FME Transformers: 2025.0
Accesses a URL via HTTP or HTTPS, using a variety of HTTP methods.
Available methods include:
HEAD
GET
PUT
POST
DELETE
OPTIONS
PATCH
COPY
LOCK
MKCOL
MOVE
PROPFIND
PROPPATCH
UNLOCK
CHECKOUT
CHECKIN
UNCHECKOUT
LINK
UNLINK
Examples
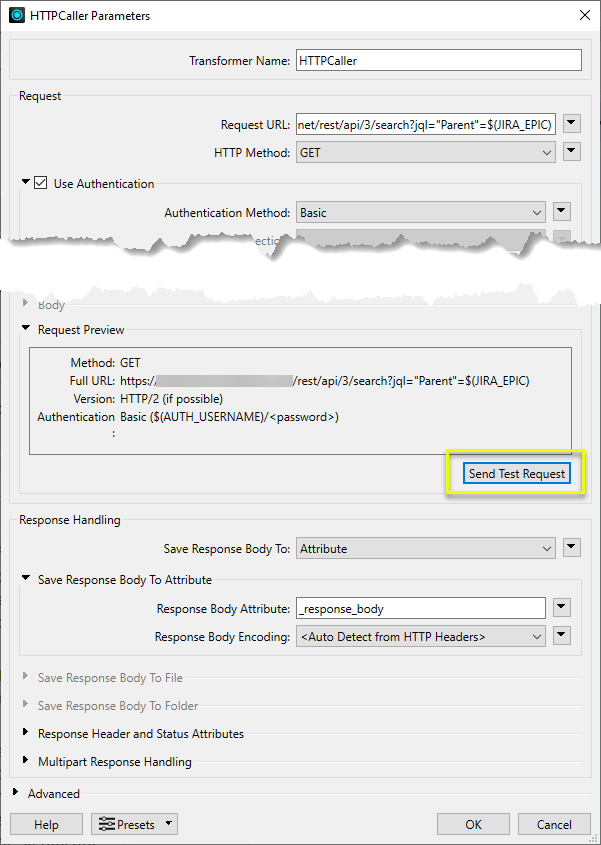
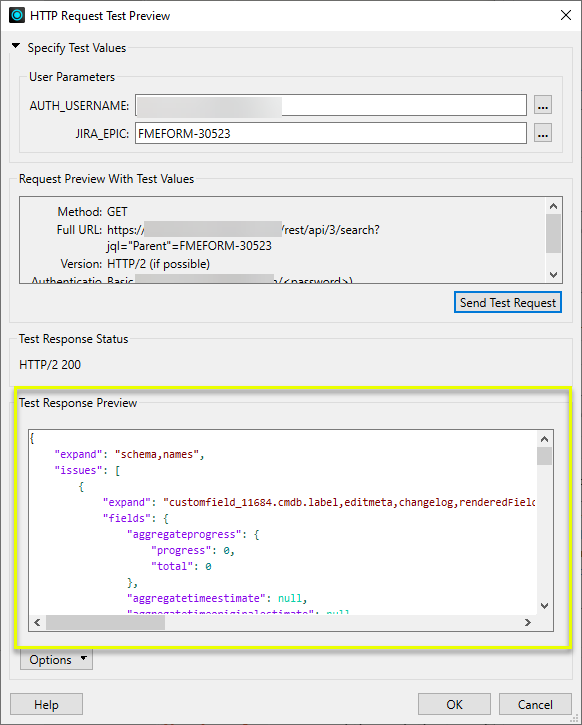
In this example, we are configuring an HTTPCaller to access Jira using the GET method.
To test the configuration, we use Send Test Request.
In the Test Request dialog, note that the user parameters used for configuration are available and populated. To test the configuration, use Send Test Request.
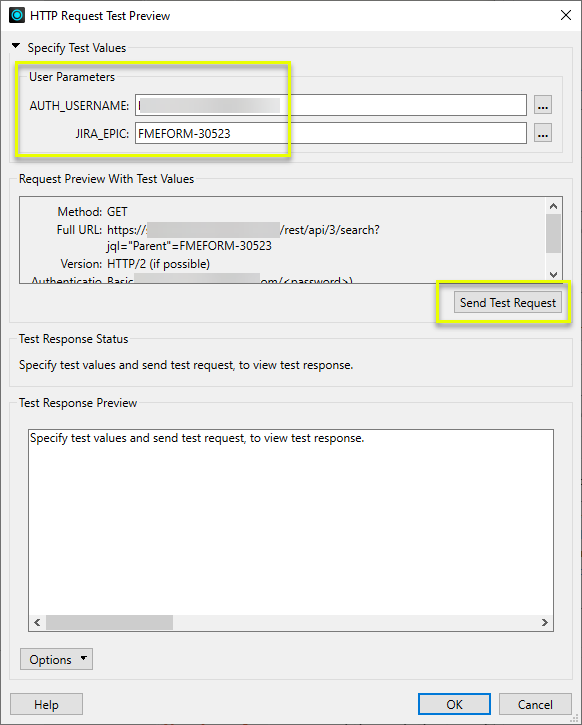
The returned results are presented in Test Response Preview.
Further testing can be done by changing the user parameter values, but these values are for testing only and will not be applied as actual values in the workspace.
Clicking OK will save the current response and any user parameter values for future reference.
Configuration
Input Ports
This transformer accepts any feature.
Output Ports
The HTTP response body may be saved to an attribute, or a file. By default the body is saved to the attribute identified by the Response Body Attribute parameter.
The HTTP response status code will be stored in the attribute named by the Status Code Attribute parameter. By default this is the _http_status_code attribute. For more information on HTTP Status Codes, please refer to https://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec10.html.
