Database Connection
Connection File
This parameter identifies the pathname of a connection file to be used to connect to an Enterprise Geodatabase.
A connection file provides the necessary information to connect to the SDE server, such as the server name or the username.
The connection file must be a *.sde file and have the proper format for a connection file as defined by Esri. Connection files can be created in ArcCatalog.
Check this option to override the User and Password from the connection file. Overriding credentials is required for Connection Files that do not have saved credentials.
Note: This parameter is ignored if the Connection File is using OS Authentication.
Version
Indicates which transaction mechanism the Geodatabase writer should use. Within ArcGIS, there are currently two transaction mechanisms: edit sessions, and (regular) transactions. An edit session corresponds to a long transaction. During an edit session, edits made by other users do not become visible until the edit session is ended. If a translation does not complete successfully and the Geodatabase writer is using an edit session, then all the edits will be discarded.
Select this parameter to use the SDE connection provided in the file.
The name of the SDE version to which FME connects. If not specified, FME connects to the version sde.DEFAULT, or equivalent. This parameter is only applicable when dealing with versioned tables or layers.
The historical marker name of the dataset to be read (used in multi-versioned databases that have archiving enabled). Note that the version name is case-sensitive, and that the historical data is read-only.
The specific date and time of the archived dataset to be read (used in multi-versioned databases that have archiving enabled). Note that historical data is read-only.
Constraints
Remove Table Qualifier
Specifies whether to keep the table qualifier. The full name of a table in a database is of the format:
<prefix>.<table_name>
Depending on the database format, the prefix can be <database_name>.<owner_name>, <owner_name>, or <schema_name>.
Selecting this parameter indicates that the reader should return the table name without any prefixes. This is useful, for example, when creating a workspace that will be passed on to another organization using the same table names, or performing a translation to another database format but with a different user name.
When this parameter is selected during workspace generation, the source feature types will be the table names without any prefix; otherwise, they will contain the owner name as a prefix. It is recommended that you do not change this parameter after generating the workspace, because it is possible for no features to be successfully passed onto the writer (since the writer is expecting feature types with different names).
Note: Even when this parameter is selected, if the table is owned by a user other than the current user, the prefix will not be dropped. This is to ensure that the reader will find the correct table.
Tables
After specifying the database connection, click the Browse button (...) to select tables for import. A connection window appears while the system retrieves the tables from the database.
Once the Select Tables dialog appears, you can select one or more tables. Click OK to dismiss the window and add the selected table name(s) to the Tables parameter.
Enter any SQL where clause that constrains the attributes of the layers selected in the layer list (for example, NUMLANES=2).
Specifies whether to only translate features that contain some kind of geometry.
Specifies whether or not to resolve the domain code found in feature classes and tables into the domain value.
This means that when an attribute of a feature has a coded value domain associated with it, another attribute will also be added that represents the textual description of the coded attribute. The new attribute will be <attribute-name>_resolved, where <attribute-name> is the name of the attribute containing the code.
Specifies whether or not to resolve the subtype field values found on feature classes and tables into the name of the actual subtype.
Specifies whether to read the network portion of network features. When checked, junctions will be read as points (geodb_point) and edges will be read as lines (geodb_polyline). Additionally, none of the network related attribution will be supplied on the features.
Checking this option can significantly speed up reading of network features.
Determines whether to read relationship features present in a source dataset. When this parameter is checked, feature types containing simple relationships will be ignored, and feature types containing attributed relationships will be treated as non-spatial tables. When this parameter is unchecked, relationships will be read normally as either simple or attributed. The speed of reading features is vastly improved if relationships are ignored.
Determines whether complex edge features should be split. When split, complex edge features are read at the element level rather than the feature level. The element level represents the logical view of the geometric network. As a result, no network connectivity information is lost.
These are the attributes that each FME feature stores when this option is checked:
|
Attribute Name |
Contents |
|---|---|
|
geodb_element_id |
The element ID of the logical edge element. |
|
geodb_element_index |
An attribute created and assigned by FME. It is used to order the edge elements within a complex feature. The index begins at zero, not one. |
|
geodb_from_junction_element_id |
The junction element ID that corresponds to the from endpoint. Note: This is the from endpoint of the edge element, not the edge feature. |
|
The junction element ID that corresponds to the to endpoint. Note: This is the to endpoint of the edge element, not the edge feature. |
Specifies whether or not to split multi-part annotations into separate features for each 'element' when reading. If checked, a single feature for each element (usually a word) in a multi-part annotation will be produced on reading, resulting in feature-specific attributes such as angle and text position being stored according to the location of each element. If the parameter is unchecked, multi-part annotations will be read normally, as a single feature storing a single set of attributes describing the positioning of the text.
