Smooths lines derived from line segments, points or raster data, and replaces a series of line segments with the optimal combination of straight lines and embedded arc segments required to create smooth curving lines.
This process provides a truer representation of real-world features and can reduce file sizes by up to 80%.
Using the Curvefitter, you can:
- Compress file sizes
- Smooth jagged polylines
- Process adjacent area features
- Restore arcs in legacy data
- Automatically process data
In addition to processing simple line features, Curvefitter preserves feature topology when smoothing boundaries of adjacent area features.
Before the advent of enhanced geometry, FME was forced to stroke arcs into line sections to be able to process that data. Many other GIS packages that did not support arcs also ended up forcing the stroking of arcs, the net results being a great amount of data that could be represented by arcs but isn't. The Curvefitter transformer will allow a user to replace such stroked line segments with true mathematical arc segments. It will likewise permit the replacement of surveyed line features with an arc representation.
Example: Parcel Data
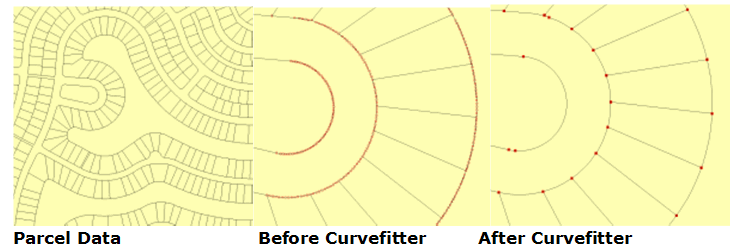
Procedure
A subset 6.1 MB Esri shapefile (provided by Grays Harbor County, in Washington State) was extracted and converted into four different formats: DWG file (3.8 MB), MapGuide SDF (4.5 MB), Esri Personal Geodatabase (5.4 MB) and ArcGIS 9.2 File Geodatabase (1.89 MB).
Each file was then processed using the following Curvefitter settings: Precision 0.1 feet; Flattening 0.1; Compression Weight 1; Smoothness Weight: 1; Accuracy Weight: 1; Preserve Shared Boundaries: Yes.
Parcel Data Test Results
| Data Format | Before Curvefitter | After Curvefitter | File Size Reduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| AutoCAD DWG | 3.8 MB | 1.6 MB | 58% |
| MapGuide SDF3 | 4.5 MB | 1.6 MB | 64% |
| Esri Personal Geodatabase | 5.4 MB | 4.8 MB | 11% |
| Esri ArcGIS 9.2 File Geodatabase | 1.89 MB | 1.07 MB | 77% |
Usage Notes
-
Null geometries that are input will be output unchanged.
-
For more information and examples, see How to get the most from the Curvefitter
Configuration
Output Ports
The curve-fit representations of the input are output to this port. They will have all attributes of the original features.
All geometries that contain only non-fittable geometries (for example, solids, surfaces, or degenerate geometries) are output through this port. They will have all attributes of the original features, and an extra fme_rejection_code attribute.
Parameters
|
Precision |
Precision is the main transformer parameter that guides the curve fitting process. It sets the maximum deviation allowed at any point along the polyline between the original and the resulting polyline. |
|
Flattening |
Allows very flat curves to be represented by straight segments. Any curve that has a mid-ordinate less than this amount will be replaced by a straight segment. A typical value is 10% of the precision setting. |
|
Compression Weight Smoothness Weight Accuracy Weight |
The values of the three Weight parameters determine the importance of the three factors relative to each other. Compression is the reduction in the number of vertices. Smoothness is the tangency of consecutive segments – how close the end angle of a segment is to the start angle of the next segment. Accuracy is how closely the resulting curve overlays the original. |
|
Preserve Shared Boundaries |
This parameter is useful when area features that form a coverage are sent into the transformer. If it is set to No, then each feature is considered independent of all others, and if any features shared boundaries, gaps or overlaps may be introduced. If it is set to Yes, then the input data is decomposed into boundary lines, these are Curvefitted, and then the areas are reassembled. In this case, no gaps will be created. If only linear or non-adjacent area features are input into the transformer, No is the best choice. |
|
Shared Boundaries Tolerance |
The minimum distance between boundaries in 2D before they are considered shared, in ground units. If the tolerance is Automatic, a tolerance will be automatically computed based on the location of the input geometries. |
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters. There are a number of tools and shortcuts that can assist in constructing values, generally available from the drop-down context menu adjacent to the value field.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more.
When setting values - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors - strings and expressions containing String, Math, Date/Time or FME Feature Functions will have those functions evaluated. Therefore, the names of these functions (in the form @<function_name>) should not be used as literal string values.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
|
Special Characters |
A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| Date/Time Functions | Date and time functions are available in the Text Editor. |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Creating and Modifying User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Dialog Options - Tables
Transformers with table-style parameters have additional tools for populating and manipulating values.
|
Row Reordering
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
|
|
Cut, Copy, and Paste
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
Cut, copy, and paste may be used within a transformer, or between transformers. |
|
Filter
|
Start typing a string, and the matrix will only display rows matching those characters. Searches all columns. This only affects the display of attributes within the transformer - it does not alter which attributes are output. |
|
Import
|
Import populates the table with a set of new attributes read from a dataset. Specific application varies between transformers. |
|
Reset/Refresh
|
Generally resets the table to its initial state, and may provide additional options to remove invalid entries. Behavior varies between transformers. |
Note: Not all tools are available in all transformers.
FME Community
The FME Community is the place for demos, how-tos, articles, FAQs, and more. Get answers to your questions, learn from other users, and suggest, vote, and comment on new features.
Search for all results about the CurveFitter on the FME Community.
Keywords: smooth smoother generalize generalizer