). Aggregates are treated as single objects.
Output features are identified as being on the front or back side of the slicing plane, and are flagged as having been sliced or not. Front and back are relative to the plane, with front being in the direction of the plane's normal vector and back being the inverse. Features that are entirely coincident with the plane are considered to be on the front side.
The slicing plane is defined by:
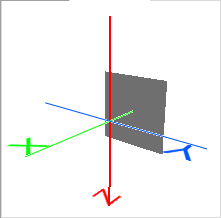
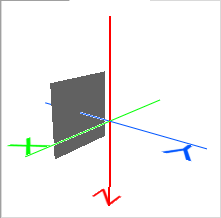
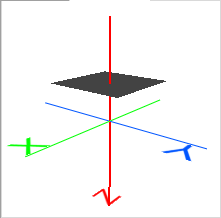
- Fixed X, Fixed Y, or Fixed Z: Specifying a single axis point in ground units. The normal vector of the plane (determining front and back) is in the positive direction along the fixed axis.
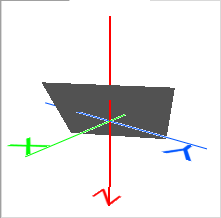
- Point and Normal: Specifying a single 3D point on the slicing plane and another point defining the direction of the normal vector from that point.
|
Plane Type |
Orientation |
|---|---|
|
Fixed X
|
|
|
Fixed Y
|
|
|
Fixed Z
|
|
|
Point and Normal Variable orientation |
|
Usage Notes
- Only 3D plane geometry may be used to slice.
Configuration
Input Ports
Features with valid geometry to be sliced.
Output Ports
Features sliced as specified in parameters. Unsliced features are output with geometry unchanged.
Features with invalid or otherwise non-sliceable geometry are output here, as are any features that receive non-numeric values for any numeric parameters.
Rejected features will have an fme_rejection_code attribute with one of the following values:
INVALID_PARAMETER_PLANE_SPECIFICATION
INVALID_GEOMETRY_VERTICES
INVALID_GEOMETRY_NOT_FINITE
INVALID_GEOMETRY_NONSPATIAL
INVALID_GEOMETRY
INVALID_GEOMETRY_UNPROCESSABLE_CURVE
INVALID_GEOMETRY_UNPROCESSABLE_AREA
INVALID_GEOMETRY_UNPROCESSABLE_SURFACE
INVALID_GEOMETRY_UNPROCESSABLE_SOLID
Rejected Feature Handling: can be set to either terminate the translation or continue running when it encounters a rejected feature. This setting is available both as a default FME option and as a workspace parameter.
Parameters
|
Plane Type |
Select a plane definition mode:
|
||||
|
Fixed Value |
When Plane Type is Fixed X, Fixed Y, or Fixed Z, specify the plane position along the selected axis in ground units. |
||||
|
Custom Plane |
When Plane Type is Point and Normal, specify the following coordinates:
|
|
Plane Side Indicator |
Name the attribute to contain the sidedness of the output geometry relative to the slicing plane. Possible values are:
|
|
Sliced Indicator |
Name the attribute to contain the slicing status of output geometry. Possible values are:
|
Editing Transformer Parameters
Transformer parameters can be set by directly entering values, using expressions, or referencing other elements in the workspace such as attribute values or user parameters. Various editors and context menus are available to assist. To see what is available, click  beside the applicable parameter.
beside the applicable parameter.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more.
When setting values - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors - strings and expressions containing String, Math, Date/Time or FME Feature Functions will have those functions evaluated. Therefore, the names of these functions (in the form @<function_name>) should not be used as literal string values.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
|
Special Characters |
A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| Date/Time Functions | Date and time functions are available in the Text Editor. |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Creating and Modifying User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Table Tools
Transformers with table-style parameters have additional tools for populating and manipulating values.
|
Row Reordering
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
|
|
Cut, Copy, and Paste
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
Cut, copy, and paste may be used within a transformer, or between transformers. |
|
Filter
|
Start typing a string, and the matrix will only display rows matching those characters. Searches all columns. This only affects the display of attributes within the transformer - it does not alter which attributes are output. |
|
Import
|
Import populates the table with a set of new attributes read from a dataset. Specific application varies between transformers. |
|
Reset/Refresh
|
Generally resets the table to its initial state, and may provide additional options to remove invalid entries. Behavior varies between transformers. |
Note: Not all tools are available in all transformers.
For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
No |
| Dependencies | None |
| Aliases | |
| History |
FME Community
The FME Community has a wealth of FME knowledge with over 20,000 active members worldwide. Get help with FME, share knowledge, and connect with users globally.
Search for all results about the 3DSlicer on the FME Community.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver, Open Government Licence - British Columbia, and/or Open Government Licence – Canada.