Feature Read Mode
When set to Features, the reader outputs features stored within tables.
When set to Metadata, provides the ability to read table-level metadata. In this mode, the reader outputs one feature per feature type. The geodb_type of the feature is geodb_metadata and the entire XML metadata document belonging to the Geodatabase table is found in the attribute geodb_metadata_string.
Where applicable, the following attributes are also supplied:
- fme_feature_identifier – Indicates the name of the object ID field,
- fme_num_entries (Personal Geodb only) – Indicates the number of features in the table,
- fme_contains_spatial_column – Indicates whether the table has a geometry column (or, in Esri ArcGIS terms, whether the table is a feature class)
- fme_geometry{0} – Indicates the types of geometry the feature class contains
- fme_dimension – Indicates whether the feature class is 2D or 3D.
If the table is a feature class, the geometry of the metadata feature returned is a polygon, representing the extents of the feature class, and the coordinate system of the feature class also gets set on the feature.
When reading metadata, the Feature Type parameters are used to determine which feature types should have metadata read from them.
Read Version Differences
When checked, only the differences between two versions will be read instead of reading all the data. Differences are read as difference features that record the inserts, updates and deletes that have occurred on the connection version since the baseline version. See the Difference Features section for the structure of difference features.
To read transactional version differences, the tables/feature classes being read must be registered as versioned and for historical version differences, those tables must additionally have archiving enabled.
When comparing two transactional versions, the baseline will actually be the common ancestor of both versions to avoid conflicts where the same record was changed in both versions.
Use this parameter to select the version type to compare with when reading version differences:
- When the connection version is transactional, a transactional version must be used.
- When the connection version is historical, the historical version should be used.
- Comparing a historical version with a transactional version will result in an error.
Select a specific transactional version to serve as the baseline for difference reading.
Select a historical marker to serve as the baseline for difference reading.
Select a specific date and time to serve as the baseline for difference reading.
Use this parameter to expose Format Attributes in Workbench when you create a workspace:
- In a dynamic scenario, it means these attributes can be passed to the output dataset at runtime.
- In a non-dynamic scenario, this parameter allows you to expose additional attributes on multiple feature types. Click the browse button to view the available format attributes (which are different for each format) for the reader.
Alias Mode
This parameter controls how Geodatabase aliases are used.
- None – Aliases are ignored.
- Replace Attribute Names with Aliases – (only applicable when adding a Reader) Attributes on feature types will be named for their aliases rather than their official names. A geodb_feature_class_alias attribute will be included on each feature. Use this mode when the target format should create feature types using the aliases as attribute names.
- Expose Aliases as Metadata Attributes – For each attribute read, a second <name>_alias attribute will be added that stores the alias for the attribute in question. A geodb_feature_class_alias attribute will also be included on each feature. Use this mode when the target format is Geodatabase and the aliases should be preserved during feature class and table creation.
Using the minimum and maximum x and y parameters, define a bounding box that will be used to filter the input features. Only features that intersect with the bounding box are returned. (Note that this is the bounding box intersection only, and not a full geometry intersection that would be returned by a transformer like the SpatialFilter.)
If all four coordinates of the search envelope are specified as 0, the search envelope will be disabled.
Clip to Search Envelope
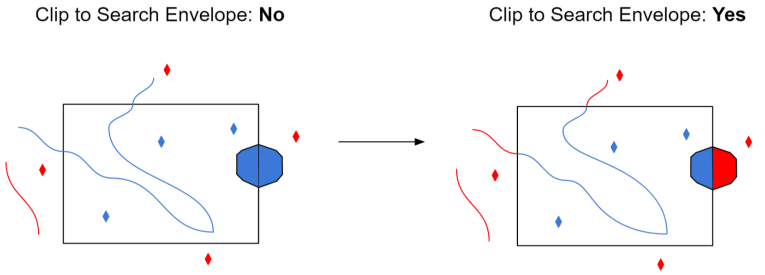
When selected, this parameter removes any portions of imported features being read that are outside the Search Envelope.
The example below illustrates the results of the Search Envelope when Clip to Search Envelope is not selected (set to No) and when it is selected (set to Yes).
- No: Any features that cross the search envelope boundary will be read, including the portion that lies outside of the boundary.
- Yes: Any features that cross the search envelope boundary will be clipped at the boundary, and only the portion that lies inside the boundary will be read. The underlying function for the Clip to Search Envelope function is an intersection; however, when Clip to Search Envelope is selected, a clipping operation is also performed in addition to the intersection.
This parameter specifies the type of spatial relationship the query features must have with the Search Features parameter or Use Search Envelope parameter, whichever is used, in order to be returned.
- When Search Features is selected, there is no default value, so this parameter must be specified.
