FME provides write access to Tableau Data Extract (.tde) files (also known as extracts).
Overview
Tableau is a business analytics and data visualization tool with optional online components for displaying visualizations in web pages.
A Tableau Data Extract file is a compressed, memory-mapped file that uses columnar store and supports standard, non-spatial data types, as well as certain spatial geometry types. It can be used with Tableau products including Tableau Desktop and Tableau Server.
Each attribute in FME is mapped to a column in a TDE file; during the writing process, spatial information is placed in an additional column with a given name. Each feature type in FME is written to a separate TDE file.
More information about Tableau and TDE files can be found at www.tableau.com.
Versions
This writer supports creation of Tableau 10.2 TDE files.
About the Writer (TDE)
The TDE writer writes features as rows into a single table in an extract file per feature type in FME. The writer provides the capability to create a single file and table with an arbitrary number of rows and columns.
The base name of the TDE file will match the feature type name. Each TDE file will have a single table named Extract present within the file that matches the attribute names and types supplied on the writer feature type.
The feature type name will be the name of the TDE file created.
Format Usage Notes
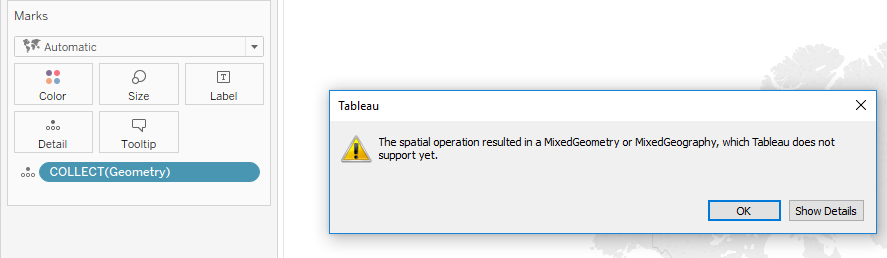
- Tableau does not support some geometry types. If you attempt to render any non-supported geometries (by dragging them into a mark in the sheets view), Tableau will open an error window indicating that they are not yet supported.
- 3D geometries are not supported. All 3D geometries will be forced to 2D if possible; otherwise, features that contain 3D geometries will not be written – they will be skipped.
- Currently Tableau supports points, lines, polygons, ellipses (as polygons), and donuts (as polygons). Certain aggregate types such as multipolygons are also supported.
