|
FME Format Type Identifier |
GIFRASTER |
|
Reader/Writer |
Both |
|
Raster/Vector |
Raster |
|
Typical File Extensions |
.gif |
GIF (Graphics Interchange Format) is an image format that supports a palette of up to 256 colors in the form of RGB 24-bit, as well as grey 1-byte continuous images.
The format was introduced by CompuServe in 1987 and has grown to be one of the dominant internet image formats.
GIF Product and System Requirements
|
Format |
FME Platform |
Operating System |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Reader/Writer |
FME Form |
FME Flow |
FME Flow Hosted |
Windows 64-bit |
Linux |
Mac |
|
Reader |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
|
Writer |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Yes |
Reader Overview
FME considers a single GIF file to be a dataset. The GIF file contains pixel data, and each pixel in the file is a point in a single FME raster feature.
Writer Overview
The writer creates a single image and draws points, lines, and polygons into it. The file name, window, size, background, color table, transparency, and interlacing of the output image are all determined in the workspace. Each feature written to the image contains special attributes used to determine the appearance of the feature.
Feature types are color entries. The color table entries are defined in the Feature Type dialog:
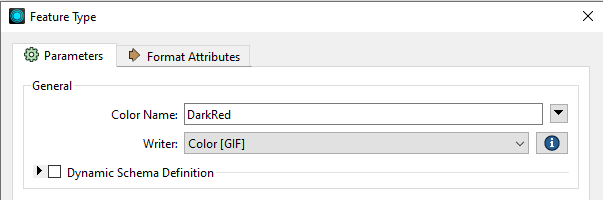
All features with the specified color name are drawn in that color.
FME Raster Features
FME raster features represent raster data and use several concepts that are unlike those used in the handling of vector data.
For comprehensive information about how FME processes raster data, see Rasters.
GIF files can only be written with square pixel dimensions.
GIF only supports rasters with a single UInt8 band that has a RGB24 palette.