- When Use Search Envelope is selected, the default value is GEODB_ENVELOPE for vector workspaces, GEODB_AREA_INTERSECT for vector FME Objects applications, and GEODB_ENVELOPE for all raster-related translations.
- When reading rasters, GEODB_ENVELOPE is the only valid value and the Search Features parameter is not supported.
Value
The value of Search Method can be one of the following:
|
Parameter |
Contents |
|---|---|
|
GEODB_ENVELOPE |
Features must be within the envelope of the feature. |
|
GEODB_ENVELOPE_BY_GRID |
Features must be within the envelope of the feature and are returned in grid order. |
|
GEODB_COMMON_POINT |
Features must have a point in common with the query feature. |
|
GEODB_LINE_CROSS |
Features must cross the query feature. |
|
GEODB_COMMON_LINE |
Features must have a common line segment with the query feature. |
|
GEODB_CP_OR_LC |
Features must have either a common point or a line crossing. |
|
GEODB_AI_OR_ET |
Features must intersect or must share an edge. |
|
GEODB_AREA_INTERSECT |
Features must intersect the query feature. This retrieves area, linear, and point features contained in or that intersect the area of the query feature. |
|
GEODB_AI_NO_ET |
Features must intersect but must not have any edge touching with the query feature. |
|
GEODB_CONTAINED_IN |
The returned features contain the query feature. A candidate feature that is an area will be returned when it encloses the query feature. If the candidate feature is a line, then it is returned if its path is coincident with the query feature. If the query feature is a point and the candidate feature is not an area, then the candidate feature will be returned if one of its vertices is the same as the query feature. |
|
GEODB_CONTAINS |
The returned feature is contained by the query feature. If both the features are linear features, then the returned feature must lie on the search feature’s path. Point features that lie on a search feature vertex are also returned. |
|
SDE_CONTAINED_IN_NO_ET |
Features must be contained within the query feature and not have any edge touching. |
|
GEODB_CONTAINS_NO_ET |
Features must contain the query feature but must not share any edge. |
|
GEODB_POINT_IN_POLY |
Returned feature must be an area feature that contains the first coordinate of the search feature. |
|
GEODB |
The returned feature must be spatially identical to the query feature. |
For more information on these search methods, see Esri technical documentation ISpatialFilter Interface.
Specifies the order that the underlying search is performed:
- OPTIMIZE: Let SDE decide which to perform first
- SPATIAL_FIRST: Perform spatial query first
- ATTRIBUTE_FIRST: Perform tabular query first (when performing a WHERE clause search)
This parameter provides a mechanism for specifying an arbitrarily complex search feature. It works with the Search Method parameter to define the spatial constraint.
|
Parameter |
Contents |
|---|---|
|
[<xCoord> <yCoord>]+ |
A list of the coordinates defining the geometry of the query feature. Note: Values must be space-delimited. For example, the following coordinate pairs will fail unless you replace commas with spaces: -97.4055,30.1331 -97.2340,30.1555 -97.2161,29.9840 -97.3995,30.0943 |
Advanced
Geodatabase annotations offer a rich set of options to place text which are often not supported or do not directly translate to other formats. By enabling this option, richer text representations are broken into simpler representations that preserve text style and placement.
To maintain accurate placement, text elements are split into separate features on line breaks, format changes, irregular character spacing, and on any curves. This option also implies that multi-part annotations will be split (see the Split Multi-Part Annotations parameter above).
Each resulting feature will have a rotation angle and a point representing the bottom left corner of the text. All the text will be bottom, left-justified without an X or Y offset.
Each feature will contain all the attributes of the original text element including all the Geodatabase format attributes. The annotation related format attributes represent the current part and not the original text element. An additional geodb_text_part_count format attribute is added to indicate the part index of the original text element.
Specify the type of memory optimizations that are used when reading multipatches with textures. The default behavior to cache texture should be used in most scenarios as it will result in better performance. If, however, memory is an issue and there are many multipatch features with associated texture materials (like the buildings of a city), then consider disabling caching to improve memory usage.
- Yes (default): Textures will be stored in local texture caches and no effort will be made to clean them. This results in better performance but higher memory usage over time.
- No: Extra effort will be made to clear texture caches. This may result in slower performance.
Note: This parameter is only applicable on releases of ArcSDE that support versioning. It is also only valid for vector features.
Specifies the name of a child version to create using the version specified by Transactional Version as the parent version. All tables will then be read from this (child) version rather than from the parent version.
All the tables read when this parameter is specified must be multi-versioned and have read, insert, update, and delete permissions with the current user. This is because this parameter is designed to be used when checking out a copy of the data in the parent version, with the intention that the child version will be modified and possibly reconciled and posted back to the parent version. The version will be created as a public version and the description given to the version will be Safe Software Created Version.