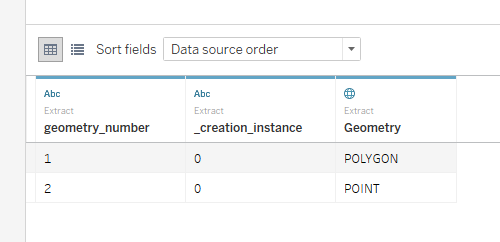
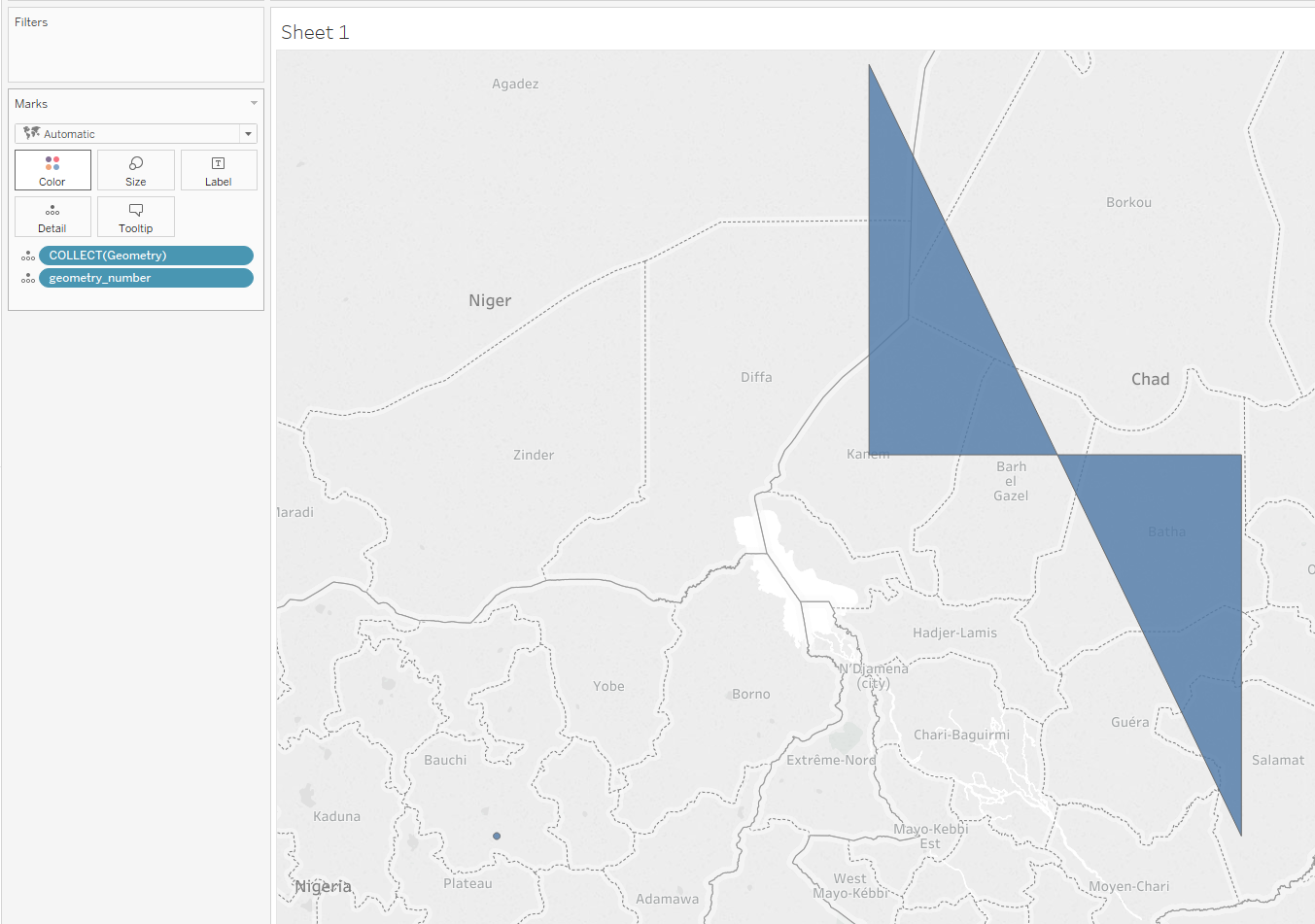
- Tableau will only render one type of geometry per mark. As such, in order to render multiple types of geometry, each row with a different type of geometry must have another attribute that allows that row to be differentiated from other rows with different geometries. For example, we could add a row with a number per geometry (1=Polygon,2=Point, etc.). Adding both of these to the same mark would allow Tableau to render both geometries at the same time.
Writer Overview
The TDE writer uses the Tableau SDK to create TDE files and add rows to them. The TDE writer provides the following capabilities:
When the first feature of each feature type is processed, a TDE file will be created or an existing one will be opened, and the table definition will be constructed.
If the Table Handling Format Parameter for a feature type is set to Create If Needed, the TDE file will be created. If one already exists of the same name, it will be appended to.
If the Table Handling Format Parameter for a feature type is set to Use Existing, then the writer will append features to the TDE file with the same base name as the feature type. If this file does not exist, translation will fail. Due to a limitation of the Tableau SDK, existing TDE files cannot be read to determine the feature IDs in use. As a result, geometry appended to an existing TDE file containing geometry will not use unique feature IDs. For this reason, appending geometry to an existing TDE file is not supported.
If the Table Handling Format Parameter for a feature type is set to Drop and Create, then the writer will drop and recreate the table before writing any features to it.
Tips for Using the Tableau Data Extract (TDE) Writer
When inserting a feature into TDE, missing and null attributes on the feature will be written out as null values. Empty string attributes on the feature will be written out as empty strings.
Troubleshooting
- Before trying to write to the TDE file, ensure that the file is not open.