Restructures and regroups incoming features based on specified Group by attributes and calculates summary statistics to form a Pivot table output.
Typical Uses
- Calculating statistics on tabular data
How does it work?
The AttributePivoter receives features with attributes, restructures and regroups them based on specified Group by attributes, and calculates summary statistics based on a designated Attribute To Analyze in order to form a Pivot table output.
Like the StatisticsCalculator, the AttributePivoter groups features according to selected attributes, and computes statistics on a single attribute for all features in each group (Grouping by rows). Beyond this, the AttributePivoter allows for the order of these row grouping attributes to be specified so that a logical nesting of additional summary rows can be generated. In addition, the AttributePivoter also allows for new attributes to be generated dynamically based on the unique values of a selected attribute (Grouping by Column) with values populated by statistics performed on the resultant groupings.
Note: Because the AttributePivoter generates attributes dynamically, you must set any writer feature types to dynamic mode if you want to include these attribute in the output. This is described in more detail in Result Grouping and Tabular Structure.
Group Rows By and (optionally) Group Columns By define a logical nesting of row groups.
For each such logically nested group, the AttributePivoter computes summary statistics, which it emits as table rows through the Summary port. The value for the most specific row grouping attribute for the summary row is given a value of “<attrName> <description>”, where <attrName> is the name of the row grouping attribute, and <description> is the value given to the “Row Group Summary Line Description” parameter.
For example, if grouping by an attribute called “Region_RSS”, the summary row over all regions would have a value of “Region_RSS Total” for the “Region_RSS” attribute, assuming the row group summary line descriptor is left with the default value of “Total”.
Input features are grouped by “grouping attributes”, and statistics are computed on the specified analyzed attribute in each group. There are two kinds of grouping attributes which work together to define these groups:
- Row Grouping Attributes: The user specifies an ordered set of attributes that divide the statistics into rows. There is a single row of result data for each unique set of values for the specified set of row grouping attributes.
- Column Grouping Attribute: The user can optionally specify a single attribute to define columns in the resulting rows. If specified, each unique value of the column grouping attribute contributes a column of statistical data to the result, for each statistic being computed. Additionally, if there is more than one unique value for the column, a summary column will be generated for each statistic.
If no column grouping attribute is selected, each row will contain a single computed result for each selected output statistic.
Because the row grouping attributes are ordered, they effect a logical nesting of groups. At the lowest level, a complete set of unique values is represented as a single row of the result. One level up is the logical grouping consisting of the set of rows where all row grouping attributes are unique except for the last one specified. This logical nesting carries up to the first specified row grouping attributes.
A row resulting from a complete set of unique data values is known as a “data row”. There is an additional “summary row” generated for each logically nested grouping, which summarizes the data for the data rows contained in the grouping.
The sequence of resulting rows form a table with the following attributes:
- All of the row grouping attributes, whose combined values specify the actual group
- For each pivot summary type, an attribute with the corresponding statistic, computed over all features in the row group.
- If there was more than a single column group defined, each of the attributes in (2.) will be repeated for all column groups, along with a summary value (that is, a “grand total”) computed over the attribute values over all column groups. The method for computing the summary value depends on the statistic it is representing:
- Count and Sum statistics are summarized with the sum of the computed statistics for the row group.
- Average statistics are summarized with the average of all values in the row group.
- Min values are summarized by the minimum of all occurrences of the analyzed attribute for the group.
- Max values are summarized by the maximum of all occurrences of the analyzed attribute for the group.
The first data feature and first summary feature emitted will contain additional attributes containing the schema information needed to write the data out by a feature type configured for dynamic writing.
