Document
If specified, limits the reader to specific pages and/or page ranges in the PDF document. Separate multiple page ranges and page numbers with commas. For example: 1-2,4.
If checked, specify the Password required to open the PDF document.
Spatial
Spatial group parameters are related to reading Content Objects. These Content Objects are vector drawings, raster images, and text features that each have a particular location within a PDF page. (This is in contrast to the Non-Spatial group parameters, which relate to features that make up entire pages, or that do not have a location within a page.)
Controls whether to read raster image content objects.
- Yes (default): The reader will produce image objects as raster features.
- No: Image objects will be skipped.
Controls how to read text content objects. It is distinct from Non-Spatial Text, which controls whether to read entire pages of text as features.
- Feature Per Block (default): The reader will produce one text feature per block of text as defined within the PDF document. This may include as little as one character, or entire paragraphs of text.
- Feature Per Character (Text): The reader will produce one text feature per character.
- Feature Per Character (Vector): The reader will produce one vector feature per character by stroking the text character.
- Ignore: Text objects will be skipped.
Controls whether the to read vector drawing content objects.
- Yes (default): The reader will produce vector drawing objects as features with 2D vector geometry.
- No: Vector drawing objects will be skipped.
Controls which coordinate units the reader should use for feature geometry.
- Geospatial (if possible) (default): For content objects within a geospatial map frame, the reader will produce features with geospatial coordinates and coordinate system. If no map frames exists, or if a content object is not within any map frame, then features will be produced with coordinate in page points.
- Page Points: Feature geometry will use page points (1/72 of an inch on the page) for coordinate values.
Advanced
Controls whether the reader should attempt to make donut geometry from sets of related polygon geometries.
- Yes (default): Features with multipolygon geometry will be converted to donut geometry where applicable.
- No: Features with multipolygon geometry will be produced as-is.
Controls how the reader should convert Bezier curves to line geometries.
- Flatness (default): Bezier curves will be converted to lines with enough points such that the distance between the line segments and the actual curve does not exceed 0.25 page points.
- Number of Points: Bezier curves will be converted to lines with exactly N points, where N is the value of the Interpolated Points Per Bezier Curve parameter.
Controls how many points the reader should use to stroke Bezier curves. It is only relevant when the Bezier Interpolation Mode has the value Number of Points.
The value of this parameter must be greater than or equal to 2.
Non-Spatial
Non-Spatial group parameters are related to features that make up entire pages, or that do not have a location within a page. (This is in contrast to the Spatial group parameters, which relate to Content Objects such as vector drawings, raster images, and text.)
Controls which metadata objects the reader should produce:
- Document Info: The reader will produce a feature that contains information about the entire PDF document. This may include attributes such as the creation time of the document, the authoring software, or the document title.
- Pages: The reader will produce one feature per page of the document, with attributes describing the dimensions of the page.
- Map Frames: The reader will produce one feature per map frame in the document. A map frame is a region of a page that is associated with some unit of measurement, and may be associated with a geospatial location.
Controls whether to read the text of each page as a feature.
- Yes: The reader will concatenate all text within each page as a text feature.
- No (default): The reader will not read text-pages.
Controls whether to read each Tagged Table as a feature type, and each table row as a feature. A Tagged Table is a PDF table that has been created with software that embeds metadata about which text objects are within the table, in a similar way to an HTML table. Microsoft Excel for Windows is an example of a program that may create tagged tables when converting to PDF.
- Yes: The reader will read each tagged table row as a feature.
- No (default): The reader will not read tagged tables.
Controls whether to render an image of each page and produce it as a raster feature.
- Yes: The reader will render will each page as a raster feature.
- No (default): The reader will not read rasterized-pages.
Raster Size
Controls how the reader should determine the size of the raster when rasterizing pages.
- Scale (default): Raster size will be determined with the Pixels Per Point parameter.
- Custom: Raster size will be determined with the Raster Height and Raster Width parameters.
Controls the number of pixels for each page point when rasterizing PDF pages. It is only relevant when the Raster Size Mode is Scale.