If Child Version Name specifies a version that already exists, an error will be output. The child version will be owned by the user specified by Username; therefore, if the owner is specified as part of the value for this parameter, the owner must be the same as Username. If the translation is aborted, then the child version created will be deleted.
By default, this parameter is left empty and therefore no child version is created.
Note: Version names are case-sensitive and therefore the value supplied for this parameter is also case-sensitive.
This optional parameter specifies the WHERE clause used to constrain features read from an archived table. The dates must be in FME date format, and will be converted to the format expected by the underlying database.
One or both of the GDB_FROM_DATE or GDB_TO_DATE column names must be specified in order to form a valid where clause. If the GDB_FROM_DATE is not specified, the creation date of the archive will be assumed. If the GDB_TO_DATE is not specified, the current date will be assumed. ArcGIS uses transaction time to record changes to the archive, not valid time. Also note that the features returned will be simple; no complex feature information such as feature-linked annotations or network roles are available.
Example of a ‘moment’ query:
The following demonstrates an example of using the archive where clause to perform a ‘moment’ query, which will return all features existing in the database as of 9:00 am on May 1, 2017
GDB_FROM_DATE <= 20170501090000 AND GDB_TO_DATE > 20070501090000
Example of a ‘range’ query:
The following demonstrates an example of using the archive where clause to perform a ‘range’ query, which will return all features inserted after 9:00 am on January 1, 2016 and updated or deleted before 11:59 pm on December 31, 2016
GDB_FROM_DATE > 20160101090000 AND GDB_TO_DATE < 20161231235959
Specifies whether a check should be performed on features read from Geodatabase to determine if they are simple.
Note: This is an expensive check, and it impacts reader performance.
If this parameter is set to Yes, the format attribute geodb_feature_is_simple is set to Yes if the geometry is simple, and No if it is not.
Specifies whether feature-linked annotations should have their text, angle, and position properties merged as attributes onto the main feature to which they are linked, when reading.
- Yes: This will produce a list attribute (as detailed in Annotations), with all annotation attributes set. The annotation table(s) does not need to be explicitly read.
- No: Feature-linked annotations will be read as annotations when encountered.
Strip Braces off GlobalID and GUID
In some programs (for example, ArcGIS Pro), GlobalID and GUID attributes contain braces:
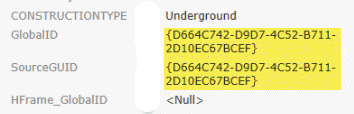
When set to Yes, this parameter removes the braces from the GlobalID and GUID attributes for compatibility with programs where these attributes do not contain braces.
The default is No.
When enabled, the database connection persists for the duration of an FME session.
For example, it may be desirable to maintain a connection when running a batch of 100 workspaces on the same database connection, which saves the processing time required to make and break a database connection.
FME considers the database connection to be the same when the database name, the username, and password are the same.
SQL to Run Before Read
This parameter allows for the execution of SQL statements before opening a table for reading. For example, it may be necessary to create a temporary view before attempting to read from it.
For detailed information about SQL functions, click the corresponding menu item in the .
Available menu options depend on the format.
Multiple SQL commands can be delimited by a character specified using the FME_SQL_DELIMITER directive, embedded at the beginning of the SQL block. The single character following this directive will be used to split the SQL block into SQL statements, which will then be sent to the database for execution. Note: Include a space before the character.
For example:
FME_SQL_DELIMITER ; DELETE FROM instructors ; DELETE FROM people WHERE LastName='Doe' AND FirstName='John'
Multiple delimiters are not allowed and the delimiter character will be stripped before being sent to the database.
Any errors occurring during the execution of these SQL statements will normally terminate the reader or writer (depending on where the SQL statement is executed) with an error. If the specified statement is preceded by a hyphen (“-”), such errors are ignored.
SQL To Run After Read
This parameter allows for the execution of SQL statements after a set of tables has been read. For example, it may be necessary to clean up a temporary view after creating it.
For detailed information about SQL functions, click the corresponding menu item in the .
Available menu options depend on the format.
Multiple SQL commands can be delimited by a character specified using the FME_SQL_DELIMITER directive, embedded at the beginning of the SQL block. The single character following this directive will be used to split the SQL block into SQL statements, which will then be sent to the database for execution. Note: Include a space before the character.
For example:
FME_SQL_DELIMITER ; DELETE FROM instructors ; DELETE FROM people WHERE LastName='Doe' AND FirstName='John'
Multiple delimiters are not allowed and the delimiter character will be stripped before being sent to the database.
Any errors occurring during the execution of these SQL statements will normally terminate the reader or writer (depending on where the SQL statement is executed) with an error. If the specified statement is preceded by a hyphen (“-”), such errors are ignored.