Examples
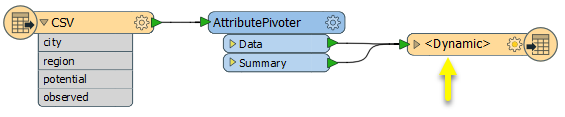
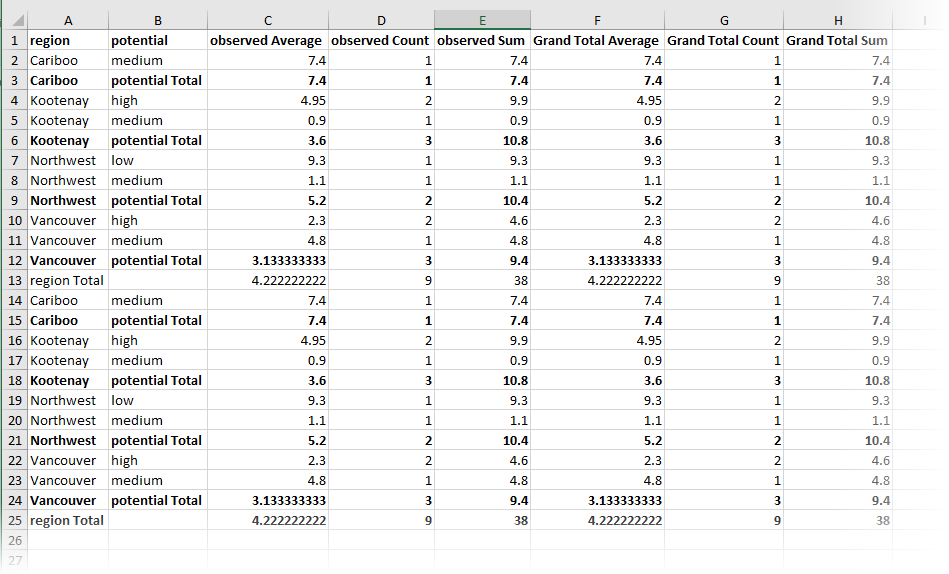
In this example, we start with a simple CSV table of statistics to be pivoted and analyzed. The CSV features are routed into an AttributePivoter.
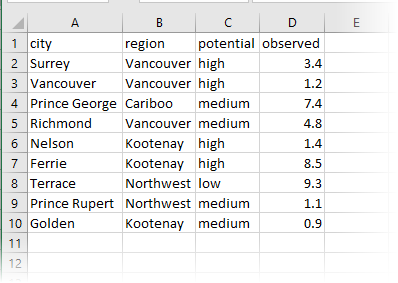
In the parameters dialog, we choose to Group Rows By region, then potential. The order is important.
The Attribute to Analyze is observed - the column containing our statistics. We have requested Count, Sum, and Average calculations.
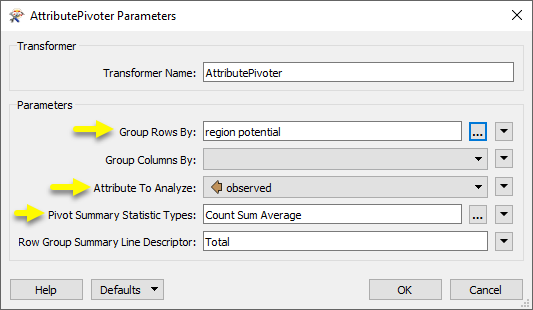
The output (via a dynamic Excel writer) now contains the added statistics.
Usage Notes
- The AttributePivoter can only be used to analyze one attribute at a time. If you need to analyze more than one attribute, consider the StatisticsCalculator.
Configuration
Input Ports
Features with attributes for analysis.
Output Ports
A single new feature will be output containing all computed statistics for each completely defined row group. The attributes on these features are described in the “Result Grouping and Tabular Structure” section.
The first row emitted from the Data port will contain information to define the schema for a dynamically configured feature type.
For each logically nested grouping as described in the “Result Grouping and Tabular Structure” section, a summary row will be emitted prior to the first data row for the group. It provides summary information for all rows contained in the group. An overview summary of all rows will always be generated.
The first row emitted from the Summary port will contain information to define the schema for a dynamically configured feature type.