For example, If a page is 400 points in width and 600 points in height, then a Pixels Per Point value of 0.25 would produce a raster with 100 columns and 150 rows. This might be useful for creating a thumbnail.
Controls the number of rows in rendered rasters when rasterizing PDF pages. It is only relevant when the Raster Size Mode is Custom.
Controls the number of columns in rendered rasters when rasterizing PDF pages. It is only relevant when the Raster Size Mode is Custom.
Use this parameter to expose Format Attributes in FME Workbench when you create a workspace:
- In a dynamic scenario, it means these attributes can be passed to the output dataset at runtime.
- In a non-dynamic scenario, this parameter allows you to expose additional attributes on multiple feature types. Click the browse button to view the available format attributes (which are different for each format) for the reader.
A search envelope (also known as a bounding box) is a rectangular area that defines a geographic area. In FME, the easiest way to define a search envelope is to use search envelope parameters.
Defining a search envelope is the most efficient method of selecting an area of interest because FME will read only the data that is necessary – it does not have to read an entire dataset. Search Envelope parameters apply to both vector and raster datasets and can be particularly efficient if the source format has a spatial index.
Most FME readers have parameters to define the search envelope of data that is being read:
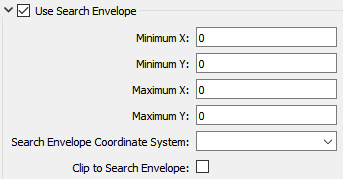
The parameters include the x and y coordinates of the bounding box as well as a parameter that defines the coordinate system.
How to Define the Bounding Box
Using the minimum and maximum x and y parameters, define a bounding box that will be used to filter the input features. Only features that intersect with the bounding box are returned. Note that the bounding box intersection is not a full geometry intersection (based on spatial relationships) that would be returned by a transformer like the SpatialFilter.
Search Envelope Coordinate System
Specifies the coordinate system of the search envelope if it is different than the coordinate system of the data. The coordinate system associated with the data to be read must always be set if this parameter is set.
If this parameter is set, the minimum and maximum points of the search envelope are reprojected from the Search Envelope Coordinate System to the reader’s coordinate system prior to applying the envelope.
The underlying function for Use Search Envelope is an intersection; however, when Clip to Search Envelope is checked, a clipping operation is also performed.
- When checked (set to Yes), this option instructs FME to clip features to the exact envelope boundary. FME removes any portions of imported features being read that are outside the search envelope.
- When left unchecked (set to No), features that overlap the boundary will be included in their full (unclipped) form.
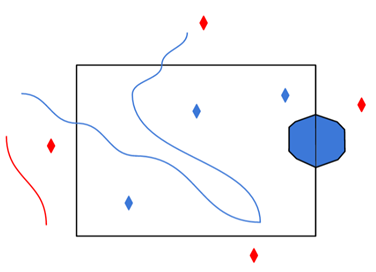
|
Clip to Search Envelope: No |
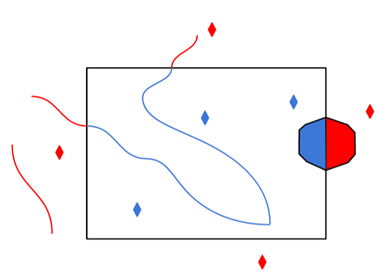
Clip to Search Envelope: Yes |
|---|---|
|
Any features that cross the search envelope boundary will be read, including the portion that lies outside of the boundary.
|
Any features that cross the search envelope boundary will be clipped at the boundary, and only the portion that lies inside the boundary will be read.
|
|
The search envelope includes the bounding box and the extent of the raster.
|
The search envelope includes only the area within the bounding box. The raster size will still match the bounding box, but the area without data will be filled with Nodata values to represent the absence of data, if the source raster has them. Raster Nodata may be a single value across all bands, a single value per band, or a separate alpha or transparency band that indicates the lack of data values (this is more common in images than other types of rasters).
|