Creating a Custom Format
There are two ways to start:
- Export as a Custom Format.
- Use the Custom Format wizard.
Note: FME Hub contains a library of custom formats that are available either for free or licensed purchase. Some FME Hub formats are included with an FME installation, and can be accessed from the Readers and Writers Gallery. However, FME Hub is always updated as new formats are added, so we recommend checking back periodically to see what's new.
Exporting as a Custom Format
Using the Custom Format Wizard
To initiate the Custom Format wizard, select Tools > Browse Readers and Writers, and click the New button in the Custom Formats area at the bottom of the Gallery window.
The Custom Format wizard will guide you through the following steps:
Select the Source Format
Select the format of the source data.
Locate Source Data
Locate the source data from which you want the Custom Format to read. The source data will supply the schema in the custom format. The resulting custom format can later be applied to any datasets in the original format.
Note: If the custom format will be merging data from multiple formats, pick one format here. Once you create the Custom Format, you can use FME Workbench to Edit the Custom Format and add additional readers.
If the source format has specific default parameters that you want to change, you can edit them here by clicking the Parameters button. For help with Parameters, click the Help button in the parameter box.
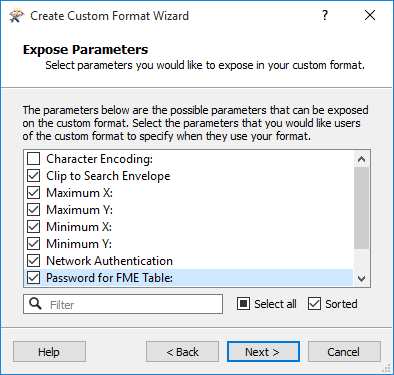
Expose Parameters
This list contains the possible parameters (depending on the selected format) that can be exposed on the custom format. Select the parameters that you would like users to specify when they use the format. For example, there may be parameters that are likely to change from workspace to workspace.
The parameters listed here will depend on your source data, and the ones you select will determine which parameters will be shown when you use the format in a translation.
Name the Custom Format
Enter a short name and a description for the new format. When the format is saved to the Reader and Writer Gallery, the short name appears in the Short Name column, and the description appears in the Name column.
Note: You can use only ASCII characters in Short Names.
Create the Custom Format
Click Finish. Another instance of FME Workbench will start, displaying the custom format's feature types on the canvas. The FME Workbench title bar displays the default filename and file location. Like a regular workspace, you can do the following:
- Include transformers
- Edit feature types
- Merge feature types
- Fanout feature types
- Add additional readers
- Add destination feature types
- Set format parameters
The only visible difference between a Custom Format and a Workspace is that there is no destination dataset. You can, however, add destination feature type definitions, which become the source schema for the custom format.
Save the Format
Select File > Save. The custom format will be added to the Reader and Writer Gallery. All custom formats in the gallery are preceded by a custom format icon, to distinguish them from standard FME-supported formats:

FME will automatically assign a default .fds file extension. The new
format will be stored, by default, in Documents\FME\Formats. This custom format can later be applied to any datasets in the original format.
Editing a Custom Format
From the Reader and Writer Gallery, choose the format, then click the Custom Formats > Edit button.
Deleting a Custom Format
From the Reader and Writer Gallery, choose the format, then click the Custom Formats > Delete button.
Pre-installed Custom Formats
An FME installation includes a number of readers that are implemented as custom formats. Like custom formats you create, they are identified with a custom format icon in the Reader and Writer Gallery. However, FME custom formats cannot be edited or deleted. You can identify an FME custom format by the disabled Edit and Delete buttons in the Custom Formats area.