Parameters
| Group Rows By | One or more attributes are chosen to specify how features are grouped to form the rows of the resulting table. Unlike most “Group By” parameters, the user has the opportunity to specify the order of the grouping attributes, so that nested summary groupings can be generated, adding a hierarchical structure to the resulting table. |
| Group Columns By | Optional: In addition to row groups, the user can select an attribute whose unique values will generate new attributes, hence “pivoting” the data and further subdividing the groupings on which the statistics are calculated. |
| Attribute to Analyze | A single attribute is chosen upon which to compute statistics. The features are grouped according to the row and column grouping attributes, and statistics are calculated over all values of this attribute within the features in each group. |
| Pivot Summary Statistic Types |
The user can choose to compute multiple types of summary statistics simultaneously. Each chosen statistic type will be represented as a separate column within each column group of the result table. One or more of the following statistic types may be selected.
|
| Row Group Summary Line Descriptor | Enter a name for the Summary line of each Row Group. The default descriptor is Total. |
Editing Transformer Parameters
Using a set of menu options, transformer parameters can be assigned by referencing other elements in the workspace. More advanced functions, such as an advanced editor and an arithmetic editor, are also available in some transformers. To access a menu of these options, click  beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
beside the applicable parameter. For more information, see Transformer Parameter Menu Options.
Defining Values
There are several ways to define a value for use in a Transformer. The simplest is to simply type in a value or string, which can include functions of various types such as attribute references, math and string functions, and workspace parameters. There are a number of tools and shortcuts that can assist in constructing values, generally available from the drop-down context menu adjacent to the value field.
Using the Text Editor
The Text Editor provides a convenient way to construct text strings (including regular expressions) from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and constants, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Using the Arithmetic Editor
The Arithmetic Editor provides a convenient way to construct math expressions from various data sources, such as attributes, parameters, and feature functions, where the result is used directly inside a parameter.
Conditional Values
Set values depending on one or more test conditions that either pass or fail.
Parameter Condition Definition Dialog
Content
Expressions and strings can include a number of functions, characters, parameters, and more.
When setting values - whether entered directly in a parameter or constructed using one of the editors - strings and expressions containing String, Math, Date/Time or FME Feature Functions will have those functions evaluated. Therefore, the names of these functions (in the form @<function_name>) should not be used as literal string values.
| These functions manipulate and format strings. | |
|
Special Characters |
A set of control characters is available in the Text Editor. |
| Math functions are available in both editors. | |
| Date/Time Functions | Date and time functions are available in the Text Editor. |
| These operators are available in the Arithmetic Editor. | |
| These return primarily feature-specific values. | |
| FME and workspace-specific parameters may be used. | |
| Creating and Modifying User Parameters | Create your own editable parameters. |
Dialog Options - Tables
Transformers with table-style parameters have additional tools for populating and manipulating values.
|
Row Reordering
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
|
|
Cut, Copy, and Paste
|
Enabled once you have clicked on a row item. Choices include:
Cut, copy, and paste may be used within a transformer, or between transformers. |
|
Filter
|
Start typing a string, and the matrix will only display rows matching those characters. Searches all columns. This only affects the display of attributes within the transformer - it does not alter which attributes are output. |
|
Import
|
Import populates the table with a set of new attributes read from a dataset. Specific application varies between transformers. |
|
Reset/Refresh
|
Generally resets the table to its initial state, and may provide additional options to remove invalid entries. Behavior varies between transformers. |
Note: Not all tools are available in all transformers.
Reference
|
Processing Behavior |
|
|
Feature Holding |
Yes |
| Dependencies | None |
| FME Licensing Level | FME Base Edition and above |
| Aliases | |
| History |
FME Community
The FME Community is the place for demos, how-tos, articles, FAQs, and more. Get answers to your questions, learn from other users, and suggest, vote, and comment on new features.
Search for all results about the AttributePivoter on the FME Community.
Examples may contain information licensed under the Open Government Licence – Vancouver and/or the Open Government Licence – Canada.