In addition, the HTTP response headers will be saved in the list attribute specified by the Multipart Header List Attribute parameter. By default the headers are stored in the _headers{} list attribute. For a list of common HTTP response headers, please refer to https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_HTTP_header_fields.
If an error occurs while accessing the URL, the feature will be output via the <Rejected> port. In addition, an error message will be set in the attribute named by the Error Attribute parameter.
Rejected Feature Handling: can be set to either terminate the translation or continue running when it encounters a rejected feature. This setting is available both as a default FME option and as a workspace parameter.
Parameters
|
Request URL |
This parameter identifies the URL which will be accessed by the transformer. The transformer can access http and https URLs. The URL can be entered directly in the transformer, or be built up from attribute values. |
||||||||||||||||
|
HTTP Method |
Select an HTTP method to access the server. Most requests will use the GET method. Requests that upload data will typically use the PUT, POST or PATCH method, although an upload body can also be provided with the DELETE method. The HEAD, DELETE, and OPTIONS methods can be useful when accessing a REST API. Additional methods are available. |
||||||||||||||||
|
Use Authentication |
If enabled, provide authentication details as needed.
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Query String Parameters |
This table can be used to create additional URL query parameters. The parameters will be appended to the URL given in the Request URL parameter. This can be useful when accessing a REST API endpoint which requires many parameters. The parameter names and values can be entered directly or constructed from attribute values. |
||||||||||||||||
|
Headers |
This table can be used to create custom HTTP headers which will be sent along with the request. This can be used to customize the request that FME will make to the server. Header names and values can be entered directly or constructed from attribute values. In addition, the Name column provides a list of commonly used header names. |
||||||||||||||||
|
Body |
These parameters are only enabled when HTTP Method is PUT, POST, DELETE, or PATCH. An upload body is not required; for example, DELETE requests often have no upload body.
|
|
Save Response Body To |
This parameter allows users to set the destination for the HTTP response body. The body may be saved to an attribute, to a file specified by the user, or to a new file in a directory specified by the user. Note If you are downloading a very large response body with the HTTPCaller, it is recommended that you save it to a file. This avoids creating a large attribute on the feature.
|
||||||
|
Save Response Body To Attribute |
When this option is selected, each HTTP response body will be saved to an attribute of the feature which made the request. The following parameters are enabled for this option.
|
||||||
|
Save Response Body To File |
When this option is selected, each HTTP response will be saved to a file. The following parameters are enabled for this option.
|
||||||
|
Save Response Body To Folder |
When this option is selected, the HTTPCaller will create a new file for each feature that is processed.
|
||||||
|
Response Header and Status Attributes |
|
||||||
|
Multipart Response Handling |
It is rare, but possible for an HTTP server to return a multipart response. That is, a single HTTP request will result in an HTTP response which contains several different parts. A multipart response will have a Content-Type header which begins with "multipart", such as "multipart/mixed". The HTTPCaller has the Feature Output option to split such responses into multiple features. Because multipart responses are very rare, the default behavior is to not split multipart responses into multiple features. These parameters are only enabled when response bodies are being saved to attributes, or to a folder.
|
|
Concurrent Requests |
|
||||||||||
|
Retry Failed Requests |
When enabled, the HTTPCaller will attempt to retry requests which have failed, or have returned an HTTP error.
|
||||||||||
|
Rate Limiting |
|
||||||||||
|
HTTP Client Options |
|||||||||||
|
HTTPS Client Certificate
|
In a typical HTTPS connection, the server provides a certificate which is authenticated by the client. This ensures that the connection is secure. It is also possible for the client to authenticate themselves to the server via a certificate, called a client certificate. This is called “Mutual TLS” and it allows the server to only accept connections from clients with a valid certificate. This type of authentication is rare, typically only used when advanced security is required. When using a client certificate, a private key is also required.
|
||||||||||
|
Advanced Security |
|
Editing Transformer Parameters
Transformer parameters can be set by directly entering values, using expressions, or referencing other elements in the workspace such as attribute values or user parameters. Various editors and context menus are available to assist. To see what is available, click  beside the applicable parameter.
beside the applicable parameter.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more.
When setting values - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors - strings and expressions containing String, Math, Date/Time or FME Feature Functions will have those functions evaluated. Therefore, the names of these functions (in the form @<function_name>) should not be used as literal string values.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
|
Special Characters |
A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| Date/Time Functions | Date and time functions are available in the Text Editor. |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Creating and Modifying User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Table Tools
Transformers with table-style parameters have additional tools for populating and manipulating values.
|
Row Reordering
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
|
|
Cut, Copy, and Paste
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
Cut, copy, and paste may be used within a transformer, or between transformers. |
|
Filter
|
Start typing a string, and the matrix will only display rows matching those characters. Searches all columns. This only affects the display of attributes within the transformer - it does not alter which attributes are output. |
|
Import
|
Import populates the table with a set of new attributes read from a dataset. Specific application varies between transformers. |
|
Reset/Refresh
|
Generally resets the table to its initial state, and may provide additional options to remove invalid entries. Behavior varies between transformers. |
Note: Not all tools are available in all transformers.
For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
No |
| Dependencies | None |
| Aliases | HTTPDeleter HTTPFetcher HTTPFileUploader HTTPHeader HTTPMultipartUploader HTTPUploader |
| History |
|
FME Community
The FME Community has a wealth of FME knowledge with over 20,000 active members worldwide. Get help with FME, share knowledge, and connect with users globally.
Search for all results about the HTTPCaller on the FME Community.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver, Open Government Licence - British Columbia, and/or Open Government Licence – Canada.