Brings lines, segments, end points or vertex points of features together if they are within a certain distance of each other and (optionally) if they have one or more attributes in common.
How does it work?
The difference between the AnchoredSnapper and the Snapper is that anchor features are considered to be accurate and consequently do not move.
A short cleanup step is performed after snapping. This step will remove duplicate points, and may create aggregates to preserve overlapping, directed segments.
Any feature that undergoes dimensional collapse as a result of being snapped will be output through the Collapsed port.
Example
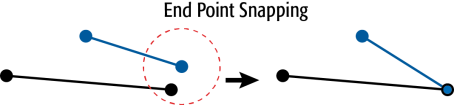
The example below illustrates end points of two line features snapping together.
The example below illustrates an endpoint and a vertex of a line snapping together.
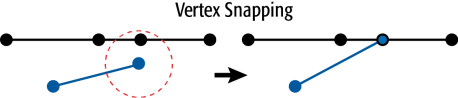
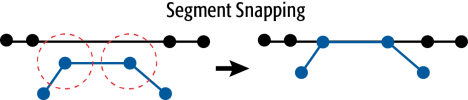
The example below illustrates vertices of a segment snapping to another segment.
Usage Notes
- The Snapper snaps to the first suitable candidate that is found and then ignores the other possible candidates. If this is not what you're looking for, the CoordinateRounder may be useful instead.
- You can clean up a dataset by using a Snapper before trying more complex actions, such as building polygons. Other transformers that are often used in this context are the LineExtender and Intersector.
- The AnchoredSnapper transformer provides slightly different functionality by identifying a set of features which will not be moved and will be snapped to by another set of features.
Configuration
Output Ports
Features whose geometry is changed by the transformer.
Features that leave the transformer without being changed.
- If a line or area feature snaps down to a single location, it will be output as a Point geometry, through the Collapsed port.
- If an Aggregate, MultiArea, or MultiCurve geometry has any parts snap down to a single location, a Point geometry for each part will be bundled up into a MultiPoint geometry and output through the Collapsed port. The remaining parts which did not snap down to a single location (if any) will be output as a group through the Snapped port.
Features whose geometry is unsnappable (for example, having a non-finite coordinate) will be rejected and output via this port.
Rejected features will receive an explanatory fme_rejection_code attribute.
Rejected Feature Handling: can be set to either terminate the translation or continue running when it encounters a rejected feature. This setting is available both as a default FME option and as a workspace parameter.
Parameters
| Group By |
If Group By attributes are selected, features are only snapped to other features with the same values in the group by attributes. |
| Complete Groups |
When All Features Received: This is the default behavior. Processing will only occur in this transformer once all input is present. When Group Changes (Advanced): This transformer will process input groups in order. Changes of the value of the Group By parameter on the input stream will trigger processing on the currently accumulating group. This may improve overall speed (particularly with multiple, equally-sized groups), but could cause undesired behavior if input groups are not truly ordered. There are two typical reasons for using When Group Changes (Advanced) . The first is incoming data that is intended to be processed in groups (and is already so ordered). In this case, the structure dictates Group By usage - not performance considerations. The second possible reason is potential performance gains. Performance gains are most likely when the data is already sorted (or read using a SQL ORDER BY statement) since less work is required of FME. If the data needs ordering, it can be sorted in the workspace (though the added processing overhead may negate any gains). Sorting becomes more difficult according to the number of data streams. Multiple streams of data could be almost impossible to sort into the correct order, since all features matching a Group By value need to arrive before any features (of any feature type or dataset) belonging to the next group. In this case, using Group By with When All Features Received may be the equivalent and simpler approach. Note: Multiple feature types and features from multiple datasets will not generally naturally occur in the correct order. As with many scenarios, testing different approaches in your workspace with your data is the only definitive way to identify performance gains. |
| Snapping Type |
When this parameter is set to End Point Snapping, the transformer:
When this parameter is set to Vertex Snapping, the transformer does the following:
When this parameter is set to Segment Snapping, the transformer does the following:
|
| Snapping Distance |
Snapping Distance specifies the distance, in ground units, that the snapping occurs between features. |
|
Tolerance |
When Snapping Type is Segment Snapping, this transformer performs data cleaning that is meant to improve the robustness of the results when they are used in other algorithms by ensuring that no two vertices in the snapped output are within tolerance of each other. If Tolerance is set to Automatic, a tolerance will automatically be calculated for the cleaning operation, based on the size of the inputs. Otherwise, a custom tolerance may be used. |
| Add Additional Vertex |
This parameter applies only when the end point of a feature is being snapped. It controls how lines are modified when they are snapped.
|
| Save Short Lines |
Any features entering the transformer whose length is less than or equal to the Snapping Distance would normally collapse to a point. Enabling this setting will instead ensure that lines shorter than the Snapping Distance are unmodified, and are output as Untouched. |
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters. There are a number of tools and shortcuts that can assist in constructing values, generally available from the drop-down context menu adjacent to the value field.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more.
When setting values - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors - strings and expressions containing String, Math, Date/Time or FME Feature Functions will have those functions evaluated. Therefore, the names of these functions (in the form @<function_name>) should not be used as literal string values.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
|
Special Characters |
A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| Date/Time Functions | Date and time functions are available in the Text Editor. |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Creating and Modifying User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Dialog Options - Tables
Transformers with table-style parameters have additional tools for populating and manipulating values.
|
Row Reordering
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
|
|
Cut, Copy, and Paste
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
Cut, copy, and paste may be used within a transformer, or between transformers. |
|
Filter
|
Start typing a string, and the matrix will only display rows matching those characters. Searches all columns. This only affects the display of attributes within the transformer - it does not alter which attributes are output. |
|
Import
|
Import populates the table with a set of new attributes read from a dataset. Specific application varies between transformers. |
|
Reset/Refresh
|
Generally resets the table to its initial state, and may provide additional options to remove invalid entries. Behavior varies between transformers. |
Note: Not all tools are available in all transformers.
FME Community
The FME Community is the place for demos, how-tos, articles, FAQs, and more. Get answers to your questions, learn from other users, and suggest, vote, and comment on new features.
Search for samples and information about this transformer on the FME Community.